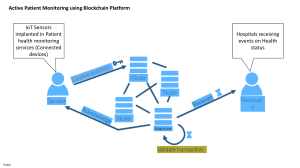
THE IMPACT OF BLOCK CHAIN Business Information Systems APRIL 26, 2023 STUDENT ID: 2121804/1 2121804/1 Introduction Blockchain is a tool recently developed with a variety of usage inside the different aspects of the organization in relationship to the corporate strategy. Is essential to evaluate the hard and soft aspects of the impact that blockchain has upon the failure and success of its appliance to the corporate strategy, and how can it facilitate or challenge the company in order to archive expected standards. Therefore is essential to identify the characteristics of the blockchain since its creation and the current development to optimize the entire value chain, satisfying a modern approach to transactional processes, as well as sufficient implementations inside the value chain. In depth analysis and collection of information related to blockchain may help to facilitate the understanding of the impact that this new tool has upon to the food sector and its contribution to the growth of the company DeliverEat after successfully being established. 1 2121804/1 Identify and evaluate the characteristics and significance globally of blockchain. Blockchain Characteristics and Evaluation. Blockchain was initially developed in 2008 by a group or a person under the pseudonym of “Satoshi Nacamoto” and issued to the public as a distributed ledger. Based on the work created by Stuart Haber, Dave Bayer and W. Scott Stornetta, with the initial intention of implementing the blockchain within the bitcoins cryptocurrencies, creating so the first digital currency, and utilise the bitcoins cryptocurrencies to solve double spending digital transactions, that is an imperfection in the digital transaction protocol, which in the same digital token can be used in multiple digital transactions. (Oberhaus, 2018) (Marr, 2018). Developing this blockchain process inside the digital transactions with the help of the cryptocurrencies, which avoid any type of imperfection as the case of the double spending issue, will effectively facilitate and improve the era of digitalisation. This process also, prevent third party transaction processing such a paypal, apple pay google pay, etc. Drastically improving and accelerating the whole transactional process, due to any failure coming from the third party involvement. A blockchain is a share ledger, or also called distributed ledger technology (DLT) which is a digital data geographically distributed across institutions, countries and sites. With the particular characteristic of not being a centralized database (a data that is store, located and maintained in a single central place), consequentially it does not have a single central point of failure and thus, benefiting for not depend on a central administrator. (Government Office for Science, 2016) (Scardovi, 2016) (Majaski, 2021). Adopting a digital transaction process that avoids single centralised administration will evade any type of disturbance coming from a single failure in the central database, preventing so a snowball catastrophe from a single damage on the central administrator. Blockchain, possesses the attribute of continuously grow a list of different records in blocks, securely stored and linked throughout CHF (cryptographic hash function) creating a chain, as every single block keeps important information from the previous block, such as: Trusted timestamping, which is a process of securely keep records of creation and modification time of any document; A cryptographic hash that is a hash algorithm with a special property desired for the cryptographic application; And finally, a transaction data in a form of a Merkle tree. (Menezes et al., 2018) (Majaski, 2021). The cryptogram functions count with many forms of authentication in order to be extremely secured, such as: InfoSec (information-security) applications, which is a practice and reducing the risk of inappropriate or unauthorized access to information/data, including unlawful use, inspection, deletion, disruption, modification, disclosure, devaluation, corruption or any type of recordings of such a information. (Curry et al., 2018) (Joshi et al., (2017) (Fletcher, 2016). Therefore, this makes the blockchain information strongly hard to access manipulate or corrupt from unauthorized source, satisfying a high level of security and thus, the tranquillity of the users. Such a process that avoids third party involvements also prevent the whole process to be hacked or any type of information being filtrated due to the nature of the current “clumsy” and tedious transactional process. 