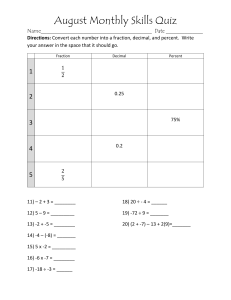
EL-W506T Manual The All new advanced sharp scientific calculator 1 Introduction • The Sharp EL-W506T has 640 functions including a dual unlimited table mode, probability distribution mode, equation solving mode, up to 4 x 4 matrices and very easy to use statistics features. • Great for AP maths students, IEB Maths students, Technical maths students and university or Technicon students. 2 Modes • 0: NORMAL (slide 6) • 1: STAT (slide 64) • 2: TABLE (slide 84) • 3: COMPLEX (slide 92) • 4: EQUATION (slide 99) • You can do fractions, sums, integration, differentiation, conversions etc. • Univariate and bivariate data and statistics calculations • Unlimited dual table mode with asymptotes • Calculations involving complex numbers. Switch between polar and rectangular coordinates. • Solve 2 and 3 variable linear equations, quadratic equations and cubic equations. 3 Modes • 5: MATRIX (slide 107) • 6: VECTOR (slide 124) • Calculate using up to 4 x 4 matrices, find inverses and transposes of matrices. • Do vector calculations • 7: DISTRIBUTION (slide 131) • Calculate various probability distribution t values • 8: DRILL (slide 141) • Practice mental maths by answering questions posed by the calculator. 4 Important Buttons • • • • • • • turns the calculator on. turns the calculator off returns calculator to Normal (calculation mode) Arrows are used to move between answer or menu screens or move the cursor. is used to access any orange functions is used to access any blue functions is used to delete (backspace) • changes the answer from a mixed fraction, to an improper fraction to a decimal. • is used to find the answer or as enter. 5 Normal Mode Press or 6 Normal Mode • Press or • 52 scientific constants and 44 conversions • Solve for X • Integrate and differentiate at a point • Sum and multiply a Tn pattern • Highest common factor and lowest common multiple 7 Resetting the Calculator • Press • You have three options • 0: DISP • Pressing clears whatever calculation was on the screen of the calculator. You can also press to do this. • 1: MEMORY • Pressing clears all the memory values out of the calculator (A-F). Press to confirm • 2: RESET • Pressing resets the calculator back to “out of the box” settings. Press to confirm • You can also reset the calculator by pressing the button on the back with the tip of a pen. 8 Math • Press • You should see this screen. • Now press to see screen 2 of the Math menu 9 Math – Engineering Units • • • • • • • • • • • Press Choose for ENG. SYMBOL k = 1000 M = 1 000 000 G = 1 000 000 000 T = 1 x 1012 m = 0.001 𝜇 = 0.000001 n = 0.000000001 p = 1 x 10-12 f = 1 x 10-15 10 Math • Converting hours to seconds • Press • Converting hours to minutes • Press 11 Math • Ipart returns the whole number part of a decimal / mixed fraction • Press • Fpart returns the fraction part of a mixed number fraction. • Press 12 Math • Int returns the whole number part of answer. • Press • Press • Press 13 Math • The (%) function allows you to include a percentage into the calculation. • E.g. Find the final value if R5000 is compounded annually at a rate of 7% p.a. for the next 10 years. • Our formula is • 𝐴 =𝑃 1+𝑖 𝑛 • 𝐴 = 5000 1 + 7% 10 14 • Press 15 SETUP • Press 16 0: DRG • Press • You have the following options: • 0: DEG • Change all calculations to use degrees • 1: RAD • Change all calculations to use radians • 2: GRAD • Change all calculations to use gradians 17 1: FSE • Press • You have 5 options: • 0: FIX • Press • Choose the number of decimal places you would like to round your calculations off to, e.g. • Now type in 18 1: FSE • Press • Option 2: • 1: SCI • Press • Choose the number of significant figures you would like. • E.g. Press • Now press 19 1:FSE • Press • Option 3: • 2: ENG • Press • Choosing ENG changes your scientific notation to display in multiples of three. • Choose your number of significant figures (e.g. press ) 20 1: FSE • Press • Option 4 • NORM1 • Press • Gives the normal settings on the calculator. • Displays numbers between – 999 999 999 and 999 999 999, or outside of these parameters it displays them as scientific notation. • NORM2 • Press • Displays numbers between 0 and 999 999 999 and in scientific notation outside of these parameters. Note the 3 digit punctuation to make it easier to read numbers in this form. 21 2: Editor • Press • You have 2 options: • 0: W-VIEW • 0: EXACT • Gives the fraction, or surd answer, press to get the decimal form of the answer • 1: APPROX • Gives the decimal answer first, and the fraction answer is given after is pressed. • 1: LINE • Gives the old way of writing fractions with the “r” 22 3: Contrast • Press • Use your and buttons to change the colour of the contrast / colour of your text on your calculator. • Press once you are happy with your screen. 