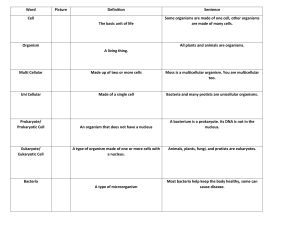
Version 2 TAXONOMY UNIT TEST v2 - SBI3U 2011 Name: ___________________ Part A: Multiple Choice and Matching 1. Which taxon includes all of the others? a. genus b. family Total Marks = 50 25 marks d. class e. species c. order 2. Which statement about binomial naming is correct? a. It was devised by the Swedish botanist Carolus Linnaeus. b. It uses two names to identify an organism: one for the genus and another for the species. c. It is used today by biologists, to classify living organisms. d. It is used by scientists who speak different languages. e. all of the above 3. Which of the following is not a method used for nutrition by bacteria? a. photoautotrophs d. all of the above are used by bacteria b. chemoautotrophs e. none of the above are used by bacteria c. chemoheterotophs 4. Which label is pointing to a sample of streptococcus? a. A b. B c. C d. D e. none of these 5. Which of the following is not a characteristic of a member of the kingdom protista? a. are only heterotrophic d. most are microscopic and unicellular b. more recent than the bacteria e. are classified as eukaryotes c. have membrane-bound organelles 6. Which of the following is not true about animal-like protists (protozoa) a. all are heterotrophic. d. they are mostly terrestrial. b. in general, they move to obtain food. e. reproduction is usually asexual. c. classified largely by locomotion type. 7. Under adverse or threatening conditions, members of the protozoans may form resting cells called a. spores. d. ectoplasms. b. endodonts. e. cysts. c. encrustacenas. Version 2 8. Which of the following is not true about the life cycle of fungi? a. There is wide variety in fungal life cycles. b. Fungi reproduce both asexually and sexually. c. The haploid spores are produced in sporangia. d. Spores are usually dispersed by animals. e. Asexual reproduction includes fragmentation. 9. Which of the following is not a characteristic of an organism in the animal kingdom? a. multicellular d. are studied by zoologists b. eukaryotic e. are autotrophic c. no cell wall 10. Which of the following is one of the body layers in an animal? a. epiderm d. ectoderm b. meriderm e. none of the above c. entoderm 11. Which of the following is true about reproduction in sponges? a. They are hermaphroditic. b. Eggs and sperm are produced at the same time in the same sponge. c. Fertilized eggs develop into stationary larva. d. They do not produce asexually. e. None of these statements is true. 12. Which of the following statements is/are correct? I. Members of the Bacteria domain are capable of photosynthesis. II. Phytoplankton belong to the Protist kingdom. III. Members of the Animal kingdom have autotrophic capabilities. IV. Members of the Fungi kingdom obtain their food by absorption. a. I and II d. I, II, and IV b. I, III, and IV e. II, III, and IV c. I and IV 13. Clams are in the phylum a. Porifera b. Mollusca c. Cephalochordata d. Cnidaria e. Platyhelminthes 14. What are methanogens, thermoacidophiles, and halophiles? a. cyanobacteria d. slime moulds b. bacteria e. archaea c. protozoans 15. Which of the following is not included as a member of the arthropods? a. spiders d. tick b. crabs e. centipedes c. starfish Version 2 All multiple choice answers must be recorded in this table. Circle the answer as you do each question so you can easily check your answers. When you are finished answering all the multiple choice questions transfer your answers to this table. Question Answer 1 2 3 4 5 6 Question Answer 11 12 13 14 15 16 17. a. b. c. d. e. 7 8 9 10 Match each term with the correct statement below. [5] binomial nomenclature f. Fungi species g. Plantae taxa h. Animalia Bacteria i. phylogeny Protista j. dichotomous _____ no nucleus, heterotrophic or autotrophic, reproduce asexually, live everywhere _____ multicellular, heterotrophic, reproduce sexually, live either on land or in water _____ most single-celled, eukaryotic, some heterotrophs, some autotrophs, reproduce sexually or asexually, live everywhere _____ a two-part key used to identify living things _____ a method of naming organisms by using two names (genus and species) _____ most multicellular, heterotrophic, reproduce sexually or asexually, most live on land _____ multicellular, autotrophic, reproduce sexually or asexually, most live on land _____ the history of the evolution of a species or a group of organisms _____ a group of organisms that look alike and can interbreed under natural conditions to produce fertile offspring _____ categories used to classify organisms Version 2 18. a. b. c. d. e. Match each term with the correct statement about protists below. [5] Algae Ascomycotes mating strains radially symetric Oomycotes f. g. h. i. j. coelmates phagocytosis hyphae Nematoda ectoderm _____ starfish _____ water moulds _____ forms skin and nerves _____ autotrophs with chlorophyll and carotenoids _____ simplest organisms to have a digestive tract _____ earthworms _____ engulfing food to eat _____ a network of fine filaments _____ sac fungi _____ combine to form zygospores Part B: Short Answer 1. 