2 2121804/1 Blockchains and commonly administrated by a P2P (Peer to peer) computer network distributed ledger for public usage, where a point network or diagram usually called “Node” or “Data nodes”, conjointly are introduced to a coordinating process or protocol in order to reach a consensus, in any data value during a digital transaction or other type of computing. This process is denominated consensus algorithm, which is a protocol to agreeing on what transactions commit to a data base, considering also the exact order, and thus add a validate transaction block. (Iansiti, 2017) According to Bernanrd Lunn (2018) adopting a blockchain transaction process as a payment rail, which is a payment platform in charge of transferring money from a payer to payee, will facilitate millions of transactions within seconds avoiding any type of fraud or disturbance. Utilising Blockchain as a payment rail transaction process that could avoid the interference and intermediate payments to third parties which allow millions of transactions in seconds for the users and companies, counting also with a strong security system that is not dependant of a central administration, is a solid way to step into the new era of digital transactions as a company and individuals. Therefore, is important to consider in depth some of the benefits of including it in the company, analysing the organisational opportunities and challenges in the specific sector desired. The Analyse the organisational opportunities and challenges of the food sector by blockchain. Every business depends on information. The quickest the information travels, the more reliable the information would be facilitating the business processes. Therefore, blockchain plays an important role inside the organization as it provides a transparent, shared an instant information that is only accessible to permissioned members, store in such an immutable ledger avoiding any type of breach or filtration in the information (IBM, 2020). As an organization being able to speed up any transactional process will contribute to the growth of it, as more processes can be archived in certain amount of time. Blockchain provide also a much reliable and secured information of such a process, making it more accessible and costumer friendly, rather than third party involvements that hinder the smooth flow of the transactional process. Blockchain is such a flexible and reliable tool that can be used efficiently in almost every process related to the organization such as: order tracks, accounts, production, payments, and many more. Contributing so with a much more transparent information, as all the members share the same single validated information. Which in the end to end transaction of such an information can be verified in detail, providing so much more efficiencies, opportunities and confidence, not only to the organization itself, but also to the costumers that make usage of the products and services (IBM, 2020). For our organization DeliverEat, is essential to count in such a reliable tool that facilitate all transactional process as the food sector will benefit immensely from faster orders, payments, production and tracking orders as it is our value, providing the costumer a quicker response, with a transparent and reliable information with immutable record as the transaction can not be alter, and in order to fix a error in any transaction, another transaction block must be created to reverse the error, and so both transaction can clearly be visible (IBM, 2020). 3 2121804/1 A smart contract, which is a program stored in the blockchain with the intention of automatically run once certain criteria is met, such as defining conditions for corporate bond transfers, execution of agreements without intermediary’s involvements or time wasting, etc. Allowing blockchain to take over these duties will benefit companies such as DeliverEat with speed, efficiency and accuracy by automating the execution of the contracts, avoiding paperwork processes or manually filling documents. (IBM, 2020). By automating the management of these processes DeliverEat can be confident to be receiving accurate and timely data, assuring the information and records are completely confidential within the network members with permission of access to the information or records kept (IBM, 2020). Another important benefit DeliverEat can benefit from blockchain is the solid security it possesses, as non transaction can be removed or deleted, not even the system administrator. All validated transactions are constantly recorded, and so this makes all transactions immutable (IBM, 2020). This would help DeliverEat to keep a record from all validated transactions without having to stress about losing the information, or beneficially alter for corruption. Transparency in every transaction not only will have a huge impact inside the company as everything will run smoothly but also in the image of how the company is being perceive from the outside, with a more reliable figures and clearness. of consumers say that knowing where food comes from is veryto-somewhat important. ¹ of Americans surveyed said they would pay up to 36% more for products that are responsibly made and transparently sourced. ² of consumers surveyed said they would be more loyal to a brand that offers complete transparency. ³ (IBM, 2020). IBM Supply Chain Intelligence Suite- Food Trust | IBM As it can clearly be appreciated in the previous picture transparency not only will bring benefits as efficiency in the process but also will improve the position of the company and its growth. According to IBM consumers are willing to put they money in companies that feel more reliable and trustful, with 94% of consumer desiring to be loyal to a company that offers complete transparency, as they may feel identified with the organization, and thus generation a much better reputation and a long with it, improvement, development and growth of the organization. 