23 4: - - - - or ENTRY • Press • When you are in the Writeview mode of the editor you will see a blank line at 4. • When you are in the Line mode of the editor, you will see ENTRY. • Press • If you choose you will be able to insert numbers between other characters. • If you choose you will be able to write over / replace numbers in the expression 24 5:Recurring Decimal • Press • Press to turn the recurring decimal on • Lets test the recurring decimal – press 25 6: Decimal Point • Press • Choose for the dot. • Choose for the comma. 26 7: Name • Press • Use your and arrow keys to choose the letter or digit you want. • Use the and arrow keys to move the cursor along • Press when you are done. • Switch off your calculator ( ) to see your name. 27 User Defined Shortcuts • Your user defined keys allow you to save a shortcut key to your favourite orange and blue functions. • E.g. we want to save sin-1 into our D1 key • Press • Now whenever you press you will get the following on your screen 28 ALGB - Substitution • Use this function to substitute in values of x for any expression. • E.g. Find the value of 𝑥 3 − 7𝑥 + 3 if 𝑥 = −2 • Press 29 SOLVER – find 𝑥 • Find the value for x when an expression is equal to 0. • E.g. Find x when 0 = 3 sin 𝑥 − 2 • Press 30 Logs • You have a base ten log ( ) and an any base log ( ). • E.g. Find the value of log 100. • Press • E.g. Find the value of log 3 81 • Press 31 DMS Functions • Finding time in a speed-distancetime calculation. • E.g. How long does it take to travel 450km at an average speed of 117km/h? • Press • Press • Press • The answer is 3 hours, 50 minutes and 46.154 seconds. 32 DMS Functions • Adding / Subtracting Time • E.g. find the length of time spent on a bus if the bus left at 9.45 and arrived at 12.32. • Press • The answer is 2 hours and 47 minutes • To change back to a fraction notation press 33 DMS Functions • Changing minutes to hours • E.g. How many hours are 470 minutes? • Press to clear any chain calculations • Press • Press to change it into fraction or decimal format (remember to use your button). 34 𝜋 • The button gives a constant value of pi to 9 decimal places. • Press • This value can be used in calculations. • E.g. Find the area of a circle with radius = 7.5cm. • Our formula is 𝐴 = 𝜋𝑟 2 • Substitute in 𝐴 = 𝜋 7.5 2 • On the calculator we can press 35 Prime Factorization • Press to find the prime factors of a number. • E.g. find the prime factors of 153. • Press • Now press 36 Shortcut for Class Marks • When you want to convert between your test results and another total (e.g. percentage), you can use this shortcut • E.g convert 35 out of 40 into a total out of 100. • Type in 37 Class marks Continued • For your next student’s mark, you simply type in the mark and press the equals button. • For e.g. your next student gets 23 out of 40. • Press • Press to change from a mixed number to an improper fraction to a decimal. 38 Adding Fractions • We use our 3 5 • E.g. Add + • Press button 3 2 7 39 Integer Divide • When dividing by a number that is not a perfect divisor of the number, the answer is normally displayed as a fraction. • We can use to find the quotient and remainder of a division sum. • E.g. Press 40 Memory Keys • You have several memory spaces on the calculator: A- F, X, Y and M • You can use your key and the memory key you want to use to type in the memory key. • If you want to store something into the memory key use • E.g. Store the value of 3 into A • Press 41 Memory Keys • To see what is stored in a particular memory slot, you can press and the memory key. • E.g. Press to see what we had previously stored in A • To see a complete list of everything currently stored in the memory slots press 42 Random Function • Press • 0: Random • Gives random numbers between 0 and 1 to 3 decimal places • 1: R-Dice • Gives random numbers between 1 and 6 • 2: R.Coin • Gives random numbers between 0 and 1 • 3. R.Int • Gives random numbers between any 2 digits typed in 43 Random Functions • Press • Press • Keep pressing to keep generating random numbers • Press 44 Random Functions • Press • Generate random numbers between 1 and 52 • Press • Remember that your numbers on your screen will be different to those displayed here. 45 Pythagoras / Rectangular Coordinates to Polar coordinates • Convert (4; 5) into polar coordinates. • Press 46 Polar coordinates to Rectangular coordinates • Convert the polar coordinates 5, 30 (r, 𝜃) to rectangular coordinates. • Press • Your X and Y values are saved in your X and Y memory keys. Press to see them. 47 Integration • Finds the definite integral • Use • E.g. Find 4 2 −3 𝑥 +7 • Press 48 Differentiation • Finds the derivative at a point • Use • E.g. Find 𝑥=2 • Press 𝑑 𝑑𝑥 𝑥 4 − 4 when 49 Constants • There are 52 constants available on the calculator. • Press • Press the number for the constant you want to insert into the expression. 