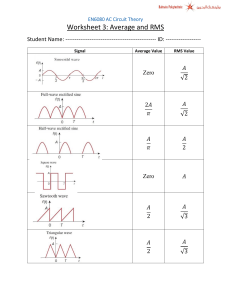
Chapter 18C: Alternating Current Contents: 7. Alternating Current 18-7 Alternating Current Current from a battery flows steadily in one direction (direct current, DC). Current from the electricity supply varies sinusoidally (alternating current, AC), reversing in direction. Voltage varies sinusoidally: where 𝑉0 = peak voltage (V) 𝜔 = angular frequency (s−1) 𝜔 = 2𝜋𝑓 where 𝑓 = frequency (Hz) so 𝑉 = 𝑉0 sin 2𝜋𝑓𝑡 𝑉 = 𝑉0 sin 𝜔𝑡 Alternating Current 𝑉 = 𝑉0 sin 2𝜋𝑓𝑡 where 𝑉0 = peak voltage. The 'peak-to-peak' voltage 𝑉𝑝𝑝 = 𝑉0 − −𝑉0 = 2𝑉0 Frequency 𝑓 is number of complete oscillations per second and period 𝑇 is time for one complete oscillation 1 𝜔 2𝜋 𝑓= ; 𝑓= ; 𝑇= 𝑇 2𝜋 𝜔 e.g. Mains frequency in SA is 50 Hz so period of waveform is 1 1 𝑇= = = 0.02 s = 20 × 10−3 s = 20 ms 𝑓 50 Alternating Current If voltage V across resistor, current in resistor given by "Ohm's law" for DC and AC: 𝑉 𝑉0 𝐼 = = sin 𝜔𝑡 = 𝐼0 sin 𝜔𝑡 𝑅 𝑅 where 𝐼0 = 𝑉0Τ𝑅 = peak current Note if 𝑉 = 𝑉0 sin 2𝜋𝑓𝑡 then 𝐼 = 𝐼0 sin 2𝜋𝑓𝑡 - the two sinusoidal* waveforms are "in phase" (the maxima and minima coincide with each other) *sinusoidal: sin or cos function Alternating Current Because 𝑉 and 𝐼 go equally positive and negative, the average value of each is zero. But power 𝑃 = 𝐼𝑉 = 𝐼2 𝑅 so 𝑃 = 𝐼02 𝑅 sin2 2𝜋𝑓𝑡 Now sin2 varies between 0 and 1 with average value 1Τ2 The average power is then 1 2 1 2 ത ത 𝑃 = 𝐼0 𝑅 or 𝑃 = 𝑉0 Τ𝑅 2 2 (since also 𝑃 = 𝑉 2 Τ𝑅) or 𝑃ത = 𝐼ഥ2 𝑅 (𝐼ഥ2 = average of 𝐼2 ) Alternating Current If we now take the square root of 𝐼ഥ2 (= 𝐼02 Τ2) we get the rms (root-mean-square) current, similarly for rms voltage: 𝐼rms = 𝐼ഥ2 = 𝑉rms = 𝑉2 = 𝐼rms and 𝑉rms are sometimes called "effective" values of current and voltage because they can be substituted into the (dc) formulae for power: 2 𝑅 etc 𝑃ത = 𝐼rms 𝑉rms = 𝐼rms 𝐼0 2 𝑉0 2 = 0.707 𝐼0 = 0.707 𝑉0 Alternating Current Normally, when we specify an ac voltage we give the rms value, e.g. "mains voltage in South Africa is 230 V" means this is the rms value 𝑉rms = 𝑉0Τ 2 . The peak voltage is 𝑉0 = 2 𝑉rms = 2 230 = 325 V Example 18-13 (modified): Calculate the resistance and peak current in a 1500 W hairdryer connected to a 230 V ac line. 𝑃ത 1500 𝐼rms = = = 6.5 A 𝑉rms 230 𝐼0 = 2 𝐼rms = 2 6.5 = 9.2 A 𝑉rms 230 𝑅= = = 35.4 Ω 𝐼rms 6.5