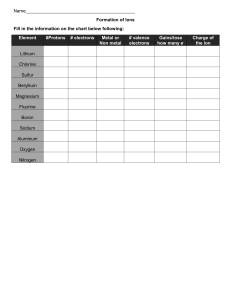
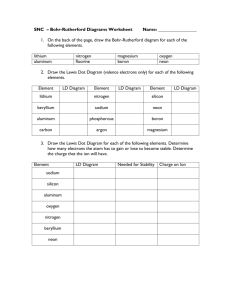
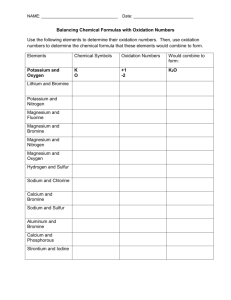
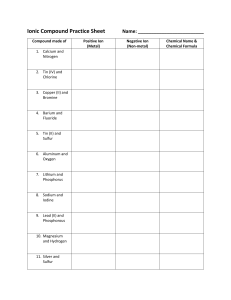
Element Symbols Matching Cards Cut out the cards and give them a good shuffle. To play with one person, lay the cards face up on the table and see if you can pair up the fact card with the element symbol. Check your pairs using the answer sheet. You could challenge yourself by timing each go and seeing if you can get faster with each attempt. To play with 2 or more people, lay the cards face down on the table in a grid. Take it in turns to flip over two cards. If they form a pair then you can keep them. If they do not, then turn them back over. See if you can remember where the matching cards are when others turn them over. Check your pairs using the answer sheet. The winner is the person with the most correct pairs when all of the cards have been matched. Hydrogen Hydrogen is the most abundant element in the universe. The planet Jupiter is composed mostly of hydrogen. Hydrogen can be used as a pollutionfree fuel for hydrogen-powered cars and buses. Hydrogen is a gas at room temperature. Helium Helium gets its name from helios, the Greek word for the Sun, because it was detected in the Sun many years before it was found on Earth. Helium is the second most abundant element in the universe. It is present in all stars. Helium is a gas at room temperature. 1 H 1 4 He 2 Lithium Lithium has the lowest density of all metals. It can float on water. Lithium gives the red colour to some fireworks. It is present in almost all igneous rocks and mineral springs. Lithium is a solid at room temperature. Beryllium Emeralds are compounds containing beryllium. Some of the oldest emerald mines were developed by the Romans in Egypt 2000 years ago. Beryllium played a role in the discovery of the neutron when James Chadwick bombarded it with alpha particles. Beryllium is a solid at room temperature. Boron Before 1808 the only source of boron was from Lake Yamdrok Cho, in Tibet. It is essential for the cell walls of plants. Several boron compounds are being studied as a possible treatment for brain tumours. Boron is a solid at room temperature. 7 Li 3 9 Be 4 11 B 5 Carbon Carbon is found naturally as diamond, graphite and anthracite (a type of coal). Diamond is the hardest known material. Carbon is essential for life and makes up 18.5% of the human body. Living things get almost all of their carbon from carbon dioxide. Carbon is a solid at room temperature. Nitrogen Nitrogen makes up 78% of the air. Nitrogen is needed to build DNA and amino acids (the building blocks of proteins). The nitrogen cycle is the process of nitrogen circulating between the atmosphere, soil and living things. Nitrogen is a gas at room temperature. Oxygen Oxygen makes up 21% of the atmosphere. Living things use oxygen for aerobic respiration. Life can exist in rivers, lakes and oceans because oxygen is soluble in water. Oxygen is a gas at room temperature. 12 C 6 14 N 7 16 O 8 Fluorine Fluorine is the most reactive of all the non-metal elements. The first time it was produced commercially was for the atom bomb in the Second World War. Compounds of fluorine are used in toothpaste and sometimes added to drinking water to prevent cavities in teeth. Fluorine is a gas at room temperature. Neon Neon gets its name from the Greek word neos which means new. Neon does not react with any other element. When an electric current is passed through neon it glows red. This process is used to make advertising signs stand out. Neon is a gas at room temperature. Sodium We need to eat about 3g of sodium a day, to replace what is lost in urine and sweat. However, the average person eats 10g. Extra sodium may contribute to high blood pressure. Sodium makes up 2.6% of the Earth’s crust, but it is very reactive so is never found naturally in its pure form. Sodium is a solid at room temperature. 19 F 9 20 Ne 10 23 Na 11 Magnesium Magnesium is an essential element in the chlorophyll found in plant leaves. Without magnesium, photosynthesis would not take place and the world would be a very different place! Magnesium is essential for enzyme function and humans need to take in 250-350mg of magnesium a day. Magnesium is a solid at room temperature. Aluminium Aluminium is the second most malleable (easily shaped) metal. It is the most abundant metal in the Earth’s crust (8.1%) but is usually found combined with other elements in minerals such as bauxite and cryolite. Aluminium is a solid at room temperature. Silicon Silicon is one of the most useful elements to humanity. Silicon is the second most abundant element on Earth and makes up 27.7% of the Earth’s crust by mass. Silicon has a higher density in liquid form than it does when it is a solid. Silicon is a solid at room temperature. 24 Mg 12 27 Al 13 28 Si 14 Phosphorus Phosphate is essential to all living things. It forms the backbone of DNA and RNA and is part of the molecule ATP, which is essential for energy transfer in living things. We store 750g of phosphate in our bodies, mostly as calcium phosphate in our bones and teeth. Phosphorus is a solid at room temperature. Sulfur Sulfur dioxide is produced when coal is burned. Sulfur dioxide in the atmosphere causes acid rain. Sulfur occurs naturally as a yellow element, often in volcanic areas. Intestinal gas can have a nasty odour because of the sulfur compounds released as waste by bacteria in the gut. Sulfur is a solid at room temperature. Chlorine Chlorine is a toxic gas that was used as a chemical weapon in the First World War. In the past it was used to make the anaesthetic chloroform. We now know that chloroform can cause liver damage, so its use is strictly regulated. Chlorine is a gas at room temperature. 31 P 15 32 S 16 35.5 Cl 17 Argon Argon is the third most abundant atmospheric gas, making up 0.94% of the Earth’s atmosphere. When it is ionised, argon emits a violet glow. Argon is a gas at room temperature. Potassium Potassium is essential to life; it is found in all cells. Sardines, nuts, raisins, chocolate and potatoes contain a lot of potassium. Mining extracts about 35 million tonnes of potassium a year, it is mostly used to produce fertilisers that replace the potassium in the soil that crops use up. Potassium is a solid at room temperature. Calcium Calcium is essential for healthy growth of teeth and bones. The average human contains about 1kg of calcium. Hard water contains calcium compounds. When these compounds precipitate out in caves they form stalactites and stalagmites. Calcium is a solid at room temperature. 40 Ar 18 39 K 19 40 Ca 20