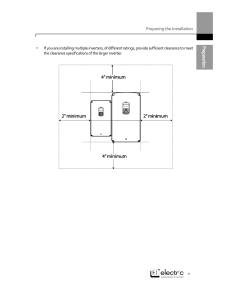
Aero Induc on Problem Statement 1. Li is the component of this force that is perpendicular to the oncoming flow direc on.It contrasts with the drag force, which is the component of the force parallel to the flow direc on. An airfoil generates li by exer ng a downward force on the air as it flows past. According to Newton's third law, the air must exert an equal and opposite (upward) force on the airfoil, which is li . As the airflow approaches the airfoil it is curving upwards but as it passes the airfoil it changes direc on and follows a path that is curved downwards. According to Newton's second law, this change in flow direc on requires a downward force applied to the air by the airfoil. Then Newton's third law requires the air to exert an upward force on the airfoil; thus a reac on force, li , is generated opposite to the direc onal change. In the case of an airplane wing, the wing exerts a downward force on the air and the air exerts an upward force on the wing. DRS (Drag reduc on system) is used to reduce drag and increase the speed of a Formula 1 car. The DRS uses an actuator controlling a flap in the middle of an F1 car’s rear wing that can be opened when drivers push a steering wheel bu on a er they enter a designated part of each track. These areas are known as DRS ‘Ac va on’ zones. The open flap reduces rear wing surface area and so serves to reduce aerodynamic drag, rapidly increasing straightline speed. In races, this is allowed when a driver is running within one second of a car ahead – even if this car is being lapped. In prac ce and qualifying, DRS can be used at will, but only within the set ac va on zones. The various parts of an F1 car related to aerodynamics are: front wing barge board area side pod area floor diffuser rear wing misc (brake ducts, nose cone area, engine cover and side pods etc 2. The 2009 F1 season was an incredible season in the sense that Brawn GP, despite being a new entrant to the sport, won both the Drivers Championship (Jenson Bu on) and the Constructors Championship. The main reason for the sudden success of Brawn GP was the use of the innova ve-yetcontroversial Double Decker Diffuser for its car (BGP 001), which gave it a major aerodynamic advantage over teams like McLaren, Ferrari and Red Bull. The diffuser is at the rear of the car and is a route to get downforce by using the airflow under the car's floor. The BGP 001 had a different central channel to its diffuser with the shape of the structure being used to create advanced type of double-decker design. The diffuser's controversial aspect was the hole in the rear which increases the speed of airflow as it heads towards the higher rear venturi sec on, where it expands and creates more downforce. Downforce is important for F1 cars since Downforce is cri cal when driving at high speeds and taking corners, as without it, the car can easily spin out of control. Therefore, downforce plays a crucial role in improving a car's stability. The greater the downforce, the more grip the car has. 3. Many people wonder why F1 cars, which travel at high speeds, don’t fly off the track. The aerodynamic elements of a Formula 1 act the opposite way the plane wings operate. So even at 300 kph or more, the car is sucked to the ground. The distance to the floor is also so low that the Bernoulli effect makes more air pass over the car that below it. That's properly called ground effect. It's somehow banned nowadays but all the car winglets try to maximize it anyway. So the addi on of downforce generated by the front and rear wing, plus the ground effect generated between the floor and the ground, lets them be fast and not fly while going that quickly. When they lose those wings, or when the car wheels “climb” over the other car's wheels, then they can really fly high. Mark Webber’s crash at the European GP in Valencia. 4. Ground clearance is the distance between the lowest point of the car component and the ground. Basically, ground clearance will be useful to maintain the quality and stability of the car. The higher the ground clearance, the safer it is to use. Low ground clearance is common in racing cars because it improves the handling of the vehicle. A car with low ground clearance s cks close to the ground more strongly, and is therefore less likely to topple or roll over when abrupt and sharp turns are made. In contrast, a car with a higher centre of gravity is more likely to be acted upon by outside forces that can move it laterally on the track and cause it to roll over. The ground clearance of an F1 car can be op mized by having an uneven height for the car. Obviously a lower car means more downforce meaning the car s cks to circuit be er around corners. Its not just racing cars but street cars also follow this to some extent. The front bumper has the lowest ground clearance followed by the sec on between the front and rear res, and followed yet by a rear bumper usually with the highest clearance. Using this method, the air flowing under the front bumper will be constricted to a lower cross sec onal area, and thus achieve a lower pressure and faster speed. Ground clearance is adjusted for different tracks to suit its needs. For example, Monza does not require a high ground clearance since it mainly consists of long straights and only 2 major corners (Curva Grande and Parabolica). Thus high stability is not really required in Monza. While Hungary on the other hand has atleast 4 major high speed corners where stability is required, thus it will have a high ground clearance. 5. The major difference between Open and Closed wheel race cars is the ground clearance. Since the wheels are outside the body, f1 cars have lower ground clearance and thus it s cks to the ground since it directs the airflow and is faster while nascars have their wheels under the body and cant direct the airflow and are slower. But in the aspect of drag, nascars are be er. The drag coefficient of a nascar is 0.29, which is much be er than that of an f1 car (0.7-0.10) In Downforce again, nascars are be er. They can generate a downforce of between 3500 pounds to 5000 pounds, while f1 cars (without drs) can generate only 1600 pounds of downforce, thus making it slower. But the overall handling of nascar is be er than an f1 car since they have a higher ground clearance, resul ng in extra stability while f1 cars have a lower ground clearance, which gives it lower stability and relying more on the drivers. Thus, there are more crashes in f1 than nascar.