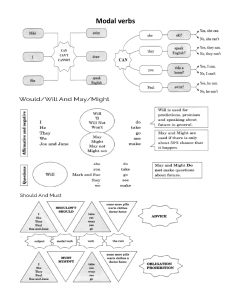
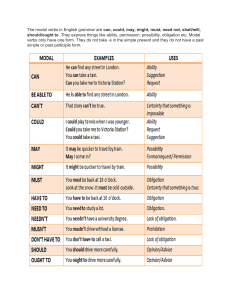
ENGLISH FOR ACADEMIC & PROFESSIONAL PURPOSES LET’S TEST YOU BRAIN ● Which reading strategy involves quickly glancing through a text to get a sense of its main ideas and overall structure? ● When encountering a complex academic passage, what strategy can you use to break down the content into manageable sections for better understanding? ● Explain the concept of making “inferences” while reading an academic text and how it contributes to a deeper understanding of the content. The reading strategy that involves quickly glancing through a text to get a sense of its main ideas and overall structure is called "skimming." Skimming is used to rapidly identify the key points, headings, and overall flow of a text without delving into every detail. It's particularly useful for previewing content and determining whether the text is worth reading more thoroughly. ● When encountering a complex academic passage, a useful strategy to break down the content into manageable sections for better understanding is "chunking." Chunking involves dividing the content into smaller, logical segments or chunks, such as paragraphs or sections. By focusing on one chunk at a time, you can digest the information more effectively and grasp the relationships between different parts of the passage. ● The concept of making "inferences" while reading an academic text refers to drawing conclusions or making educated guesses about information that is not explicitly stated in the text. Inferences are based on the reader's prior knowledge, context clues, and the information provided in the text. ● They require critical thinking and a deep engagement with the material. Making inferences contributes to a deeper understanding of the content by enabling readers to connect the dots between what is explicitly mentioned and what is implied. This process encourages readers to think beyond the surface level, consider different perspectives, and develop a more nuanced comprehension of the subject matter. Inferences also allow readers to fill in gaps, infer motivations, and analyze the author's intentions, leading to a richer interpretation of the text's meaning. A. Direction: identify whether each passage can be an academic text or non-academic text. Write A if it is academic and N if it is non-academic. _____1. Some educators suggest that the distinction between conversational and academic language is somewhat arbitrary and that it is the situation, community, or context that is either predominantly social or academic. _____2. The current study showed that COVID-19 pandemic lockdown affected the academic performance of most participants with varying degrees. _____3. In his reverie he remembers how nature marked the season it happened. _____4. I believe they are the first and last and the closest things I have to say about my own life. _____5. The current study showed that the most popular device that students used to access the online materials was the smart phone followed by laptop, while the least used tool was the personal computer ● ● ● ● ● A - This passage discusses a topic in an analytical manner and uses language that suggests it's discussing a concept or theory. A - This passage refers to a study and discusses the impact of a specific event on participants' academic performance. N - This passage seems to be more of a personal reflection or creative expression, not discussing academic concepts. N - This passage appears to be a personal statement or introspection, not focused on academic content. A - This passage presents research findings and data related to students' use of different devices for accessing online materials. Direction: Read and answer the questions below. Write your answers on a separated sheet of paper. 1. What is the easiest writing assignment you have done so far? 2. How about the most difficult writing assignment you have done? 3. Based on your answer, what do you think is academic writing and its differences from other kinds of writing? WHAT IS ACADEMIC TEXT? ● ● ● Academic text is a type of text or writing that is written by professionals in a given field. and is also intended for a scholarly audience. Nature and Characteristics of an Academic Text An academic text is a written language that provides information, which contain ideas and concepts that are related to the particular discipline. Essay, Research Paper, Report, Project, Article, Thesis, and Dissertation are considered as academic texts. EXPLICITNESS -Academic writing demands use of appropriate signposting strategies which allow your readers to trace the relationship of the various parts found in your study. -So, if you intend to show that there will be a change in your line of argument , then make it clear by using however: It is apparent that the government hopes to provide assistance to the poor. However, making dole outs available to “the poorest of the poor” seems to work not in the long term. If a sentence leads to providing a reason in another sentence, make it explicit by using an appropriate phrases like: While several cabinet members had proposed measures to counter the increasing power rates proposed by MERALCO, it was not until the expose of Garcia that the breakdown of power charges on consumers was fully explained. Partly this was because even retirement benefits of MERALCO employees are being charged on all power users. Other useful phrases would be: 