Organization
#
ftp.a.ma.am
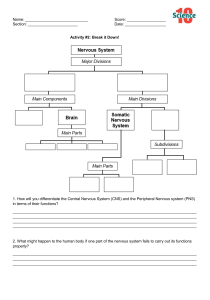
NERVOUS SYSTEM
Peripheral
Central Nervous System
""
Nervous
System
* two divisions
""
"
" """
{ÑÑenTeTrÑ}
Efferentcmotorlmf.IE/ErEwEmsl0nIn
◦
conducts Impulses from
sensory receptors to the
* two subdivisions
Somatic
CNS
Autonomic
Nervous
system
Uanaanua.mu#
Nervous
system
f
f
◦
conducts Impulses
from the CNSTO
Skeletal muscles
o
conducts impulses
from the CNSTO
smooth muscle
Flow of Information
CNS
PNS
Afferent DIVISION
sympathetic DIVISION
Parasympathetic Division
/
Efferent DIVISION
Autonomic Nervous system
( ANS)
/
Somatic Nervous System
/
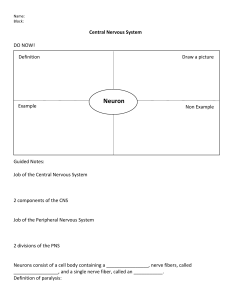
Nervous TISSUE
I> composed
of
1. Neurons ( nerve cells )
types
two cell
2.
Parts of
Supporting ( glial) cells
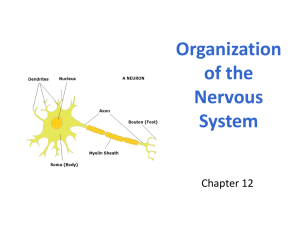
Neuron
a
"
"
- %%aµn
nucleus
☆
L
WH
ee"
postsynaptic
,fe
]
dendrites
* neuron is a secretory
¥eM
""
"
* each neuron can
have only
'
myelin sheath
synaptic
cell body
cleft
telodendrla
Terms to know
Nucleus :
a cluster
of
neuron cell
bodies
in
the CNS
Ganglion
a cluster
of
neuron cell
bodies
in
the PNS
:
Tract
:
a
Nerve
:
a
bundle of axons
the CNS
in
bundle of axons
in
the PNS
Structural Classification Of Neurons
Multipolar Neuron
:
has atleast 3. processes
cone
Bipolar
Neuron
:
axon
,
extending from
extending from
cell
loneaxon , one dendrite )
pseudo unipolar
:
has 1- Short process
bifurcates
2.
Oligodendrocytes
extending from
into a central and
cell
3. microglia
4.
ependymal
cells
}
CNS
body that
peripheral process
5. Schwann cells
located in
body
body
letypesof Supporting ( glial) cells
1. Astrocytes
cell
atleast 2 dendrites )
has 2 processes
6. satellite cells
}
one axon
( but multiple dendrites )
located
PNS
in
*
myelination of
*
myelination
axons
of
* severed axons
CNS IS done by
oligodendrocytes
axons in the PNS IS done by Schwann cells
in the
Electrical
2. types
a
In the
CNS cannot
signals
neuron can
signals
that
Action Potentials
of
dissipates
otwotypes
1.
over distance
.
.
PNS)
generate
Graded Potentials
0
in
:/ On movement
electrical
of
regenerate ! Cltcan regenerate
maintains
◦
0
.
travel
intensity
distance
over
longer distances
Excitatory Postsynaptic
I
>
Potential ( EPSP )
you need EPSP
2. Inhibitory postsynaptic
to cause action
can be done by spatial
or
potential
temporal summation
Potential ( IPSP)
The Action
+30
Potential
5
1.
resting
2.
depolarizing
3.
membrane
4.
rapid
membrane
stimulus
depolarizes to threshold
Nat entry depolarizes cell
.roÉ
?.,. .z. . -,----s----a--_
potential
" " " " " " " " " ""
:¥É
¥
6
4
6.
Kt moves
7
Kt channels
.
out
8. Kt Channel
Of cell
remain open
close
9. cell returns to
-
50 =
-
-
-
-
-
3
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
,
( hyperpolarization )
less Kt leaks out
resting
membrane
threshold -55mV
of
cell
potential
Factors that Affect Action Potentials
Hyperkalemia
/
increased Ktintneblood
less
*
negative resting membrane
Kt
increased
%
kt
Outside the cell
potential
reaches threshold
frequency
Increased AP
Hypocalcemia
potential faster
decreased Caztmthe blood
increased Nat
increased
influx
.
.
Apfreauency
.
.
.no calcium to compete with
.
less
.
.
-
Nat
negative resting membrane potential
seen / nchrostek 's
sign
can cause muscle cramps
Hypokalemia
decreased K'
-
In the
k+
K' →
blood
-
more
negative resting
mem
.
potential
decreased Apfreauency
Hypercalcemia
Increased Caztmtne blood
less Nat
influx
.
.
.
more
.
.
competes with Nat
negative resting
decreased Apfreauency
can cause muscle
-
weakness
membrane
potential