15 marks List all the taxa in order starting from the domain down to the species level. [3] Domain _______________ ________________ _______________ _______________________ _______________ ________________ species 2. What are two major differences between prokaryotes and eukaryotes? [2] 3.a) What are the two parts of a scientific name? [1] b) What is an important advantage of a scientific name over a common name? [1] 4. Name2 different ways bacteria reproduce and specify if the method is sexual or asexual. [2] Version 2 5.a) Explain extracellular digestion. [1] b) Name a kingdom and an organism in that kingdom that obtains nutrients by extracellular digestion. [1] 6. Choose only one of the following comparisons. [4] compare archaea and bacteria OR compare protists and fungi OR compare protists and animals Version 2 Part C: Charts and Diagrams 1. 10 marks Name the following organisms. [4 x 0.5 = 2] a) ___________________________ b) ____________________________ c) _________________________ d) ____________________________ 2. Use the table below to answer the following questions. Common Name red squirrel short-tail weasel groundhog mink eastern chipmunk river otter fisher muskrat black-footed ferret Family Sciuridae Mustelidae Sciuridae Mustelidae Sciuridae Mustelidae Mustelidae Cricetidae Mustelidae Scientific Name Tamiasciurus hudsonicus Mustela erminea Marmota monax Mustela vison Tamias striatus Lutra canadensis Martes pennanti Ondatra zibethica Mustela nigripes a) Which animal is the least closely related to all the others? [1] ________________- b) What is the most specific taxa that a fisher and a short tailed weasel have in common? [1] ____________________________________ c) Which organism in the family Mustelidae is least closely related to the other members of the same family? [1] ___________________________________ d) What phyla do all these organisms belong to? [1] __________________________ Version 2 3. Use the following diagram of the classes of chordates in the phylum Chordata to answer the questions below. a) What characteristic is missing from the Urochordata that is found in the Agnatha? [1] b) What characteristic is shared by reptiles, birds and mammals? [1] c) List 3 questions that would need to be asked to decide the correct class for a fish. [1] d) What is the name given to a list of questions that help scientists to determine the correct taxonomic classification of an organism? [1] Version 2 ANSWERS TAXONOMY UNIT TEST v2 - SBI3U 2011 Name: ___________________ Total Marks = 50 Question Answer 1 D 2 E 3 D 4 C 5 A Question Answer 11 12 C/D 13 B 14 E 15 C 6 D/E 7 A 8 D 9 E 10 D A 17. a. b. c. d. e. Match each term with the correct statement below. [5] binomial nomenclature f. Fungi species g. Plantae taxa h. Animalia Bacteria i. phylogeny Protista j. dichotomous ___D__ no nucleus, heterotrophic or autotrophic, reproduce asexually, live everywhere ___H__ multicellular, heterotrophic, reproduce sexually, live either on land or in water ___E__ most single-celled, eukaryotic, some heterotrophs, some autotrophs, reproduce sexually or asexually, live everywhere ___J__ a two-part key used to identify living things ___A__ a method of naming organisms by using two names (genus and species) ___F__ most multicellular, heterotrophic, reproduce sexually or asexually, most live on land ___G__ multicellular, autotrophic, reproduce sexually or asexually, most live on land ___I__ the history of the evolution of a species or a group of organisms ___B__ a group of organisms that look alike and can interbreed under natural conditions to produce fertile offspring ___C__ categories used to classify organisms Version 2 18. a. b. c. d. e. Match each term with the correct statement about protists below. [5] Algae Ascomycotes mating strains radially symetric Oomycotes f. g. h. i. j. coelmates phagocytosis hyphae Nematoda ectoderm __D___ starfish __E___ water moulds __J___ forms skin and nerves __A___ autotrophs with chlorophyll and carotenoids __I___ simplest organisms to have a digestive tract __F___ earthworms __G___ engulfing food to eat ___H__ a network of fine filaments ___B__ sac fungi ___C__ combine to form zygospores Part B: Short Answer 1. 