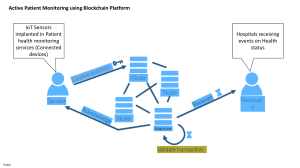
COMSATS INSTITUTE OF INFORMATION AND TECHNOLOGY Department of Computer Science The Convergence of IoT and Blockchain: Challenges and Opportunities. INTRODUCTION. The concept “Internet of things” generally refers to connecting things with the internet. These devices ranges from household appliances to the sophisticated tool used in industrial processes, thus making them able to send and receive data through the internet. This architecture is built with the help of sensors that collect data from the surroundings, which is processed by the microcontroller, and then according to that control signals are passed to the interconnected things. Although this cutting edge technology provide enormous benefits but at the same time there are some challenges which needs to be addressed. Another cutting edge technology which need to be discussed here is Blockchain. It is a distributed database of records which are called blocks. Each block contains the record of all the transactions that have been executed and shared among peers and are encrypted by cryptographic hash. Each transaction is verified by all the participants and then added in the block. The main advantage of Blockchain over the conventional client/server architecture is that the records of transactions is difficult (nearly impossible) to alter or temper. IoT and Blockchain are cutting edge technologies that plays an important role in shaping the future of mankind. While both offer numerous benefits, these technologies also come with certain limitations as well. Combining both technologies can overcome these limitations. This aim of this research is to find the constraints in implementing IoT with the peer-to-peer approach. In particular, Blockchain which provides a secure and efficient solution. Also the aim is to carry a literature review in order to understand the possibility of convergence of IoT and Blockchain. The following are the Research objectives. In Which domains we can use Blockchain technology beyond crypt currencies? Is Blockchain applicable to IoT? Challenges and Opportunities to the proposed system? LITERATURE REVIEW The creator of Bitcoin, Satoshi Nakamoto[1] described Blockchain technology as “Peer-to-peer structure” that can create trust between sender and receiver in a trustless environment. The Bitcoin commands are grouped into a structure called block. Each block will be connected to the previous one by keeping the cryptographic hash of the previous transaction and the public key of next owner. Each time a transaction is made the digital signature will be passed to next owner. The nodes in Blockchain which have high computational capabilities and can operate complex task are called miners. The hash assigned to a block will be verified by all the blocks. Once hash is verified, the block will be added to Blockchain. This is known as consensus mechanism. Block hash represent the work done by the miners and is called proof-of work. [2] The term “Internet of things” generally refers to connecting things with the internet. These devices ranges from household appliances to the sophisticated tool used in industrial processes, thus making them able to send and receive data through the internet. This architecture is built with the help of sensors that collect data from the surroundings, which is processed by the microcontroller, and then according to that control signals are passed to the interconnected things. Although this cutting edge technology provide enormous benefits but at the same time there are some challenges which needs to be addressed.Despite the benefits provided by these services, critical privacy issues still exist. The connected devices transmit the personal information which reveals the personal preferences and behavior. This making the data vulnerable to any kind of misuse. The aim of this research is to find the constraints in implementing IoT with the peer-to-peer approach. In particular, Blockchain which provides a secure and efficient solution. Also the aim is to carry a literature review in order to understand the possibility of convergence of IoT and Blockchain. Use Cases of Blockchain beyond Cryptocurrencies. Global Payment: Global payment has become complicated and time consuming because of centralized approach as there are many intermediaries that are involved in verifying the transaction. There are many remittance companies that are already using Blockchain such as Bitspark and Apra [3]. Vehicular Cyber System. The autonomous driving vehicles are based on vehicular cyber system[4] for improving road safety and efficiency. But the security and privacy is a key concern. Blockchain with its features such as decentralization, anonymity and security can play an important role in this regard. Smart Home: Blockchain in the context of smart home can be integrate with IoT, to provide a secure way to communicate with the home appliance from a far off location. [5]However integrating both cutting edge technologies in this context is not straight forward. As there are many challenges regarding high resources for POW, master nodes and low scalability of Blockchain.[5] Health Care: Personal health record is a sensitive information and need to be dealt with high security. Such records can be stored in Blockchain. The private key is responsible for granting access to the authorized person.[6] Identity Management: With Blockchain users can take store his/her information in a block. And share it through cryptographic communication. The users can be verified with the help of digital signatures. Once the information is stored in a block, it cannot be changed. Blockchain Identity as a Service is a type of IDaaS which is designed to provide an identity and authentication management. The BIDaaS is a private Blockchain. The service offering user has access to BIDaaS, but only read permission not write permission.