50 Conversions • Press • E.g. Convert 3 pounds into kilograms. • Press • Press the key and look for where lb → kg • Press • Press 51 Summing • Use to find the sum of a sequence. • E.g. Find σ8𝑛=1 3𝑛2 − 2𝑛 + 5 • Press 52 Multiplying/ Product • You can also multiply patterns (second year maths) by using • E.g. Find ς4𝑛=1 3𝑛 + 2 • Press 53 Converting to Binary • We can convert numbers in decimal notation into binary notation, as well as add, subtract, multiply and divide with binary numbers. • We use • E.g. Convert 259 into binary notation. • Press 54 Adding in Binary • Press • E.g. Add 10101 + 10000111 • Press • Lets convert the answer back to decimal notation by pressing 55 Percentages • We use to find various shortcuts for different percentage calculations. • E.g. What is the selling price if the price before VAT is R86.90? • Press 56 HCF or GCD • To find the highest common factor we use • E.g. Find the HCF of 56, 72 and 108. • Press 57 LCM • To find the lowest common multiple we use • E.g. Find the LCM of 14, 18 and 32. • Press 58 Degrees, Radians and Gradians • We can change our angle units from degrees to radians to gradians and back again by using • E.g. convert 30˚ into radians. • Press • To convert back to degrees again press • Note: You can also use the Setup menu to change back to degrees (slide 17). 59 Absolute Values • We use to find absolute values • E.g. Find the absolute value of 5 – 7. • Press 60 Negative Button • To make a number negative press before typing in the number • Note- if you type in or (or any other combination of the two) you will get an error. • If you press the arrow button the calculator will move the cursor back to where the error was made. 61 • E.g. Find the value of • -30 + -80 - -40 • Press 62 Previous Answer • You can use the answer from the previous calculation in your next calculation by pressing • E.g. What is 85 added to the difference of 78 and 19? • First we find 78 – 19 • Press • Then we find 85 + the previous answer by pressing 63 Statistics Mode Press 64 Statistics Mode • Press • You have several options • 0: SD • Does statistical analysis for univariate data • 1: a + bx • Does statistical analysis for bivariate data • 2: a + bx +cx2 • Does statistical analysis for quadratic data • The rest of statistical analysis options are not relevant to students. 65 Univariate Data • Press • Insert data by typing in the data point and pressing • E.g. Type in the data points below: • Press 66 • Press to change the screen from the data table to the calculation screen. • You can also press back to the data table. to go • Press 67 • 0: Statistics Val • Gives the various values for the statistics. • Press to see each of the screens. • Press to clear away the statistics. 68 • Press • Press the corresponding number and to find each of statistics values given individually 69 • Press • Press to find the sum of all the x values, and press to find the sum of the x values squared. 70 • Press • Again, press the corresponding number and then to find the minimum, quartile 1, median, quartile 3 or maximum value of x 71 Linear Regression • Press • You can input the data in two different ways: • First type in all the x-values (pressing after each one) then use your arrow keys to move to the top of the ycolumn, and type in all the corresponding y-values (pressing after each one). • Alternatively, type in the x-value, press , type in the y-value and then press . This method is better for showing relationships to students. 72 • E.g. Type in the data: • Press X Y 3 7 4 11 5 15 6 19 7 23 8 27 9 31 73 • Now press to change from the data table to calculation screen. • Press 74 • 0: Statistics Val • Press • Press + to see each of the screens. • Press to clear away the statistics and do other calculations. 75 • 1: Regression Val • Press • Gives the regression line yintercept (a) and the gradient (b). • Gives the correlation coefficient. 76 • 2: Variable • Press • Press the corresponding number or letter ( ) to find each individual statistics value. 77 • 3: Sum • Press • Finds the sum of the various variables, and their squares, cubes and multiples. • Press the corresponding numbers and to find each individual statistics. 78 • 4: Min/ Max • Press • Find the minimum and maximum data points for x and y values. 