AAE 301 Problem Set 4
School of Aeronautics and Astronautics, Purdue University Fall 2023
Issued 9/15; Due 9/22 11:59pm
All work should be done by hand (without the use of a calculator/computer) unless specified otherwise.
Show all work for full credit. If you have code, publish as PDF and attach to the end of your homework.
Exercise 2.4.1 (modified version, use information given in this homework)
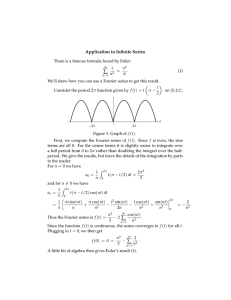
Problem 1. Consider the function f in L2 (0, 2⇡) given by
f (t) = 2
= 1
0t<⇡
⇡ t < 2⇡.
if
if
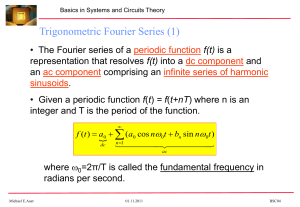
Find the sine and cosine Fourier series expansion (3.1) for f , that is, find the Fourier series for f of the form:
f (t) = a0 +
1
X
↵k cos(kt) +
k
sin(kt).
k=1
Choose a partial Fourier series approximation p100 (t) for f (t). Then plot p100 (t) and f (t) on the same graph.
Compute the error
s
Z 2⇡
1
2
kf pn k =
|f (t) pn (t)| dt
2⇡ 0
in Matlab. Does this Fourier series converge for t = j⇡ where j is an integer, and if so what does it converge
to; see the Dirichlet convergence Theorem 2.3.4.
Problem 4. Consider the function f in L2 (0, 2⇡) given by
f (t) = 4 + 2 cos(2t)
4 sin(2t) + 4 cos(3t) + 8 sin(3t) + 6 cos(5t)
4 sin(8t).
Compute the norm kf kL2 (0,2⇡) for this function. Express f as a Fourier series of the form f =
Plot the power spectrum for f .
P1
1
ikt
.
2⇡ikt
.
ak e
Problem 5. Consider the function f in L2 (0, 1) given by
f (t) = 2
4 cos2 (⇡t) + 4 cos(2⇡t) + 6 cos(6⇡t)
10 sin(6⇡t) + 12 cos(8⇡t)
Compute the norm kf kL2 (0,1) for this function. Express f as a Fourier series of the form f =
Plot the power spectrum for f .
1
P1
1
ak e
C)
According
。
to
pn (t )
=
Theorem
2 3.
.
flj π t ) + f (i π
y
4
=
, it
a
si
s points
convergesto discontinuo
让
5
Problem
On 510
1
ft
ZILOSETTITACOSLZET
a
2 21011294
521051 Eat
fit
2
GLOSLGET
105in LET
0525L
cos
210512714746205262 7 10514169 74121051824
2
1
Wo
2T
2
90 0
41 2
I
93 6
its de
11511
542
f
Iga
b
B
10
4
12
30510
44
as
3 51
94 6
a s
Hsi
94 6
of
e
44
142
ikat
90 0
I
a
94 1
fu
e
at
ein't f
6 e isotutpeilott
ji
it't
tests i
é
1220518kt
3611914
C
34
I
i
4 7
2
1 0
I
2
I
4
K
clear all
close all
clc
%--------------------------------------------------% Calculations & Output
%--------------------------------------------------% Initialize arrays for t and p
t = linspace(0, 2 * pi, 10000);
p = zeros(size(t));
%---------------------------
Problem 1
%--------------------------% Create piecewise function
syms t1;
f1 = piecewise(0 < t1 <= pi, 2, pi < t1 <= 2*pi, -1);
% Calculate fourier approximation of function
p1 = p;
for k = 1:1:100
p1 = p1 + (sin(k * t) / (k * pi)) * (3 - 3 * cos(pi * k));
end
p1 = p1 + (1 / 2);
% Calculate error of fourier series
error1 = 0;
for k = 101:1:10000
error1 = error1 + ((3 - 3 * cos(pi * k)) / (pi * k)) ^ 2;
end
error1 = sqrt(error1) / sqrt(2);
%---------------------------
Problem 1 Plots
%--------------------------% Function and Fourier Approximation plots
figure(1)
hold on
fplot(f1)
plot(t,p1)
axis([0,2 * pi,-1.5,2.5])
xlabel('t')
legend('Function','Fourier Series')
title('The graph for f(t) and p100(t) [Problem 1]')
%---------------------------
1
Published with MATLAB® R2022b
2