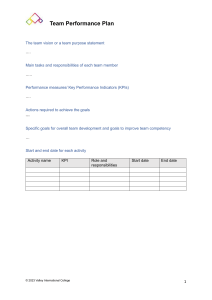
Demand planning Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are essential metrics that organizations use to assess the effectiveness of their demand forecasting and planning processes. Accurate demand planning is crucial for optimizing inventory levels, reducing excess inventory, improving customer satisfaction, and controlling costs. Here are some common KPIs used in demand planning: 1. Forecast Accuracy: Forecast Error: This KPI measures the difference between the forecasted demand and the actual demand. Common metrics used to assess forecast error include Mean Absolute Error (MAE), Mean Absolute Percentage Error (MAPE), and Mean Squared Error (MSE). 2. Inventory Turnover: Inventory Turnover Ratio: This KPI indicates how many times a company's inventory is sold and replaced over a period. A higher turnover ratio often indicates more accurate demand planning and efficient inventory management. 3. Stockout Rate: Stockout Percentage: This metric measures the frequency with which products are out of stock. A lower stockout rate indicates better demand forecasting and inventory management. 4. Fill Rate: Fill Rate Percentage: This KPI assesses the percentage of customer demand that can be met from available stock. A higher fill rate indicates better inventory and demand planning. 5. Customer Service Level: Service Level Percentage: This KPI measures the percentage of customer orders fulfilled on time and in full. A higher service level percentage reflects better demand planning and customer satisfaction. 6. Lead Time Accuracy: Lead Time Variance: This metric evaluates the accuracy of lead time forecasts. Accurate lead time predictions are essential for proper demand planning and inventory management. 7. Demand Variability: Coefficient of Variation (CV): CV measures the relative variability of demand. Understanding demand variability helps in optimizing inventory levels and forecasting methods. 8. Excess and Obsolete Inventory: Excess Inventory Value: This KPI quantifies the value of excess inventory that a company holds due to inaccurate demand planning. Obsolete Inventory Value: This metric assesses the value of obsolete or expired inventory that could not be sold. 9. Demand Forecast Bias: Bias Percentage: This KPI measures any systematic overestimation or underestimation in demand forecasts. A balanced forecast with minimal bias is ideal. 10. Forecasting Horizon Accuracy: Horizon Accuracy Percentage: This KPI evaluates how well demand forecasts align with actual demand at different time intervals, such as daily, weekly, or monthly. 11. New Product Forecast Accuracy: Accuracy for New Products: This metric assesses the accuracy of demand forecasts for new or innovative products, which can be more challenging to forecast accurately. 12. Supplier Performance: Supplier On-Time Delivery: This KPI measures how often suppliers deliver products on time. Supplier delays can disrupt demand planning and inventory management. 13. Sales and Operations Planning (S&OP) Process Efficiency: S&OP Cycle Time: This metric evaluates the time it takes to complete the S&OP process, which includes demand planning. A shorter cycle time can improve responsiveness to changing demand. 14. Forecast Collaboration and Alignment: Forecast Alignment Score: This KPI measures the alignment between demand planning and sales forecasts. Improved collaboration can lead to more accurate demand planning. These KPIs provide insight into the effectiveness of an organization's demand planning process and help identify areas for improvement. Effective demand planning is critical for optimizing costs, improving customer satisfaction, and maintaining a competitive edge in the market.