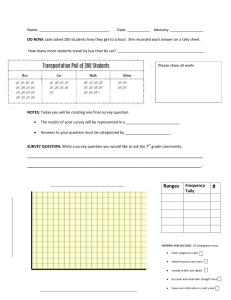
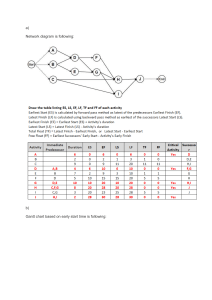
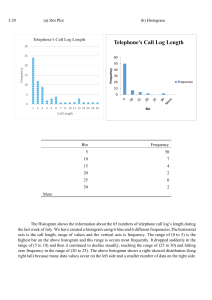
Quality is said to be the ability of a product or service to meet the customers needs. It then stands to reason that Total Quality Management is the management of the entire organisation to excel in all aspects of products and services that are important to the customer. As such, the quality emphasis flows through the entire organisation from supplier to the customer, requiring a never-ending process of continuous improvement. Total Quality Management tools help operations managers to identify, analyse as well as assess quantitative and qualitative information that is relevant to the business. These tools can identify procedures, statistics, ideas, cause and effect concerns and other issues important to the organisation. FLOW CHART Definition The flowchart has been around since the 1920s and was created by Frank and Lillian Gilbreth. They were initially created to “describe computer algorithms” but have today evolved to be used to demonstrate “a variety of business workflows and processes.” It is also said to be a representation of a flow of information arranged to show the solution to a task (through a step-by-step or algorithmic approach). A flowchart illustrates the process or steps as boxes of various kinds in a specified order with connected boxes and arrows. Uses A flowchart is significant in its use in that it provides a breakdown of the process by showing the initial steps(s), possible intermediary steps and subsequent outcome(s). The tasks are organised in such a way that that the information displayed is chronological and can be identified by type (eg. date, process, decision among other classifications). A flowchart has to be distinctly readable and this is the most important aspect of the display. The higher or clearer the readability, the better it is for the information to be understood as a visual representation/description of the process. If it is not readable in a clear way, it may become complicated and cause confusion. Types/Examples of Flowcharts and Histograms (Najay’s Portio) ***Not Overstepping Najay. Just had some info I thought was useful (for examples of flowcharts). There are various types/examples of flowcharts: https://nulab.com/learn/strategy-and-planning/flowchart-guide/#:~:te xt=Flowcharts%20have%20been%20around%20since,Engineers% 20(ASME)%20in%201921. References https://www.aicpa-cima.com/resources/article/quality-management-t ools-tqm-six-sigma-cost-of-quality-and-efqm What is histogram (From Marcia Green) A histogram is used to summarize discrete or continuous data. In other words, it provides a visual interpretation of numerical data by showing the number of data points that fall within a specified range of values (called “bins”). It is like a vertical bar graph. However, a histogram, unlike a vertical bar graph, shows no gaps between the bars. Parts of a Histogram 1. The title: The title describes the information included in the histogram. 2. X-axis: The X-axis are intervals that show the scale of values which the measurements fall under. 3. Y-axis: The Y-axis shows the number of times that the values occurred within the intervals set by the X-axis. 4. The bars: The height of the bar shows the number of times that the values occurred within the interval, while the width of the bar shows the interval that is covered. For a histogram with equal bins, the width should be the same across all bars. Importance of a Histogram Creating a histogram provides a visual representation of data distribution. Histograms can display a large amount of data and the frequency of the data values. The median and distribution of the data can be determined by a histogram. In addition, it can show any outliers or gaps in the data. Histogram - Examples, Types, and How to Make Histograms (corporatefinanceinstitute.com)