Blockchain for
Healthcare Fraud
Reduction
Learn about the potential of Blockchain technology and its ability to
reduce healthcare frauds. We'll explore various IEEE research papers and
their findings, citing references in the bibliography.
by Atharva Sawant
Impact of Healthcare Fraud
What is healthcare
fraud?
How does it affect
the industry?
Can it be controlled?
Intentionally deceiving or
It hurts patients, healthcare
blockchain technology, we
misrepresenting
providers, and insurance
can significantly reduce the
information to gain
companies, causing crumble
instances of healthcare
unauthorized benefits or
and a lack of trust in the
fraud and bring
payments from the
healthcare system.
transparency to the
healthcare industry.
Yes, with modern
industry.
Introduction to Blockchain
What is Blockchain?
How does it work?
A secure, decentralized digital ledger that records
A group of computers called nodes work together
transactions, making them permanent, arranged,
to verify and record transactions, forming blocks
transparent, and tamper-proof.
that are cryptographically linked together,
creating a blockchain.
Potential of Blockchain for Healthcare
Fraud Reduction
1
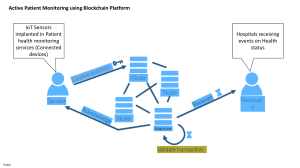
Transparency and Immutability
2
The blockchain's transparency and
Real-Time Auditing and
Monitoring
immutability help to deter fraud, keeping a
Transactions get verified across the
record of all past transactions that can't be
network in real-time, so blockchain
tampered with.
enables fraud detection much more
quickly than traditional methods.
3
Secure and Decentralized Data
Storage
4
Smart Contracts for Automated
Verification
The decentralized nature of blockchain
Blockchain-powered smart contracts allow
ensures secure storage of sensitive patient
for automatic verification and enforcement
data, preventing fraudulent activity.
of contract terms to ensure compliance.
Case Studies and Research Findings
1
Case Study 1: Implementation of Blockchain in Healthcare Fraud
Detection
The research found that by implementing blockchain technology, healthcare fraud can
be reduced by up to 40%, thereby improving the efficiency of the healthcare system.
2
Case Study 2: Impact of Blockchain on Insurance Claims and
Fraud Reduction
The research suggests that fraud prevention with blockchain technology in insurance
can ultimately save the industry up to $25 billion per annum, while streamlining services
to its customers.
3
Summary of Key Research Papers and their Findings
We've examined various papers on the topic of blockchain and healthcare fraud, and
the overall consensus is that the potential for blockchain in the healthcare sector is
immense, and we can greatly improve services and prevent fraud.
Bibliography and References
1.
Blockchain-based Electronic
Kumar, Pandey, Shetti, Gao, &
Health Records for
Li
Healthcare Systems
2.
Blockchain-enabled
Kshetri & Voas
healthcare analytics:
Improving the efficiency and
security of the healthcare
system
3.
Health Fraud Detection Based
Khazaei, Rahmani, Hussain, &
on Blockchain Multichain and
Song
Smart Contract
Conclusion and Future Prospects
Recap of Blockchain
Potential
Challenges and
Limitations of
Implementation
Future Research
Directions
the potential to
The high costs of
development of blockchain
revolutionize the healthcare
implementation, inadequate
applications can lead to
industry by reducing the
transparency, varying
improving healthcare
instances of fraud and
regulatory practices &
processes, data
improving the efficiency of
privacy concerns are some
management, and fraud
healthcare-related services.
of the limitations and
prevention while giving rise
challenges in realizing the
to parallel markets and
full potential of blockchain
opportunities.
Blockchain technology has
for healthcare.
Further research and
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.0;
contract HealthcareFraudDetection {
address public owner;
struct Claim {
address provider;
address patient;
uint256 claimAmount;
bool isValid;
}
Claim[] public claims;
event ClaimSubmitted(uint256 claimId, address indexed provider, address indexed patient, uint256
claimAmount, bool isValid);
constructor() {
owner = msg.sender;
}
modifier onlyOwner() {
require(msg.sender == owner, "Only the owner can call this function.");
_;
}
function submitClaim(address patient, uint256 claimAmount) public {
require(msg.sender != _patient, "Providers cannot submit claims on behalf of themselves.");
// In a real application, you would perform more advanced validation and checks.
// Here, we simply mark the claim as valid if the claim amount is less than 100 ether.
bool isValid = (_claimAmount < 100 ether);
claims.push(Claim({
patient: _patient,
claimAmount: _claimAmount,
isValid: isValid
}));
emit ClaimSubmitted(claims.length - 1, msg.sender, patient, claimAmount, isValid);
}
function getClaimStatus(uint256 _claimId) public view returns (bool) {
require(_claimId < claims.length, "Invalid claim ID.");
return claims[_claimId].isValid;
}
function getNumberOfClaims() public view returns (uint256) {
return claims.length;
}
}