79 • 5: Coefficient • Press • Gives the various linear regression variables and the correlation coefficient. 80 Quadratic Patterns • We can use the quadratic stats mode to help us with second common differences patterns. • Press 81 • Typing in the data can be done using the same methods as the linear regression mode. • E.g. Press n Tn 1 8 2 13 3 24 82 • Press to change to the calculation screen • Press • This gives us our quadratic equation: • 𝑇𝑛 = 3𝑛2 − 4𝑛 + 9 83 Table Mode Press 84 Table mode • We can use table to find the coordinate pairs for graphs. • There are two functions • The table mode is also unlimited, so you can continue in either direction for as long as you want to without running out of space. • Press 85 Tan graph • Let’s create a tan graph: • 3tan(x – 45) • Press • To make an X press • Press 86 • Press • Start at 0, so press • Make your step 15 so press • Use your and arrow keys to scroll through the table. • Note the asymptotes at x = -45 and x = 135. • Note that you can go in either direction without running out of space. 87 Simple and Compound Interest • Press • Let’s demonstrate simple interest first • Our formula is 𝐴 = 𝑃 1 + 𝑖 × 𝑛 • A = ? P = 1000, i = 9% p.a. • Press 88 • Ignore function 2 for the time being and press • Leave your start and step as 0 and 1 respectively so press • Use your and arrow keys to scroll through the table. • Remember that X = the number of years. 89 • Now let’s compare the simple interest with compound interest. • Press once, so that the simple interest formula is still on the screen. • We are going to use the same values as the simple interest but in the compound interest formula. • Press • Press 90 • Leave your start and step as is, so press • Use your and arrow keys to scroll through the table. • We can ask – When does the compound interest A value double the simple interest A value? • According to the table, after 20 years. 91 Complex Mode Press 92 Complex Numbers • Press • To make an i press • E.g. Type in 3 + 4i • Press 93 Changing between rectangular and polar coordinates. • Press • Press • This gives the hypotenuse (5) and the angle the hypotenuse makes with the x-axis. 94 Changing from polar to rectangular coordinates. • To type in the hypotenuse and the angle, we use • E.g. Press • To convert back to rectangular coordinates press 95 Conjugate Form • To find the conjugate form we use the menu. • E.g. Find the conjugate of 7 – 3i • Press 96 Argument • This function gives the angle for the rectangular coordinates. • E.g. Find the argument for 5 – 3i • Press 97 Real and Imaginary values • We can also type in the hypotenuse and angle and find the real and imaginary values for them. • E.g. Find the real and imaginary values for r = 3 and 𝜃 = 30. • Press • And press 98 Equation Mode Press 99 Equation Mode • You can solve 4 different types of equations in equation mode. • Press • 0: 2-VLE • 2 variable linear equation • 1: 3-VLE • 3 variable linear equation • 2: QUAD • Quadratic equation • 3: CUBIC • Cubic equation 100 0: 2 VLE • Press • This mode allows you to solve for 2 variables in 2 linear equations: • 𝑎1 𝑥 + 𝑏1 𝑦 = 𝑐1 and • 𝑎2 𝑥 + 𝑏2 𝑦 = 𝑐2 • E.g. Find x and y if • 3𝑥 + 7𝑦 = 9 and • −4𝑥 + 12𝑦 = 5 • Press 101 • Then • The determinant is also given 102 1: 3 VLE • We can also solve 3 variable linear equations of the form: • 𝑎1 𝑥 + 𝑏1 𝑦 + 𝑐1 𝑧 = 𝑑1 • 𝑎2 𝑥 + 𝑏2 𝑦 + 𝑐2 𝑧 = 𝑑2 • 𝑎3 𝑥 + 𝑏3 𝑦 + 𝑐3 𝑧 = 𝑑3 • The process is the same as the 2 variable linear equation mode. • Press 103 • E.g. Find x, y and z if: • 3𝑥 − 7𝑦 + 4𝑧 = 2 • 𝑥 −𝑦 −𝑧 =0 • 4𝑥 + 3𝑦 = 12 • Press 104 2: Quadratic Equation • We are able to solve quadratic equations in the form: • 𝑎𝑥 2 + 𝑏𝑥 + 𝑐 = 0 • Press • E.g. Find the x’s when • 𝑥 2 − 8𝑥 + 15 = 0 • Press 105 3: Cubic Equation • We are able to solve cubic equations in the form • 𝑎𝑥 3 + 𝑏𝑥 2 + 𝑐𝑥 + 𝑑 • Press • E.g. Solve for x: • 7𝑥 3 − 3𝑥 2 + 8𝑥 − 12 = 0 • Press 106 Matrix Mode Press 107 Matrix Mode • Solve matrices from 1 x 1 to 4 x 4 in size. • Press • To set up a matrix press • Set the size of the matrix by typing in the number of rows first and then the number of columns and press • Type in each matrix element from left to right and from top to bottom, pressing after each one. 108 • E.g. Enter the matrix 3 7 −2 • 8 −7 4 1 0 5 • Press • Type in the size of the matrix first by pressing 109 • Press 110 • Now store the matrix • Press 111 Matrix Calculations • Press • To use a matrix in your calculation, press • Choose the matrix you want to work with by pressing the number next to the name of each matrix. • E.g. Press 112 • To recall and edit the matrix press 113 • Finding the determinant • Press 