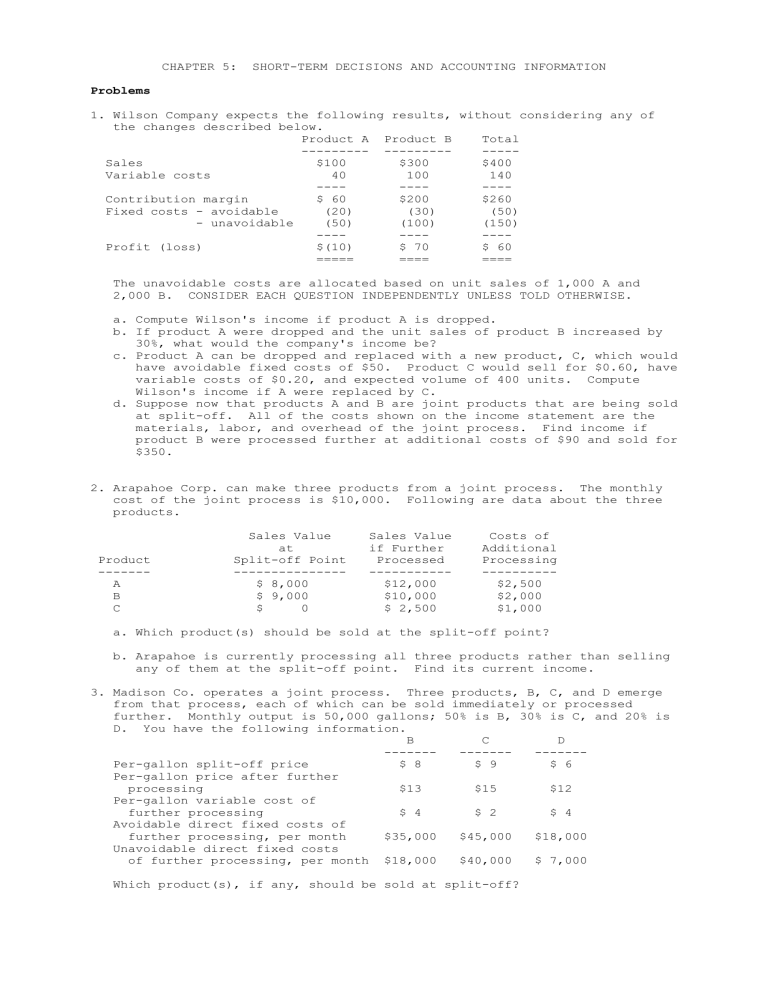
CHAPTER 5: SHORT-TERM DECISIONS AND ACCOUNTING INFORMATION Problems 1. Wilson Company expects the following results, without considering any of the changes described below. Product A Product B Total --------- ------------Sales $100 $300 $400 Variable costs 40 100 140 ---------Contribution margin $ 60 $200 $260 Fixed costs - avoidable (20) (30) (50) - unavoidable (50) (100) (150) ---------Profit (loss) $(10) $ 70 $ 60 ===== ==== ==== The unavoidable costs are allocated based on unit sales of 1,000 A and 2,000 B. CONSIDER EACH QUESTION INDEPENDENTLY UNLESS TOLD OTHERWISE. a. Compute Wilson's income if product A is dropped. b. If product A were dropped and the unit sales of product B increased by 30%, what would the company's income be? c. Product A can be dropped and replaced with a new product, C, which would have avoidable fixed costs of $50. Product C would sell for $0.60, have variable costs of $0.20, and expected volume of 400 units. Compute Wilson's income if A were replaced by C. d. Suppose now that products A and B are joint products that are being sold at split-off. All of the costs shown on the income statement are the materials, labor, and overhead of the joint process. Find income if product B were processed further at additional costs of $90 and sold for $350. 2. Arapahoe Corp. can make three products from a joint process. The monthly cost of the joint process is $10,000. Following are data about the three products. Product ------A B C Sales Value at Split-off Point --------------$ 8,000 $ 9,000 $ 0 Sales Value if Further Processed ----------$12,000 $10,000 $ 2,500 Costs of Additional Processing ---------$2,500 $2,000 $1,000 a. Which product(s) should be sold at the split-off point? b. Arapahoe is currently processing all three products rather than selling any of them at the split-off point. Find its current income. 3. Madison Co. operates a joint process. Three products, B, C, and D emerge from that process, each of which can be sold immediately or processed further. Monthly output is 50,000 gallons; 50% is B, 30% is C, and 20% is D. You have the following information. B C D ------------------Per-gallon split-off price $ 8 $ 9 $ 6 Per-gallon price after further processing $13 $15 $12 Per-gallon variable cost of further processing $ 4 $ 2 $ 4 Avoidable direct fixed costs of further processing, per month $35,000 $45,000 $18,000 Unavoidable direct fixed costs of further processing, per month $18,000 $40,000 $ 7,000 Which product(s), if any, should be sold at split-off? 4. Milton Company has three products: A, B, and C. Three machines are used to produce the products. The contribution margins, sales demands, and time on each machine (in minutes) is as follows: time time time Demand CM on M1 on M2 on M3 A 100 $45 10 15 12 B 80 $30 10 5 8 C 60 $40 5 10 5 There are 2,400 minutes available on each machine during the week. All materials needed are readily available on a just-in-time basis. a. What are the load factors for each of the three machines? b. Which machine is the bottleneck? c. How many units of A, B, and C should be produced during the week? 5. LaCrosse Company expects the following results, without considering any of the changes described below. Product A Product B Total ---------------------Sales $1,000 $3,000 $4,000 Variable costs 400 1,000 1,400 ------------Contribution margin $ 600 $2,000 $2,600 Fixed costs - avoidable (200) (300) (500) - unavoidable (500) (1,000) (1,500) -------------Profit (loss) $ (100) $ 700 $ 600 ===== ====== ====== The unavoidable costs are allocated based on unit sales