[7] Identity Management: Personal ID & Voting Current voting system has flaws, and it is hard to verify the authenticity of votes. Therefor in near future a Blockchain based voting system will provide secure voting system. [8] Is Blockchain applicable to IoT? Current IoT systems are built on centralized client/server model, which require all the devices connected to a centralized server. This model will not be able to provide an efficient solution near future, as the number of devices are increasing exponentially. Researches have shown that by the end of 2025, number of devices connected to IoT will increase upto 75.44 billion[9]. Despite these great opportunities offered by IoT technologies, maintaining the reliability and accuracy of data obtained from these devices remain a problem that has not been fully addressed. Blockchain can be a solution to the security problem of IoT systems.[10] As Blockchain technology provides a high level of security, privacy, authentication, and device authorization for the data to be recorded and can be used to secure systems that use IoT devices. Challenges of Blockchain with IoT: Although there is no doubt that Blockchain can be a solution to the centralized approach of IoT, but still the convergence of these two cutting edge technologies would cause some challenges. This research aims to explore these challenges. Some of them are given below: Scalability: The IoT network consist of heterogeneous devices, which are huge in number. Thus scalability of network will be a key concern. So these system should be able to address issues such as mechanism to deal with the growing number of devices and support scalability both on long and short term environment.[11]. Discovery of Nodes and Naming: The Blockchain technology is not designed for IoT Networks. The nodes in Blockchain are not meant to find other nodes. This approach will not work for IoT as IoT devices will keep moving which will change their corresponding IP address and topology.[12] Legal code of conduct: The Blockchain is relatively a new technology that has the ability to connect different people from different countries without having any legal code of conduct to follow. This is a serious issue for both manufacturers and service providers. This will be the major barrier in adopting Blockchain as a solution for IoT.[13] CONCLUSION AND FUTURE DIRECTIONS: Although significant research has been in this context, still there exist areas which need to be address. Some of the research questions which need to be address are The edge IoT devices have less computational capabilities. So how the miner node will be decided? New protocols and standards need to be defined? What are the rules and regulations that ensures best use of iot with Blockchain? REFERENCE [1] “Bitcoin: A peer to Peer Electronic Cash System.” Accessed: Oct. 14, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://www.goodreads.com/en/book/show/17692928 [2] S. S. Sarmah, “Understanding Blockchain Technology,” Comput. Sci. Eng., 2018. [3] “APRA details crypto-asset expectations,” Corrs Chambers Westgarth. Accessed: Oct. 14, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://www.corrs.com.au/insights/apra-details-crypto-assetexpectations [4] J. Wan, D. Zhang, S. Zhao, L. T. Yang, and J. Lloret, “Context-aware vehicular cyber-physical systems with cloud support: architecture, challenges, and solutions,” IEEE Commun. Mag., vol. 52, no. 8, pp. 106–113, Aug. 2014, doi: 10.1109/MCOM.2014.6871677. [5] A. Dorri, S. S. Kanhere, R. Jurdak, and P. Gauravaram, “Blockchain for IoT security and privacy: The case study of a smart home,” in 2017 IEEE International Conference on Pervasive Computing and Communications Workshops (PerCom Workshops), Mar. 2017, pp. 618–623. doi: 10.1109/PERCOMW.2017.7917634. [6] M. Hölbl, M. Kompara, A. Kamišalić, and L. Nemec Zlatolas, “A Systematic Review of the Use of Blockchain in Healthcare,” Symmetry, vol. 10, no. 10, Art. no. 10, Oct. 2018, doi: 10.3390/sym10100470. [7] J.-H. Lee, “BIDaaS: Blockchain Based ID As a Service,” IEEE Access, vol. 6, pp. 2274–2278, 2018, doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2782733. [8] Y. Abuidris, R. Kumar, and W. Wenyong, “A Survey of Blockchain Based on E-voting Systems,” in Proceedings of the 2019 2nd International Conference on Blockchain Technology and Applications, in ICBTA ’19. New York, NY, USA: Association for Computing Machinery, Mar. 2020, pp. 99–104. doi: 10.1145/3376044.3376060. [9] “(PDF) A Reliable Communication Framework and Its Use in Internet of Things (IoT).” Accessed: Oct. 15, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/325645304_A_Reliable_Co mmunication_Framework_and_Its_Use_in_Internet_of_Things_IoT [10] K. O. Toka, Y. Dikilitaş, T. Oktay, and A. Sayar, “SECURING IOT WITH BLOCKCHAIN,” Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci., vol. XLVI-4-W5-2021, pp. 529–532, Dec. 2021, doi: 10.5194/isprs-archives-XLVI-4-W5-2021-529-2021. [11] S. Biswas, K. Sharif, F. Li, B. Nour, and Y. Wang, “A Scalable Blockchain Framework for Secure Transactions in IoT,” IEEE Internet Things J., vol. 6, no. 3, pp. 4650–4659, Jun. 2019, doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2018.2874095. [12] V. Daza, R. Di Pietro, I. Klimek, and M. Signorini, “CONNECT: CONtextual NamE disCovery for blockchain-based services in the IoT,” in 2017 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), May 2017, pp. 1–6. doi: 10.1109/ICC.2017.7996641. [13] M. Mylrea and S. N. G. Gourisetti, “Blockchain for smart grid resilience: Exchanging distributed energy at speed, scale and security,” in 2017 Resilience Week (RWS), Sep. 2017, pp. 18–23. doi: 10.1109/RWEEK.2017.8088642.