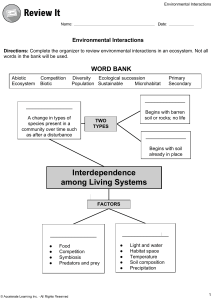
Ecosystems Biotic & Abiotic factors What do you know? On your tables there are two picture Do both meet the description of an ecosystem? You must be able to: • Define an ecosystem. • Identify examples of an ecosystem. • Examine biotic an abiotic factors in an ecosystem. • Analyze the constant reaction and interdependance between biotic and abiotic factors. Biotic Factors/ Living factors Biotic components Producers: • Plants are auototrophs Primary consumers: • Heterotrophic organisms • Dependent on plants Decomposers: • Lives on dead organic matter • Put nutrients back into the soil. Secondary consumers • Heterotrophic • Dependent on primary consumers • Carnivores Abiotic factors/ Non-living factors ABIOTIC FACTORS Climatic factors: • Light • Temperature • Water • Atmospheric gases • Wind Edaphic factors (refers to ground) • Soil type • Groundwater • pH of the soil Physiographic factors • Aspect (slope direction) • Slope • Altitude above sea level SOIL Main soil types: • Sandy soil • Loamy soil • Clay ground Soil’s water holding capacity • Clay soil = lots of water • Sandy soil = Little water • Loamy soil = Moderate water Soil-pH • Acidity/ alkalinity (the pH) of the soil affects plant growth. • Most plants grow better in soil that is slightly acidic (low pH). Soil’s air content THE MORE AIR = THE MORE OXYGEN FOR THE PLANTS • Sandy soil – Large air spaces • Clay soil – Small air spaces • Loam soil – Moderate amount of air Water & the water cycle Importance of wetlands • Important ecosystems. • Habitat & source of water for different types of plants and animals. • Acts as filtration of polluted water. • They act like giant sponges in dry years. Importance of wetlands to people • Provide water. • Plant crops and catch fish in the lakes. • Reeds to build. • St Lucia = tourist guides = job opportunity. Light Photosynthesis: • Plants get energy through photosynthesis. • Produces oxygen for respiration. • Photo Period: Light accelerates photosynthesis. • Prefer different amounts of light. E.g., Chrysanthemums = 10 hours of light needed to bloom & Namaqua daisies only open in bright sunlight. Animals and light • Diurnal animals (DAY). • Nocturnal animals (NIGHT). Light and seasonal change: • Seasons – Change in the luminous intensity of light. Temperatuur Night and day temperatures • Effect on behaviour. • E.g., Reptiles • Plants’ flowers. • Activity of desert organisms. • E.g., Cacti Temperature and seasonal change • Temperature is related to light. • Summer = temperature higher, daylight hours more. • Winter = temperature lower, daylight hours less. 1) Migration • Seasonal movement due to climatic conditions. • E.g., Swallows • Amount of food and water. • E.g., Butterflies 2) Hibernation/Wintersleep Decrease in body processes • Only active on warmest parts. • True hibernation – inactive. • E.g., Bushveld-saddle-nosed bat – heart rate 4 beats per min. Movement and behaviour Temperatuur Effects of temperature on animals 3) Estivation/Summersleep • Decrease in body activity and processes • Warm and dry – the animals take shelter – prevent water loss. • E.g., Bullfrogs buried in mud. • Air sack to provide oxygen for respiration. Temperatuur Effect of temperature on plants • Cold winter – dormant seeds or bulbs. • Peaches and plums – low temperatures – seeds germinate. • Some plants need high temperatures – to germinate. • E.g., tomatoes – need high temperatures for germination. • E.g., Peas and beans – grow best at low temperatures. Atmospheric gases and wind • The atmosphere is a blanket of gases that surrounds the earth. The three most important gases in the atmosphere: • Nitrogen 78% • Oxygen 21% • Carbon Dioxide 0,03% [Other gases (methane etc) 0,07%] Atmospheric gases and wind Wind • Rol in pollination and seed dispersal. • Rol in distribution of certain insects. • Wind has an effect on transpiration. • Plants lose more water when it is windy. • Wind also accelerates evaporation from rivers, lakes and the sea. Physiographic factors Factors relating to the physical characteristics of the land. 1) Height • Altitude above sea level. • Temperatures are lower, less oxygen, more sunlight. • 2) Slope • Steep or flat. • Steepness: How fast water flows away. • 3) View • North view: More sunlight and warmer, low moisture, succculent plants. • Southern view: Less sunlight, high humidity, ferns. Assessment 5 min 1. Assess the biotic and abiotic factors that influence you in the classroom. Name two factors for each. (4) 2. Which soil type has the best water holding capacity? (1) 3. Is the above soil type also the best for plant growth? (1) 4. How are nocturnal animalsʹ eyes adapted to see in dim light? (2) 5. How do high and low temperatures affect animalsʹ body processes?(2) Total: 10 Summary • Essential relationships between life and the environment. • Remember, our role is as custodians of the earth. Any questions?