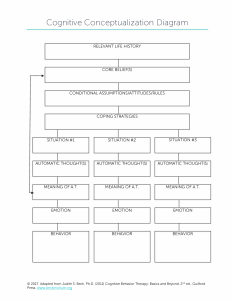
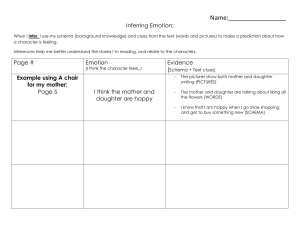
Explain the influence of emotion on one cognitive process Outline cognitive process - memory (flashbulb memory) Memory definition: The mental process of encoding, storing and retrieving information. Emotion definition: Conscious mental reactions that are directed to a specific object typically accompanied by behavioural changes in the body Flashbulb memory: A special memory mechanism; vivid and highly detailed recollection of the circumstances surrounding witnessing or receiving the news of an unexpected and emotionally arousing event Flashbulb memory and how strong emotion plays a role in forming memory Study: McGaugh and Cahill Lab experiment Aim: role of adrenaline and amygdala on emotional memory formation Procedures: Two groups: 1. Boring story about women going to the hospital visiting her husband 2. Story where a boy was involved in an car accident and his leg was amputated (with vivid details) exciting story Two week later - asked to recall specific details of the story Results: Group 2 demonstrated better recall of specific details of the story Conclusion: Emotion outlined by the study correlated to the increase of flashbulb memory Extra information: The procedure was repeated but group two (exciting story group) was injected with beta blocker call propranolol that prevented the activation of amygdala This study can be used in both the biological approach and cognitive approach with some examples: Hormones Ethical considerations in research of Hormones and pheromones Influence of emotion on other cognitive processes Ethical considerations in research of emotions on cognitive processes Describe one study that related to schema theory Definition of schema – cognitive framework or concept that organizes and interprets information based on previous knowledge; a cluster of knowledge or memory that is stored in the mind Schema theory: knowledge of the world is organized and categorized, which can influence our cognition and behaviour. One study - Cohen et al Type of study: Lab experiment IV: What they told the group – the women’s profession DV: Schema consistent traits recalled CV: The video itself. Aim : investigate the influence of schemas and stereotypes on memory Procedure: 96 students, given a vid, half of the group waitress, half librarian, sophisticated for librarian and waitress less sophisticated – schema After watching the video, recall information regarding women’s behaviour Associated traits with accordance to schemas More likely to remember schema consistent information’s This lab experiment by Cohen et al demonstrated that when prompted by different information while watching the same video, this results in a recall of traits consistent with the schema of the associated person. “also showing how leading question can affect memory”