4 2121804/1 “IBM Food Trust achieves new levels of trust and transparency, making food safer and smarter from farm to fork.” Scott Gottlieb, former FDA Commissioner DeliverEat is a company that is willing to improve the brand image and transparency, although DeliverEat’s value is to focus in facilitate and improve the efficiency on the orders, is also important for the company position themselves as a transparent and reliable company, commenting to a more sustainable environment inside and outside the organization. Therefore, blockchain play an important role in helping DeliverEat to archive their goals, and so become a company with a efficient process without having to sacrifice the reputation and brand image. Blockchain is a vital part inside the food chain, as part of the modern world, due to new regulations and compliances, in order to ensure a food safety and more transparency inside the company, where according to IBM (2020) “The Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA) rule 204 requires that companies provide traceability records digitally within 24 hours of the FDA’s request”. Therefore, as part of becoming a flexible company, willing to survive and compliance with the regulations and laws in the current world is essential to consider apply such a tool as Blockchain, as it certainly will contribute to a safer supply chain and to compliance with the new regulations established by the government (IBM, 2020). Blockchain is a relative new tool which was recently developed, and therefore is important to consider its role inside the corporate strategy to apply it correctly, in order to make the most of it, avoiding any sort of hindering inside the organization procedures. As George Lawton has stated “Blockchain is proving to be useful in the supply chain, but without a strong understanding of it and a viable use case, your organization can run into several problems along the way”. (Lawton, 2019) According to George Lawton (2019) Forrester, which is a leading global market research company, estimates that approximately 90% of the companies DLT projects that started between 2015 and late 2017 have already been discontinued or will never result in operational system, and this failure is attributed to starting a blockchain project without due consideration of a viable use or technical feasibility. Martha Bennett which is principal analyst at Forrester suggest starting from understanding what is it that the company is willing to archive when applying blockchain in order to improve the supply chain (Lawton, 2019). Applying blockchain for the supply chain requires a lot of groundwork, as majority of the experiment are designed to be tested quickly and is hard to emulate a plan for a real scale, consequentially, this causes a lot of failures when entering the market inside the hard reality, highlighting the number of important factors omitted or forgotten. Therefore, to avoid this type of situations is advised to collaborate with other companies in order to identify technologies, business processes and practices in real scenarios that can be apply to work supply chain management (Lawton, 2019). 5 2121804/1 Analyse how value is created and delivered in DeliverEat business by blockchain. DeliverEat value is to archive the quickest transportation and delivery service food by becoming the main platform for meals kit also, providing flexible solutions for its user. Therefore, blockchain plays an important role inside our organization, as blockchain can provide a solid support identifying the gaps in the supply chain and deficiencies in production. According to IBM (2020) blockchain is designed to help identifying deficiencies in production and monitoring processes for end to end traceability exposing the vulnerabilities that can be eliminated inside the food sector, and consequentially improving the entire value chain. In order to become the quickest transportation and delivery system, DeliverEat must keep the cost as low as possible inside the whole supply chain, which is something that most of the companies fail to do so. “Food Safety magazine counted 337 food safety recalls in the US. Companies surveyed put costs at up to $30 million per incident” (IBM, 2020) (Foodsafety Magazine, 2020). Which in some of the amount is from direct cost and some other from indirect cost such as: penalties, lawsuits, lost in sales and finally damage of the brand image. This without considering the number of stocks of food that is constantly wasted and consequentially the consumer trust ruined (IBM, 2020). As not all the companies can quickly identify the cause of the food incidents due to the numbers of days or weeks that take to track a mix of digital and paper food documentation across the complex network of distributors and suppliers (IBM, 2020). Therefore, blockchain can support