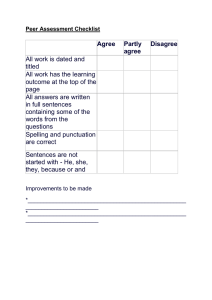
Student Name: Year 4 Rubric/Guide to Making Judgement Narrative Date: Very High High Sound Developing Emerging A thorough understanding and uses a high level of skill in both familiar and new situations. A clear understanding and uses a high level of skill in familiar situations. Is beginning to use skills in new situations. Has an understanding and uses skills in familiar situations. Understands aspects of and uses varying levels of skill in familiar situations. A basic understanding and is beginning to use skills in familiar situations. • Requires significant guidance to produce a written text ‣‣ Has difficulty recognising the structural elements ‣‣ Text may have some structural elements but may not be relevant or it is difficult to recognise the structure Text Structure The organisation of the structural components of writing a text aligns to an appropriate and effective text structure. • Text is always logically organised with the correct use of paragraphs and follows the narrative structure ‣‣ Title ‣‣ Orientation ‣‣ Series of Events ‣‣ Complication ‣‣ Resolution ‣‣ Optional Coda • Uses paragraphs correctly and consistently follows the narrative structure ‣‣ Title ‣‣ Orientation ‣‣ Series of Events ‣‣ Complication ‣‣ Resolution • Recognises the required structure and predominantly follows the narrative structure ‣‣ Title ‣‣ Orientation ‣‣ Series of Events ‣‣ Complication ‣‣ Resolution • Requires some support to recognise the structural elements of a narrative and to produce a written text ‣‣ May use a modelled text for assistance/prompts ‣‣ Some of the structural elements may have been included without assistance Ideas The selection, relevance and elaboration of ideas. • Uses brainstorming and planning techniques to assist writing • Orientation includes who, what, where, when and effectively introduces the reader to the setting, characters and its complication • Contains an interesting plot with an effective and clear ending • Uses brainstorming and planning prior to writing • Orientation includes who, what, where, when with some description detail to introduce the reader to the setting and characters • Contains a detailed plot with an ending • Complication is introduced and clear • Attempts brainstorming and planning prior to writing • Orientation includes some of who, what, where, when • Contains a brief plot with an ending • Complication is included but may not be clear • Attempts to write a narrative with the • Narrative can be jumbled and relevant requirements independently hard to interpret if left to work but lacking in some areas independently • May require support to: • Requires significant support to: ‣‣ Brainstorm ideas and plan prior to ‣‣ Brainstorm ideas and plan prior writing to writing ‣‣ Present their thoughts on paper in ‣‣ Present their thoughts on paper a logical way in a logical way Language Features and • Expectations are beyond Year 4 level, • Makes relevant vocabulary choices to for example: suit audience and purpose e.g. descriptive ‣‣ Begins to use vocabulary to express language to build up a picture of the greater precision of meaning and character, setting, mood etc. begins to understand that words can • Incorporates new vocabulary from a have different meanings in different range of sources contexts e.g. cut – slice, dice, fillet, • Verbs and tense are meaningful and segment used effectively in sentences • Correctly uses indirect speech • Makes some relevant vocabulary choices • Attempts to use relevant vocabulary • Requires significant support to use to suit audience and purpose e.g. choices but these may not always relevant vocabulary choices descriptive language to build up a picture be suitable • Relies on an illustration to tell a of the character, setting, mood etc. • Requires some assistance for verbs story. • Begins to incorporate new vocabulary and tense to be meaningful. from a range of sources • Verbs and tense are meaningful in sentences • Experiments with indirect speech • Consistent in application and expectations are beyond Year 4 level, for example: ‣‣ Begins to understand that the starting point of a sentence gives prominence to the message in the text and allows for some prediction of how the text will unfold • Writing flows and is clear • Text is short and does not always • Requires support to: • Use of synonyms, antonyms and word flow, the reader finds it confusing ‣‣ produce a piece of text that flows substitutions are used to intensify the in parts and is clear narrative • Text has missing links and words are ‣‣ use grammatical and lexical • Links are used in sentences (connectives repetitive elements correctly and conjunctions) avoiding repetition • A variety of referring words are used including pronouns Vocabulary The range and precision of contextually appropriate language choices as well as appropriate devices. Cohesion The control of multiple threads and relationships across a piece of text, achieved through using: • Grammatical elements (referring words, text connectives, conjunctions) • Lexical elements (substitutions, repetitions, word association) • Writing effectively hooks in the reader • The text is easy to read and maintains interest by the effective use of a wide variety of grammatical and lexical elements Page 1 of 2 visit twinkl.com.au Year 4 Rubric/Guide to Making Judgement Narrative Paragraphing • Consistent in using paragraphs The segmenting of text • Begins to understand the