1. This is due to the… A number of MERALCO consumers trooped to the city hall to claim the Php 500.00 cash incentive. This is due to the Supreme Court ruling that overcharges must be returned to the end users whose electric consumption for April –May period was below 100kw/hr. 2. This resulted in … With the Supreme Court ordering MERALCO to return overcharges to the end users, government offices have been tapped to operate as claim centers. This resulted in a number of MERALCO consumers trooping to the city hall to claim the Php 500.00 cash incentive. When two ideas appear rather the same, express them clearly. The study showed that 80 percent of the 200 participants involved in the study were dissatisfied with the operations of MERALCO. Similarly, the data arrived at revealed that majority of the participants were not aware of the changes imposed on them by MERALCO. If you intend your sentence to give extra information, make it clear. MERALCO has been operating as a business conglomerate involving foreign stakeholders and independent power producers or IPP. In addition, MERALCO owns major IPPs operating in the region. If you are giving examples, do it explicitly. The MERALCO issue has led to disputes between opposition and administration senators. For example, those who have been labeled as working against the president consider the issue as the administration’s way of avoiding the NBN-ZTE scandal. Structure The basic structure that is used by an academic text is consist of three (3) parts :introduction, body, and conclusion which is formal and logical. This kind of structure enables the reader to follow the argument and navigate the text. In academic writing a clear structure and a logical flow are imperative to a cohesive text. Tone This refers to the attitude conveyed in a piece of writing. The arguments of others are fairly presented and with an appropriate narrative tone. When presenting a position or argument that disagrees with one’s perspectives, describe the argument accurately without loaded or biased language. Language It is important to use unambiguous language. Clear topic sentences enable a reader to follow your line of thinking without difficulty. Formal language and the third person point of view should be used. Technical language appropriate to area of study may also be used, however, it does not mean using “big words” just for the sake of doing so. Citation Citing sources in the body of the paper and providing a list of references as either footnotes or endnotes is a very important aspect of an academic text. It is essential to always acknowledge the source of any ideas, research findings, data, or quoted text that have been used in a paper as a defense against allegations of plagiarism. Complexity An academic text addresses complex issues that require higher-order thinking skills to comprehend. Evidence-based Arguments What is valued in an academic text is that opinions are based on a sound understanding of the pertinent body of knowledge and academic debates that exist within, and often external to a specific discipline. Thesis-driven The starting point of an academic text is a particular perspective, idea or position applied to the chosen research problem, such as establishing, proving, or disproving solutions to the questions posed for the topic. Features of Academic Texts: 1. Complex - Written language has no longer words, it is lexically more varied vocabulary. - Written texts are shorter and the language has more grammatical complexity, including more subordinate clauses and more passives. 2. Formal - Should avoid colloquial words and expressions. 3. Precise - Facts are given accurately and precisely. 4. Objective - has fewer words that emphasize on the information you want to give and the arguments you want to make - mostly use nouns (adjectives), rather than verbs (adverbs) 5. Explicit - It is the responsibility of the writer in English to make it clear to the reader how the various parts of the text are related. 6. Accurate - Uses vocabulary accurately - Most subjects have words with narrow specific meanings. 7. Hedging - It is necessary to make decisions about your stance on a particular subject, or the strength of the claims you are making. 8. Responsible - You must be responsible for and must be able to provide evidence and justification for any claims you make. 9. Organize - Well-organized. - It flows easily from one section to the next in a logical fashion. 10. Plan - Well-planned. - It usually takes place after research and evaluation, according to specific purpose and plan. Purposes in Reading an Academic Text 1. To locate a main idea 2. To scan for information 3. To identify gaps in existing studies 4. To connect new ideas to existing ones 5. To gain more pieces of information 6. To support a particular writing assignment 7. To deeply understand an existing idea. Factors to Consider in Writing Academic Text 1.State critical questions and issues 2. Provide facts and evidence from credible sources 3. Use precise and accurate words while avoiding jargon 4. Take an objective point of view 5. List references 6. Use cautious language Academic Language Academic language is the language needed by students to do the work in schools. It includes, for example, discipline-specific vocabulary, grammar and punctuation, and applications of rhetorical conventions and devices that are typical for a content area (e.g., essays, lab reports, discussions of a controversial