114 • Finding the transpose of the matrix: • Press 115 • Creating an identity matrix • Press • Type in the size of the matrix you want, e.g. 116 • Changing the dimensions of a matrix • Press 117 • To create a matrix with all of the same values use the fill( function. • E.g. Create a 2 x 4 matrix with the element 3 • Press 118 • To create a matrix with random values (between 0 and 1) press • Now type in the number of rows you require and the number of columns separated by • E.g. 119 • To find the row echelon form of a matrix we first need to create a matrix 3 6 1 7 • Press • E.g. −2 8 • Now we store the matrix into A, press • Now we press • 120 • We can also find the reduced row echelon form. • Using the matrix from the previous example, we can say: 121 Finding the Inverse • First we create a 3 x 3 matrix: 2 4 7 • 8 6 4 −1 10 3 • Press • Now we press 122 Handy Hints • You can store the name of the matrix into any of the D-keys to save you time when working with the matrix. • Press • Now we can use this for calculations. • E.g. Find A2 • Press 123 Vector Mode Press 124 Vectors • Vectors work in a similar way to matrices. • Press • To create a vector, press • You can either have a vector with 2 or 3 elements. • Press 125 • To store the vector press • To recall a vector press 126 Dot product • Input a second vector: • Press • Store it • To find the dot product we press 127 Cross Product • Using the previously stored matrices, we can also find the cross product of two vectors. • Press 128 Angle between vector • We can find the angle between two vectors. • Using our previous vectors press 129 Unit Vector • To get the unit vector of a vector press 130 Distribution Mode Press 131 Distribution Mode • Press • You have 3 options: • 0:Normal • Normal Distribution • 1: Binomial • Binomial Distribution • 2: Poisson • Poisson Distribution 132 0: Normal • Press • You have 3 options: • 0: Normal pdf • Calculates the normal probability density function. • 1: Normal cdf • Calculates the cumulative normal density function • 2: Inverse Normal • Calculates the inverse cumulative normal density function 133 • 0: Normal pdf • Press • Now type in the x value, mean and standard deviation, eg. 134 • 1: Normal cdf • Press • We can find the cumulative normal density function, between two x points. • Press 135 • 2: Inverse Normal • Uses the area of the curve to find the value of x. • Press • Area = • Mean = • Standard deviation = 136 Binomial Distribution • Press • Two options: • 0: Binomial pdf • Finds the cumulative probability at a point x with the number of trials (n) and the probability of success (p) • Press 137 • 1: Binomial cdf • Press • x= • n= • p= 138 Poisson Distribution • Press • Two options: • 0: Poisson pdf • Press 139 • Press • Two options: • 1: Poisson cdf • Press 140 Drill Mode Press 141 Drill Mode • Press • Two options: • 0: Math • Asks maths questions and marks them for you. • 1: Table • Asks times tables questions for a particular number. 142 0: Math • Press • Use your and arrow keys to choose the number of questions (25, 50 or 100). • Use your and arrow keys to choose the type of questions you want to do. • Press once your selection is done 143 • You will see • The question number you are on and • The question • Type in the answer and press • If you get the answer correct you will get a tick and a new question. • If you get the answer wrong, you will get a cross and the same question. • The calculator will repeat the question until the answer is correct. • If you do not know the answer, leave the answer space blank and press 144 • Once you have answered the last question, press • You will see your mark and percentage 145 Table mode • Press • Choose the particular times table by using your and arrow keys • Choose between serial (times tables in order) or random (mixed order) by pressing or • Press once you’ve made your choice. 146 • You will see • How many questions you have left • And the question • Type in the answer and press after each one. • If you get the answer correct you will get a tick and a new question. • If you get the answer wrong, you will get a cross and the same question. • The calculator will repeat the question until the answer is correct. • If you do not know the answer, leave the answer space blank and press 147 • After the last question you will see • Press • You will see your total out of 12 and your percentage. 148 The End Visit www.mathsatsharp.co.za for free grade 8 – 12 maths, technical maths and mathematical literacy worksheets, exam papers, and memos. Download the simulator here for free ☺ Contact us with any queries: tal@smdtechnologies.com / 011 608 3633 149