of 1,000 A and 2,000 B. An exporter has offered $0.80 per unit for 200 units of A. a. Find the change in income if LaCrosse accepts the order, assuming no loss of regular sales. b. The managers believe that if they accept the special order, they will lose some sales at the regular price. Determine the number of units they could lose before the order became unprofitable. c. The managers believe that they will lose 80 units at the regular price if they accept the order. Calculate the price they must charge for the special order to increase income by $50. 6. Mays Company manufactures 200,000 units of part XYZ annually. The following information has been collected: Materials Direct labor Variable overhead Fixed overhead Total costs $200,000 110,000 50,000 100,000 -------$460,000 ======== Clemens Company has offered to provide part XYZ for $2 per unit. Assume no other productive use of the space exists. a. What would be the dollar impact if Mays accepted the offer? b. What is the maximum price Mays is willing to pay for the part? 7. Gonzalez can produce any of three products with its current production line. The heat treating equipment has 400 hours available during any given month. Per unit production, sales, and cost statistics are as follows: A B C ------Selling price $15 $20 $10 Variable cost $ 9 $12 $ 7 Required time in heat treat 1.5 hrs 2.5 hrs. 1.0 hrs Maximum demand per month 100 100 100 a. How many of each product should Gonzalez produce and sell? b. Suppose the selling price of C increases to $12. How many of each product should Gonzalez produce and sell? 8. Scottso Enterprises has the following products and costs: Unit demand per month Selling price Materials Labor and overhead Sales commission A 2,000 B 3,000 C 4,000 $500 150 180 50 $600 300 210 75 $800 350 300 100 Labor and overhead are applied to each product at a rate of $30 per machine hour. Management considers both labor and overhead to be fixed costs. a. Scottso currently has 60,000 hours available for production each month. How many units should be produced and sold for each product? b. An exporter has approached Scottso with an offer to purchase 500 units of product C for a discounted price. This is a one-time order and will not affect normal sales. No commission will be paid. What is the minimum price Scottso should accept? 9. Miami Company currently sells 3,000 units of product A for $1.25 each. Variable costs are $0.60, avoidable fixed costs are $750, and unavoidable allocated fixed costs are $1,500. An exporter has offered $0.90 per unit for 800 units of product A. a. Find the change in income if Miami can accept the order without affecting current sales. b. The managers believe that if they accept the special order, they will lose some sales at the regular price. Determine the number of units they could lose before the order became unprofitable. c. The managers believe that they will lose 270 units at the regular price if they accept the order. Calculate the price they must charge for the special order to increase income by $200. 10. Arpeggio Company manufactures 1,000 units of part XYZ annually. The following information has been collected: Materials Direct labor Variable overhead Fixed overhead $200,000 110,000 50,000 100,000 -------Total costs $460,000 ======== Mobile Company has offered to provide part XYZ for $400 per unit. If Arpeggio accepts the offer another product will be moved into the space vacated, saving $60,000 a year in rent. a. What would be the dollar impact if Arpeggio accepted the offer? b. What is the maximum price Arpeggio is willing to pay for the part?