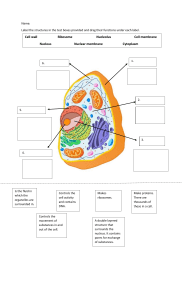
Cell Structure & Function The Cell •A cell is the smallest unit that is capable of performing life functions. Amoeba Proteus Bacteria Nerve Cell Plant Stem Red Blood Cell Microscopes and Cells • 1600’s. –Anton van Leeuwenhoek first described living cells as seen through a simple microscope. Microscopes and Cells –Robert Hooke first used a compound microscope to view thinly sliced cork cells. •Compound scopes use a series of lenses to magnify in steps. •Hooke was the first to use the term “cell”. Microscopes and Cells • 1830’s. –Mathias Schleiden identified the first plant cells and concluded that all plants are made of cells. - Thomas Schwann made the same conclusion about animal cells. Cell Theory 1. All living things are made up of 1 or more cells. 2. Cells are the smallest working units of all living things. 3. All cells come from pre-existing cells through cell division. Number of Cells Organisms may be: • Unicellularcomposed of 1 cell OR • Multicellularmade of many cells Cells can be Eukaryotic or Prokaryotic •Prokaryotes :do not have a nucleus or organelles (bacteria). •Eukaryotes: have a nucleus and organelles (plants, fungi, animals, protists) Organelles • Cell structures that have a specific function and are surrounded by a membrane that are found in eukaryotes only. Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/cells.html Prokaryotic Cells • Believed to be the first cells to evolve. • Lack a membrane bound nucleus and organelles. • Genetic material is free in the cytoplasm • Ribosomes are only other cell structure. Eukaryotic • 2 major types of eukaryotic cellsPlant and Animal cells Plant http://library.thinkquest.org/C004535/eukaryotic_cells.html Animal Cell Structures & Functions Cell Wall • Found outside of the cell membrane in plant cells & bacteria only • Contains cellulose that provides support (rigidity) & protection Cell or Plasma Membrane • Outer membrane of cells that controls movement of substances in and out of the cell • Double layer (bi-layer) • In plants and bacteria, this is within the cell wall. Cytoplasm • Gel-like mixture inside cells • Surrounded by cell membrane • Contains cell structure that carry out specific jobs ex. Mitochondrion, nucleus • Provides a medium for chemical reactions to take place Nucleoid • In prokaryotes. • Region of the cytoplasm where chromosomal DNA is located. • Singular, circular chromosome. • Smaller circles of DNA called plasmids are also located in cytoplasm. Ribosomes • Each cell contains thousands • Make proteins • Found on endoplasmic reticulum & floating throughout the cell cytoplasm Organelles Nucleus • “Control center” • Directs cell activities • Contains the genetic material (DNA) • Separated from cytoplasm by nuclear membrane (or nuclear envelope). Nuclear Membrane • Surrounds nucleus, separates DNA from cytoplasm • Made of two layers • Openings called pores allow some materials to enter and leave nucleus Chromatin • In nucleus • Genetic material (DNA) of cell in its non-dividing state. • Ie. Uncoiled chromosomes • Contain instructions for traits & characteristics Nucleolus • Dark-staining structure in the nucleus • Makes ribosomes that make proteins Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum • Network of continuous sacs, studded with ribosomes. • Internal delivery system of the cell. • Manufactures, processes, and transports proteins for export from cell. • Continuous with nuclear envelope. Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum • Similar in appearance to rough ER, but without the ribosomes. • Produces lipids, involved in carbohydrate metabolism, and detoxification of drugs and poisons. Golgi Apparatus • Protein 'packaging plant‘ • Modifies proteins and lipids made by the ER and prepares them for export from the cell. • Encloses digestive enyzymes into membranes to form lysosomes (transport pods). Lysosome • Digestive 'plant' for proteins, fats, and carbohydrates • Digestive enzymes break down cellular waste and debris • Transports undigested material to cell membrane for removal • Cell breaks down if lysosome explodes Mitochondria • Cell “powerhouse” • Membrane bound organelles that are the site of cellular respiration (use glucose to produce cell energy, ATP) • Active cells like muscles have more mitochondria Animal Vacuole • Membrane-bound sacs for storage, digestion, and waste removal • Contains water solution Plant Vacuole • Plants have large central vacuoles that store water and nutrients needed by the cell. • Help support the shape of the cell. Chloroplast • Usually found in plant cells • Contains green pigment chlorophyll • Where photosynthesis takes place • Produces plant food (sugars) and oxygen gas Cilia and Flagella Cilia Flagella • External appendages from the cell membrane that aid in locomotion (movement) of the cell. • Cilia also help to move substance past the membrane. Centrioles • Found only in animal cells. • Self-replicating • Made of bundles of microtubules. • Help in organizing cell division. Cytoskeleton • The cell’s skeleton • Made of microtubules and filaments • Give the cell shape, strength and ability to move