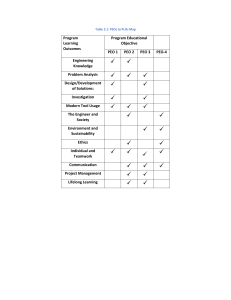
SUBJECT OVERVIEW LAW 1024 Law and Society AUGUST 2022 Centre for Commercial Law and Justice LAW 1024 Subject Overview SUBJECT OVERVIEW LAW 1024 Law and Society Course Psychology Subject Code and Title : BSc. (Hons) Semester : August 2022 Contact Hours : Lectures – 2 hours Workshop – 1 hour Tutorial – 1 hour Lecturer : Dr Paul Linus Andrews (paullinus@sunway.edu.my) Tutor : Ms Kanchana Chandran (AE-7-1) (kanchanac@sunway.edu.my) : LAW 1024 Law and Society Consultation Hours : Please email for an appointment ____________________________________________________________ SUBJECT DESCRIPTION There is no human conduct or behaviour that does not have a corresponding legal principle, concept or argument entwined in it. We live in a society that has a legal system in operation and we often take the law and its existence for granted. Hence for some the law represents what the police or the courts do. For others it represents the written laws in a country. Alternatively, law could be viewed as the set of rules that regulate and govern human behaviour as established by those who have legitimate authority to do so. The relationship between law and society is one that is fascinating as it is rooted in philosophical arguments that continue to challenge the boundaries of societal growth even today. This module explores that historical context and then considers its application in current contexts. 2 Centre for Commercial Law and Justice LAW 1024 Subject Overview SUBJECT OBJECTIVES This course prepares students to appreciate the importance of: the historical and philosophical contexts of law the various jurisprudential theories of the law the application of critical anlaysis in the understanding of the law and its impact on society SUBJECT LEARNING OUTCOMES (SLO) On completion of this subject, students should be able to: SLO1 : Explain the relevant legal and socio-legal theories and framework. SLO 2 : Apply the relevant information from statutory provisions, case reports, journal and other relevant legal materials in legal problems. SLO 3 : Present legal solutions based on socio-legal theories and frameworks effectively. PROGRAMME LEARNING OUTCOMES (PLO) After completing the programme, students will be able to: PLO1 Integrate knowledge and understanding on fundamental principles in psychology. PLO2 Apply critical and creative thinking through the scientific approach to solve problems related to mind, brain and behaviour. PLO3 Apply basic research methods in psychology and psychological skills to address sustainability issues in the community. PLO4 Demonstrate interpersonal/ social skills when interacting with others. PLO5 Communicate effectively and convey psychological information, ideas, problems and solution to experts and non-experts. PLO6 Use a range of digital applications to support work or study. PLO7 Analyse, interpret and synthesize numerical data for psychology studies. PLO8 Ability to work independently, build relationships and work with teams to make decisions, take responsibilities and accountability. PLO9 Pursue life-long learning in psychology-related fields. PLO10 Demonstrate managerial and entrepreneurial skills when addressing community issues. PLO11 Adhere to ethical and professional conduct in the community. 3 Centre for Commercial Law and Justice LAW 1024 Subject Overview MAPPING OF SLO AND PLO Subject Learning Outcome (SLO) (SLO1) (SLO2) (SLO3) PLO1 PLO2 PLO3 PLO4 PLO5 PLO6 PLO7 PLO8 PLO9 PLO10 √ √ √ PROGRAMME EDUCATIONAL OBJECTIVES (PEO): The programme aims are to produce: PEO 1: Psychology graduates who apply evidence-based psychological knowledge, research and skills to address global challenges. PEO 2: Psychology graduates who contribute to the community ethically and professionally. PEO 3: Psychology graduates who lead and work collaboratively to communicate and solve problems scientifically to address sustainability issues. PEO 4: Psychology graduates who work towards sustainability through project management and continuous development. MAPPING OF SLO AND PEO Subject Learning Outcomes (SLO) Programme Educational Objectives (PEO) PEO 1 (SLO1) PEO 3 PEO 4 √ √ (SLO2) (SLO3) PEO 2 √ 4 PLO11 Centre for Commercial Law and Justice LAW 1024 Subject Overview DELIVERY METHODS (1) Lectures The substantive aspects of legal concepts and theories presented using pre-recorded lectures uploaded on YouTube. (2) Tutorials/Workshops