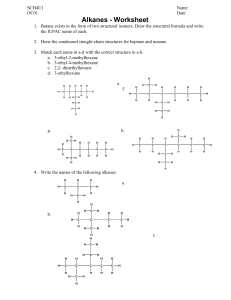
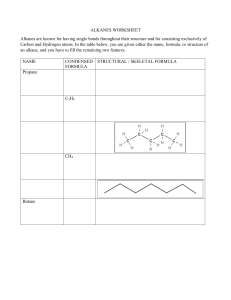
Organic Chemistry Teacher Andrea Montalvan 9A Table of contents 01 03 Lesson 01 Introduction to organic chemistry Practice Questions Now it´s your turn! 02 Lesson 02 Writing alkanes, alkenes and their combustion. Remember There will be a written Quiz on this topic once Lessons 01 & 02 are complete. Learning Objectives: Lesson 01 & 02 1.1 1.2 1.3 & 02 Understand that carbon forms a vast range of compounds and the study of their properties is known as organic chemistry. Define the term hydrocarbon as compounds formed solely by carbon and hydrogen. Write and interpret general formulae of compounds in the same homologous series, limited to alkanes. Success Criteria 01 02 Recall that carbon can have four covalent bonds and make the backbone of organic compounds. Describe the main reactions of alkanes as combustion and substitution and write example equations. 03 04 Identify and draw the structures of ethane and ethene. Identify alkenes as having at least one double bond. 01 Introduction to Organic Chemistry What you need to know… Organic Chemistry Studies the structure, properties and reactions of organic compounds that contain carbon in covalent bonding. Chains Rings Carbon atoms can join to each other to form long chains. Atoms from other elements can attach to the chain. Carbon atoms can also arrange themselves in rings. Bonds The carbon atoms in a chain can be linked in single, double, or triple covalent bonds. Carbon Atoms look like THIS Keyword!!! Hydrocarbona compound that contains carbon and hydrogen only. Whoa! Learn how to name them. These are Alkanes. They are saturated hydrocarbons. Only have single bonds. They have a recipe… All alkanes have a general molecular formula. It does not matter what happens, if your compound is an alkane their formula looks like this: And the longer the chain gets, the closer the molecules pull together. Speaking of formulas… There are 3 types of formula for any given compound ORGANIC COMPOUND XYZ A Empirical B Molecular C Structural It depends on what you want to show A Empirical Formula Molecular Formula Structural Formula Important. Simplest form. Shows the ratio of atoms in a compound. Most important. Represents exactly how many atoms of each element are in a molecule. Even more important. This formula shows how the atoms are bonded together in a diagram. B C They look like THIS Have some Examples Now it is your turn! REACH LESSON 04 TO UNLOCK THE REST OF THE CHART Fun Fact Did you know most fuels we use are alkanes? This is because they burn very exothermally. Some examples are: - Methane - Butane - Propane NEW KEYWORD!!! Homologous seriesis a family of organic compounds that: - Have the same general formula. - Have similar chemical properties. - Show gradual increase in physical properties. Meet -ALKENESAre not the same as alkanes. Alkenes are unsaturated hydrocarbons. They have a double bond between a pair of their carbon atoms. e Classwork Using your coursebook, solve questions 10.1-10.6, 10.8, 10.10 and 10.11; Chapter 10: Organic Chemistry. For 1 stamp on your punch card. 02 &03 Alkanes and Alkenes Homologous series; the cousins of the chemistry world. And how to burn them. What? - For 2 extra points What is an Alkene? Meet -ALKENESNot the same as alkanes. Alkenes are unsaturated hydrocarbons. They have a double bond between a pair of their carbon atoms. **Review Slide** Most common ones Bromine Test Activity 01 Using your Chemistry Workbook, page 127, solve exercise 10.1a. For 1 class stamp on your punch-card. Allotted Time: 5 minutes Now… Let's talk FIRE!! Boringly known as…. Combustion Combustion A chemical reaction in which a substance reacts with oxygen and produces heat (exothermal). The products of the combustion of hydrocarbons (alkanes and alkenes) are: ● ● ● Carbon Dioxide (CO2) Water (H2O) Heat/Light Combustion of Alkanes Combustion: Alkanes VS Alkenes 100% Not 100% Complete Incomplete They burn completely and leave little to no residue. The flames are blue. They do not burn completely unless there is high levels of oxygen. Can generate smoke and soot. The flames are red. Now you try! Write and balance the equation for combustion of ethane. Valid for: 1 point Another One! Write and balance the equation for combustion of propane. Valid for: 1 point Last One I Promise… Write and balance the equation for combustion of butene. Valid for: 1 point Activity 02 Using your Chemistry Workbook, page 128, solve exercise 10.2a, b and c. For 1 class stamp on your punch-card. Allotted Time: 10 minutes It´s Quizzis Time!!! Bring out your devices (no phones) and log into the Quizziz room with the code provided by your teacher.