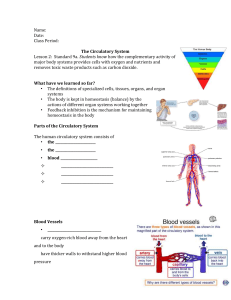
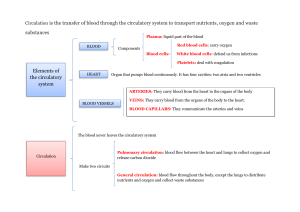
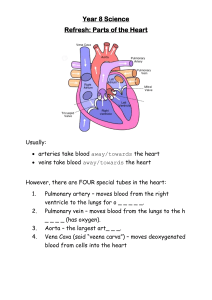
Subject: Biology Topic: Transport in animals Standard: IX Cambridge/2122 Transport in animals 1 Of 15 Thinking time Cambridge/2122 Transport in animals 2 Of 15 Thinking time State as many words as you can starting from “Circ”. (Clue: For the clue refer the image given in the slide.) Did you think of these words? To which body system these words are most related to? CIRCLE Cambridge/2122 CIRCULAR CIRCULATE Transport in animals 3 Of 15 The Circulatory System The circulatory system consists of: Heart Capillaries Along with heart and blood vessels, lungs work closely to circulate oxygenated blood in the human body. Arteries Cambridge/2122 Veins Transport in animals 4 Of 15 The Colour Differentiation We show Arteries in Red colour and Veins in Blue. This colour differentiation is NOT wholly true. The oxygenated blood transported by the arteries is bright red, but the deoxygenated and CO2 transporting blood is pale red (certainly not blue). Cambridge/2122 Transport in animals 5 Of 15 Double and single circulatory systems Cambridge/2122 Transport in animals 6 Of 15 The Two Blood Circulations: Pulmonary and Systemic Blood flows twice in the heart before it completes one full round. Pulmonary (lungs) circulation 1. The short pulmonary (lungs) circulation. 2. The long systemic (General body) circulation Thus the blood circulation in the human body is called DOUBLE CIRCULATION Systemic (General body) circulation Cambridge/2122 Transport in animals 7 Of 15 The Two Blood Circulations: Pulmonary and Systemic Let us now take a look at Pulmonary circulation and Systemic circulation Cambridge/2122 Transport in animals 8 Of 15 The Two Blood Circulations: Pulmonary and Systemic Pulmonary circulation It starts in the pulmonary artery arising from the right ventricle which soon divides into two branches that enter the respective lungs. Pulmonary veins collect the oxygenated blood from the lungs and carry it back to the left auricle of the heart Cambridge/2122 Transport in animals 9 Of 15 The Two Blood Circulations: Pulmonary and Systemic Systemic circulation It starts with the aorta that arises from the left ventricle. The aorta sends arteries to various body parts and their tissues. From there the blood is collected by veins and poured back into the heart. Cambridge/2122 Transport in animals 10 Of 15 Single circulation • Single Circulation is a circulatory system in which the blood passes through the heart once, in its passage around the body. e.g. Fish • Blood leaves the heart and is oxygenated in the gills. • The oxygenated blood goes to the rest of the body, and then returns back to the heart. • The heart has one atrium and one ventricle. Remember the ventricle is at the bottom. • The Blood which arrives at the organs of the body are at a low pressure. Single system (fish): heart -> gills –> body –> heart • Low activity and do not need to maintain temperature so less energy needed. • Blood at low pressure and flow is slow. Cambridge/2122 Transport in animals 11 Of 15 Advantage of Double circulatory system over single circulatory system • In a fish, the low-pressure blood just continues around the Fish’s body. This means that blood travels much more slowly to a fish’s body organ that does in a mammal. • This is particularly important with respect to delivery of oxygen for respiration, Any tissues that are metabolically very active need a lot of oxygen delivered to them as quickly as possible, and this delivery is much more effective in a mammal than in a fish. Cambridge/2122 Transport in animals 12 Of 15 Key words • Circulatory system : a system of blood vessels with a pump and valves to ensure one-way flow of blood • Valves : structures that allow a liquid to flow in one direction only • Oxygenated blood: blood containing a lot of oxygen • Deoxygenated blood: blood containing only a little oxygen • Double circulatory system: a system in which the blood passes through the heart twice on one complete circuit of the body • Single circulatory system: a system in which the blood passes through the heart only once on one complete circuit of the body Cambridge/2122 Transport in animals 13 Of 15 P Oxygenated blood travels from the heart to the body T Blood picks up oxygen from the lungs and gives out carbon dioxide Q Blood travels from the heart to the lungs R Oxygenated blood travels back to the heart lungs S DEOXYGENATED blood travels from the body to the heart U Body cells use oxygen and give blood CARBON DIOXIDE body’s cells Cambridge/2122 Transport in animals 14 Of 15 T Blood picks up oxygen from the lungs and gives out carbon dioxide Q Blood travels from the heart to the lungs lungs S DEOXYGENATED blood travels from the body to the heart P Oxygenated blood travels from the heart to the body U Body cells use oxygen and give blood CARBON DIOXIDE Cambridge/2122 R Oxygenated blood travels back to the heart body’s cells Transport in animals 15 Of 15