These provide an opportunity to review the subject matter and to develop the requisite skills to apply the subject matter in practical problem-solving exercises. This is to be delivered live, face to face. ASSESSMENT Students are assessed in three parts, mainly the final examination which is held at the end of the semester, and group coursework which consists of a written assignment. Examination Term Test Assignment Total 50% 10% 40%_ 100% Examination (50%) The paper is a 2-hour paper containing FOUR (4) questions. Candidates are required to answer ANY TWO (2) questions with each question allocated 25 marks. This is to be administered as a physical, face to face examination. Candidates are permitted to bring in notes prepared on a single A4 sized sheet of paper. End of Term Test (10%) The paper will contain 10 multiple-choice questions (MCQs). All 10 questions are compulsory and MUST be attempted. You must complete the test within the 30 minutes allowed. This is to be administered online on Blackboard. END-TERM TEST: TUES 15TH NOV 2022 accessible between 8.00AM – 10.00AM. Group Assignment (40%) A 3,500-word essay that seeks to assess the students’ ability to research, collect data and decipher primary and secondary materials, and to analyse and critically evaluate issues in the areas of law and society, and to communicate such arguments in writing. SUBMISSION OF ASSIGNMENT: FRI 7TH OCT 2022 AT 5PM 5 Centre for Commercial Law and Justice LAW 1024 Subject Overview SUBJECT OUTLINE Topics 1. Introduction to Law Definition of law Major Legal Systems and the Malaysian Legal System 2. Functions of Law in Society Social Control, Dispute Settlement or Conflict Resolution and Social Change 3. Natural Law Natural law theories 4. Legal Positivism Austin’s Command Theory H.L.A. Hart’s Concept of Law 5. Law and Morality Hart-Devlin debate 6. Law and Social Change Law as an Instrument of Change 7. Law, and Religion Law and religion 8. Law, Gender and Sexuality Current issues in Malaysia: Law, gender and sexuality 9. Feminist Perspectives 6 Centre for Commercial Law and Justice LAW 1024 Subject Overview MAIN REFERENCE Vago, S. (2022). Law and society. Routledge or Vago, S. (2018). Law and society. Routledge. ADDITIONAL REFERENCES Harding, A., & Shah, D. A. (Eds.). (2018). Law and Society in Malaysia: Pluralism, Religion and Ethnicity. Routledge. Urscheler, L. H., & Donlan, S. P. (2017). Concepts of Law: Comparative, Jurisprudential, and Social Science Perspectives. Routledge. Schiff, D., & Nobles, R. (Eds.). (2016). Law, Society and Community: Sociolegal Essays in Honour of Roger Cotterrell. Ashgate Publishing, Ltd. LIST OF SUGGESTED READINGS: Andrews, P.L. (2022). Chapter 1: Introduction to Law. In A. Trakic, P.L. Andrews, N. Ramasamy, C.Y. Sum, S.B. Murugan, V. Pullikutthyayanar, K. Chandran (Authors), Law for business. Malaysia: Sweet and Maxwell. Andrews, P.L. (2022). Chapter 2: The Malaysian Legal System. In A. Trakic, P.L. Andrews, N. Ramasamy, C.Y. Sum, S.B. Murugan, V. Pullikutthyayanar, K. Chandran (Authors), Law for business. Malaysia: Sweet and Maxwell. Banakar, R. (2009). Law Through Sociology’s Looking Glass : Conflict and Competition in Sociological Studies of Law. In A. Denis & Devorah KalekinFishman (Eds.), The ISA Handbook in Contemporary Sociology (pp. 58–73). Sage. Chua, Shing, L. J. K. (2003). Saying No: Sections 377 and 377A of the Penal Code. Singapore Journal of Legal Studies, 209–261. Dworkin, R. (1968). On Not Prosecuting Civil Disobedience. The New York Review of Books, 1–18. Retrieved from http://www.nybooks.com/articles/archives/1968/jun/06/on-not-prosecuting-civildisobedience/ Dyevre, A. (2014). Law and the evolutionary turn: The relevance of evolutionary psychology for legal positivism. Ratio Juris, 27(3), 364–386. 7 Centre for Commercial Law and Justice LAW 1024 Subject Overview Gomez, L. E. (2008). A Tale of Two Genres: On the Real and Ideal Links Between Law and Society and Critical Race Theory. The Blackwell Companion to Law and Society, 453–470. Harding, A. (2012). The constitution of Malaysia: a contextual analysis. Bloomsbury Publishing. Kananatu, T. (2016). Chapter 9: A Sociolegal Study of the Indian Minority in Malaysia. In D. Jayasooria & K. S. Nathan (Eds.), Contemporary Malaysian Indians: History, Issues, Challenges and Prospects. Bangi: Institute of Ethnic Studies (KITA), Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia. 8