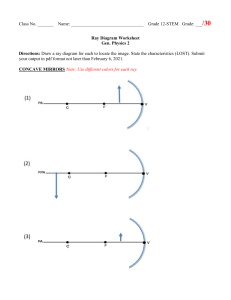
REFLECTION ON SPHERICAL MIRRORS •Concave •Convex A B QUALITATIVE CHARACTERISTICS OF IMAGES FORMED IN CONCAVE MIRROR SCIENCE QUARTER 2 – MODULE 3: RAY DIAGRAM • is a diagram that traces the path that light takes in order for a person to view a point on the image of an object. Parts of Concave Mirror f PA C F V Principal Axis a line passing through the center of the sphere and attaching to the mirror in the exact center of the mirror Center of Curvature - the center of the sphere from which the mirror was sliced Focal Point - Midway between the vertex and the center of curvature Vertex - The point on the mirror's surface where the principal axis meets the mirror Focal Length - the distance from the mirror to the focal point RULES IN RAY DIAGRAMMING FOR CONCAVE MIRROR P-F Ray - A ray of light parallel to the principal axis is reflected passing through the principal focus F-P Ray - A ray of light passing through the focus, F is reflected parallel to the principal axis C-C Ray - A ray of light passing through the center of the curvature, C reflects along its path V Ray. A ray of light directed to the vertex reflects at equal angle from the principal axis P-F RAY. A RAY OF LIGHT PARALLEL TO THE PRINCIPAL AXIS IS REFLECTED PASSING THROUGH THE PRINCIPAL FOCUS F-P RAY A RAY OF LIGHT PASSING THROUGH THE FOCUS, F IS REFLECTED PARALLEL TO THE PRINCIPAL AXIS C-C RAY A RAY OF LIGHT PASSING THROUGH THE CENTER OF THE CURVATURE, AND REFLECTS ALONG ITS PATH V RAY A RAY OF LIGHT DIRECTED TO THE VERTEX REFLECTS AT EQUAL ANGLE FROM THE PRINCIPAL AXIS LOST Location Orientation depends on the location of the image upright/erect or inverted Size Same/undiminished, reduced/diminished or enlarged Type real or virtual Location Orientation Between C and F inverted Size Reduced or smaller than object Type Real ACTIVITY A B C D A Location Orientation At C inverted Size Same size of the object Type Real B Location Orientation Beyond C inverted Size Larger than the object Type Real C Location No image being formed Orientation No image being formed Size No image being formed Type No image being formed D Location Opposite side of mirror Orientation Upright Size Larger Type Virtual https://www.pbslearningmedia.org/r esource/arct15-scilensmirrorlab/lens-and-mirror-lab/ https://quizizz.com/join • List down some applications of concave mirrors