DeliverEat with a digital food system where network participants can have access, in order to identify the gaps and track almost immediately the cause of food incident, promoting trust and transparency ensuring a better and safer food system (IBM, 2020). Reducing so the amount of money and time wasted facilitating so the way to archive DeliverEat value also providing flexible solutions to the costumers. “IBM Food Trust creates a secure, shared and permissioned record of transactions. This enables unprecedented visibility during each step of the food supply chain, so you can achieve new levels of trust and transparency, making food safer and smarter from farm to fork.” (IBM, 2020). A digital food chain working with blockchain will enable all the supply participant to work in the same level and understand each other easily in order to collaborate and operate in a more efficient way with the strength of being flexible to quickly adapt to any change due to the easy access to information and quick response to difficulties (IBM, 2020). This, will provide DeliverEat a more flexible and optimal environment that will certainly support the idea of compile the value chain throughout the different stages of it. And thus, improving the process in order to create a more realistic and archivable corporate strategy and values, considering a proper implementation to avoid at any cost the hindering of a smooth and reliable operational process thanks to blockchain. 6 2121804/1 Conclusion Its can be concluded the essential impact that blockchain may have upon the different aspects of the corporate strategy and how assertively can be used and applied correctly to develop and improve the current value chain. Is evident how blockchain help facilitating the transactional processes and many other sectors inside the organization and food sector, if utilized correctly with the sufficient knowledge. Therefore is vital of the company to understand and align the strategy and vision with the right appliance of the blockchain in order to make full use of it, and finally archive the desire goal in the current modern world. 7 2121804/1 Reference list: Curry, Michael.; Marshall Byron.; Crossler, Robert E.; Correia, John (2018). "InfoSec Process Action Model (IPAM): Systematically Addressing Individual Security Behavior". Available at: InfoSec Process Action Model (IPAM): Systematically Addressing Individual Security Behavior: ACM SIGMIS Database: the DATABASE for Advances in Information Systems: Vol 49, No SI [Accessed: 20 April 2023]. Fletcher, Martin (2016). "An introduction to information risk". The National Archives. Available at: An introduction to information risk - The National Archives blog [Accessed: 20 April 2023]. Foodsafety Magazine. (2020) A Look Back at 2019 Food Recalls. Available at: A Look Back at 2019 Food Recalls | Food Safety (food-safety.com) [Accessed: 20 April 2023]. Iansiti, Marco; Lakhani, Karim R. (2017). "The Truth About Blockchain". Harvard Business Review. Cambridge, Massachusetts: Harvard University. Available at: The Truth About Blockchain (archive.org) [Accessed: 20 April 2023]. IBM (2023) Blockchain. Available at: What is Blockchain Technology? - IBM Blockchain | IBM [Accessed: 20 April 2023]. Joshi, Chanchala.; Singh, Umesh Kumar (2017). "Information security risks management framework – A step towards mitigating security risks in university network". Available at: Information security risks management framework – A step towards mitigating security risks in university network - ScienceDirect [Accessed: 20 April 2023]. Lawton, George. (2019) 10 blockchain problems supply chains need to look out for. Available at: 10 blockchain problems supply chains need to look out for | TechTarget [Accessed: 20 April 2023]. Lunn, Bernard (10 February 2018). "Blockchain may finally disrupt payments from Micropayments to credit cards to SWIFT". Available at: Blockchain may finally disrupt payments from Micropayments to credit cards to SWIFT – Daily Fintech (archive.org) [Accessed: 20 April 2023]. Majaski, Christina (2021). Distributed Ledgers: Definition, How They're Used, and Potential. Available at: Distributed Ledgers: Definition, How They're Used, and Potential (investopedia.com) [Accessed: 20 April 2023]. Marr, Bernard (2018) A Very Brief History Of Blockchain Technology Everyone Should Read. Available at: A Very Brief History Of Blockchain Technology Everyone Should Read (forbes.com) [Accessed: 20 April 2023]. Menezes, Alfred J.; van Oorschot, Paul C.; Vanstone, Scott A. (2018). "Hash functions". Handbook of Applied Cryptography. CRC Press. pp. 33. Oberhaus, Daniel (2018). "The World's Oldest Blockchain Has Been Hiding in the New York Times Since 1995". Available at: The World’s Oldest Blockchain Has Been Hiding in the New York Times Since 1995 (vice.com) [Accessed: 20 April 2023]. Scardovi, Claudio (2016). Restructuring and Innovation in Banking. Springer. p. 36. The UK Government Chief Scientific Adviser (2016). Distributed Ledger Technology: beyond block chain. Available at: Distributed Ledger Technology: beyond block chain (publishing.service.gov.uk) [Accessed: 20 April 2023]. 8