issue.) Students who master academic language are more likely to be successful in academic and professional settings. Social language is the set of vocabulary that allows us to communicate with others in the context of regular daily conversations. Characteristics of Academic Language A. Formal - It should not sound conversational or casual. Colloquial, idiomatic, slang or journalistic expressions should particularly be avoided. Examples: Use… Consider, monitor Revise, review Solve, repair, amend Instead… Look at Go over Fix Avoiding rhetorical questions in academic writing also marks closeness with your reader as rhetorical questions constantly seek the attention of readers. Poor example: How problems be solved? can these Improved version: Certain measures must be discovered to solve the problems. B. Objective - This means it is unbiased. It should be based on facts and evidence and are not influenced by personal feelings. - Avoiding emotive language that shows biases also lessens objectivity. Poor example: The investigators were very shocked to see the outcome of the test. Improved version: The investigators did not expect the results would be different. C. Impersonal - This involves avoiding the personal pronouns ‘I’ and ‘we’. For example, instead of writing ‘I will show’, you might write ‘this report will show’. The second person, ‘you’, is also to be avoided. Example: Subjective construction: You need to conduct the experiment. Improved version: The researchers need to conduct the experiment. CAUTION -Academic writing requires tact since we often deal with knowledge that is built from established theories and concepts. Therefore, caution is need to avoid making sweeping generalizations. Consider the following examples: Government officials are corrupt Modal verbs, adverbs, or verbs Improved versions • Some government officials may be corrupt (modal verb) • Corruption is commonly linked to some key government officials (adverb) • A number of government officials tend to be linked with cases of corruption (verb) In academic writing caution needs to be observed in the following parts of your paper: 1. When a hypothesis needs to be tested. 2. Drawing conclusions or predictions from your findings which may generalize certain groups or may not be too exclusive. 3. Referencing others’ work to build on your own paper. Below are some forms that you may use in observing caution in writing: Verbs indicating caution: Tends, suggests, appear to be, think, believe, doubt, indicate Modal verbs: will, must, would, may, can might, could Adverbs of frequently: often, sometimes, usually Modifiers: quite, rather, fairly FORMALITY Formality can be achieved through: 1. Choosing expand modal forms over contracted forms (cannot instead of can’t do not instead of don’t) 2. Choosing one verb forms over two word verbs (damage instead of mess up) 3. Choosing expanded terms over its abbreviated equivalents (as soon as possible instead ASAP) 4. Avoiding colloquial/trite/idiomatic expressions ( kind of like, As a matter of fact, I need to go to the John) THANK YOU! 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Activity 1: Underline which words or expressions are considered colloquial. With the growing number of health-conscious articles, a lot of young professionals are becoming serious about maintaining a healthy life-style. It is a bit improper to assume that the meal plan does not work. Experts determined that a lot of incoming freshman students are interested in sports activities. Teachers say that a lot of incoming freshman students are interested in sports activities. Lucas (2004) got together with Castro (2002) in conducting an experiment on effectively enhancing muscle buildup. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. Activity 2: Rewrite the following sentences to observe a more formal tone. Writing can’t be done effectively if you don’t burn the midnight oil. ___________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________ Parenting is a 24/7 job. ___________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________ Watching that romcom gave the audience the feels. ___________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________ The class is cooking up something big. ___________________________________________________________________________________________________ ____________ Adventure may mean doing something epic. ___________________________________________________________________________________________________ ____________ Activity 3: Provide the counterpart singleword verb of the two-word verb. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. __________ Senate set up the Meralco committee. __________ Mothers cut down spending on rice. __________ Oil price has gone up. __________ Students come up with a solution. __________ Students looked into the problem. __________ The dollar rate went up and down. __________ Students brought up the uniform issue. __________ The school gets rid of tuition hike. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. __________ Parents turned down the proposal. __________ The proposal turned out a positive result. __________ Major oil players put off oil price hike. __________ Employees did not put up with the company’s expectations. __________ Parents could not put away money for their children’s education. __________ The chemical gives off a foul odor. __________ The class carried out a research on the frequently of using SMS.