15 marks List all the taxa in order starting from the domain down to the species level. [3] Domain Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus species 2. What are two major differences between prokaryotes and eukaryotes? [2] - PROKARYOTES HAVE NO MEMBRANE BOUND NUCLEUS OR OTHER MEMBRANE BOUND ORGANELLES AND EUKARYOTES DO - PROKARYOTES BELONG TO THE DOMAINS ARCHAEA AND BACTERIA WHILE ALL OTHER ORGANISMS BELONG TO THE DOMAIN EUKARYOTA - EUKARYOTES ARE LARGER CELLS THAN PROKARYOTES AND USUALLY MULTICELLULAR - PROKARYOTES HAVE A SMALL CIRCULAR CHROMOSOME AND EUKARYOTES HAVE SEVERAL SEPARATE CHROMOSOMES 3.a) What are the two parts of a scientific name? [1] - GENUS AND SPECIES b) What is an important advantage of a scientific name over a common name? [1] - COMMON NAMES ARE NOT PRECISE AND SCIENTIFIC NAMES ARE VERY SPECIFIC Version 2 4. Name2 different ways bacteria reproduce and specify if the method is sexual or asexual. [2] ASEXUAL - BINARY FISSION – ORGANISM COPIES CIRCULAR DNA AND DIVIDES IN HALF SEXUAL – CONJUGATION – DNA TRANSFERRED BETWEEN BACTERIA BY A PILI CREATING BACTERIA WITH NEW DNA COMBINATIONS SPORES – NOT EXACTLY A FORM OF REPRODUCTION BUT A FORM OF PROTECTING AN ORGANISM FROM DANGEROUS ENVIRONMENTAL CONDITIONS BUT COULD BE CONSIDERED ASEXUAL IF MENTIONED 5.a) b) Explain extracellular digestion. [1] the organism excretes digestive enzymes to the exterior where the food is the enzymes break down the food the organism absorbs the food Name a kingdom and an organism in that kingdom that obtains nutrients by extracellular digestion. [1] Fungi – mushrooms Animalia - Cnidaria 6. Choose only one of the following comparisons. [4] compare archaea and bacteria OR compare protists and fungi OR compare protists and animals A comparison question must state similarities and differences. Compare the same features. A) archaea and bacteria Similarities - they are both prokaryotes - both are unicellular organisms - they are both small cells although archaea are smaller than bacteria - neither has a membrane bound nucleus or other membrane bound organelles Differences - archaea are usually anaerobic while bacteria can be either aerobic or anaerobic - archaea only reproduce asexually while bacteria can reproduce both sexually and asexually - bacteria have a wider range of nutrition while archaea are usually only heterotrophs B) protists and fungi Similarities - the fungi-like protists are heterotrophs like fungi and eat dead material - both are eukaryotes - both reproduce with spores that can be sexually or asexually formed Differences - protists are usually unicellular while fungi are multicellular - fungi usually get nutrition by extra-cellular digestion while protists can be hetertrophs or autotrophs C) protists and animals Similarities - both are eukaryotes - lack cell walls - the animal like protists and animals are both heterotrophic - animals are motile and so are most animal-like protists Differences - protists are usually unicellular and animals are multi-cellular - some protists are autotrophs but not animals - animals are motile but not all protists are motile Version 2 Part C: Charts and Diagrams 1. 10 marks Name the following organisms. [4 x 0.5 = 2] a)paramecium b) ameoba c) planaria d) sponge 2. Use the table below to answer the following questions. a) Which animal is the least closely related to all the others? [1] muskrat or Ondatra zibethica b) What is the most specific taxa that a fisher and a short tailed weasel have in common? [1] family or Mustrlidae c) Which organism in the family Mustelidae is least closely related to the other members of the same family? [1] river otter or fisher (either answer is correct) d) What phyla do all these organisms belong to? [1] chordata (the answer is given in next question!) 3. a) Use the following diagram of the classes of chordates in the phylum Chordata to answer the questions below. What characteristic is missing from the Urochordata that is found in the Agnatha? [1] vertebrae b) What characteristic is shared by reptiles, birds and mammals? [1] amnion c) List 3 questions that would need to be asked to decide the correct class for a fish. [1] Does the organism have vertebrae? Does the organism have jaws? Does the organisms have lungs? d) What is the name given to a list of questions that help scientists to determine the correct taxonomic classification of an organism? [1] dichotomous key