different into paragraphs that types of paragraphs and attempts assists the reader to follow these in their writing a piece of text. • Organises information into logical and detailed paragraphs • Recognises there are different types of paragraphs • Organises information into paragraphs • Paragraphs include a topic sentence Sentence Structure The production of grammatically correct, structurally sound and meaningful sentences. • Consistent in sentence structure when • Sentences flow and are grammatically • Knows that a clause usually contains a writing. Goes beyond that expected of correct subject and a verb, that these need to Year 4, for example: • Attempts to use complex sentences agree and applies this in their writing ‣‣ Understands the difference between • Beginning to understand the difference • Uses noun and verb groups/phrases and main and subordinate clauses between main and subordinate clauses prepositional phrases to create a richer ‣‣ Begins to understand that a complex text with more specific descriptions sentence involves at least one • Uses a variety of conjunctions subordinate clause effectively Punctuation The use of correct and appropriate punctuation that aids reading of a piece of text. • Punctuation usage goes beyond that • Consistent in application and expected of Year 4, for example: appropriate punctuation has not been ‣‣ Begins to use apostrophes to signal overused the possessive form of nouns • Correctly uses quotation marks to ‣‣ Begins to recognise there is a variant signal dialogue, titles and quoted to the regular possessive form for (direct) speech proper nouns e.g. James’s house vs James’ house • Paragraph use is inconsistent • Requires some support in identifying how and where to begin a new paragraph • Paragraph use is minimal • Often requires support in identifying how and where to begin a new paragraph • •equires some support to • Requires significant support to ‣‣ recognise the requirements of a construct sentences which meet clause the requirements for Year 4 ‣‣ use noun and verb groups/phrases • Sentences are basic and lack depth and prepositional phrases to and description enhance text • Uses conjunctions however, these tend to be repetitive • Correctly uses punctuation when writing: • Often omits relevant punctuation • Uses basic punctuation (capital ‣‣ Full stops, question marks, exclamation • Requires some support to use letters, full stops, question marks, marks, capital letters, commas punctuation appropriately overuse of commas) ‣‣ apostrophes of contraction • Recognises how quotation marks are • Has difficulty applying other • Recognises how quotation marks are used in texts, however, often does punctuation appropriately used in texts to signal dialogue, titles not apply this knowledge to their (exclamation marks, apostrophes and quoted (direct) speech. Sometimes writing of contraction, quotation marks) applies this in their writing Spelling • Spelling application goes beyond that • Consistent in application • Attempts to spell more complex words The accuracy of spelling expected of Year 4, for example: • Correctly spells more complex words using spelling knowledge, for example: and the difficulty of words ‣‣ Begins to use knowledge of known using spelling knowledge, for example: ‣‣ Letter patterns e.g. double letters used. words, base words, prefixes and ‣‣ Letter patterns e.g. double letters ‣‣ Spelling generalisations suffixes, word origins, letter patterns ‣‣ Spelling generalisations ‣‣ Morphemic word families and spelling generalisations to spell ‣‣ Morphemic word families ‣‣ Common prefixes and suffixes new words ‣‣ Common prefixes and suffixes ‣‣ Word origins ‣‣ Begins to explore less common ‣‣ Word origins • Writes a large core of high frequency plurals • Correctly writes a large core of high words including homophones with ‣‣ Begins to recognise how some frequency words including homophones minimal correction suffixes change the grammatical • Uses context to identify correct spelling form of words e.g. ‘tion’ and ‘ment’ • Uses phonic knowledge to write change verbs into nouns multisyllabic words with more complex letter combinations • Inconsistent in application • Requires significant support to use ‣‣ Requires some support to use Year Year 4 spelling knowledge when 4 spelling knowledge when spelling spelling words words • Correctly spells a small bank of ‣‣ Spells most high-frequency words high-frequency words correctly ‣‣ Relies on letter-sound relationships to write most words ‣‣ Relies heavily on environmental print Editing Ability to re-read and edit own work to check for meaning, spelling, punctuation and grammar. • Re-reads and edits texts for • Minimal or no evidence of editing meaning, grammatical choices and for meaning punctuation (does not alter much of • Edits text for spelling, the content) sentence-boundary, punctuation • Displays some individual editing skills and text structure but these may often be unnecessary • Sometimes requires support with edits editing • Consistent in approach and goes beyond that expected of Year 4, for example: ‣‣ Editing own and others’ work using agreed criteria for text structures and language features • Effectively edits own and others’ work • Re-reads and effectively edits own work for meaning for meaning • Offers constructive comments to peers • Deletes or moves words/word groups to to assist them in improving their work improve content and structure Teacher Name: Page 2 of 2 visit twinkl.com.au