Python Tutorial: Objects, Data Types, and Computational Thinking
advertisement

Tutorial1
September 1, 2023
1
DAO 2702 Tutorial 1
YU Bin
Institute of Operations Research and Analytics
National University of Singapore
Email: binyu@u.nus.edu
Website: https://binyu.site/
2
Agenda of Tutorial
• Recall the last week lecture
– Kahoot game to recall the concept
– Extra exercises by hands-on
– Q&A
• Week 11 & 12 is project consultation
– Each team has 20mins to consult and discuss. (Also welcome to drop the email out of
tutorial session)
2.1
Kahoot Game
Kahoot link
2.2
Lecture Content
Let us recall the concept we learn at lecture ### Python objects We introduce three type objects:
integer, float, and string
objects
example
integer
float
string
print(1)
print(1.0)
print(‘1’)
[1]: print(type(1))
<class 'int'>
1
[2]: print(type(1.0))
<class 'float'>
[3]: print(type('1'))
<class 'str'>
2.2.1
Data type conversions
We could use int, float, and str to convert each other
[4]: print(type(1),type(str(1)),type(float(1)))
<class 'int'> <class 'str'> <class 'float'>
Note: the original type is integer, then use str to convert integer to string, lastly use float to convert
integer to float
2.2.2
Computational thinking
Computational thinking is a set of problem-solving methods that involve expressing problems and
their solutions in ways that a computer could also execute. The fundamental of computational
thinking involves the understanding of control flows, i.e., the order in which the program’s code
executes. The control flow of a Python program is regulated by conditional statements, loops, and
function calls. In this lecture, we will focus on the concepts of the first two.
credit to Dr. Xiong Peng
2.2.3
Boolean type expressions
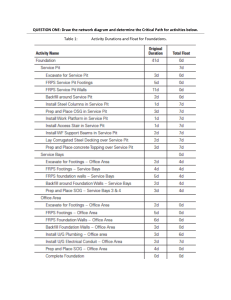
The comparison operators are used to compare two values, and a boolean value is returned.
[5]: print(1==3)
print(1!=3)
print(1>=3)
print(1<=3)
print(1<3)
print(1>3)
#
#
#
#
#
#
Operator
Name
Example
==
!=
>=
<=
>
<
Equal
Not equal
Greater than or equal to
Smaller than or equal to
Greater than
Smaller than
x
x
x
x
x
x
1==3 is false
1!=3 is true
1>=3 is false
1<=3 is true
1<3 is true
1>3 is false
False
True
2
== y
!= y
>= y
<= y
> y
< y
False
True
True
False
2.3
2.3.1
Exercise
Question 1
Currently, COE (certificate of entitlement) are five categories, with prices of \$100000, \$129890,
\$82801, \$11402, and \$131000 respectively. Please write the code to input the category and
output the price.
[6]: # read the input of user
cat = input('the category is ')
# if-else if statement
if cat == 'A':
print('$100000')
elif cat == 'B':
print('$129890')
elif cat == 'C':
print('$82801')
elif cat == 'D':
print('$11402')
elif cat == 'E':
print('$131000')
the category is A
$100000
Question 2 You are the game designer of Valorant and need to calculate the behavior of each
player based on the kills, deaths, and assists. The formula of player behaviour is as follows
2 ∗ 𝐾𝑖𝑙𝑙 + 0.5 ∗ 𝑎𝑠𝑠𝑖𝑠𝑡 − 1.23 ∗ 𝑑𝑒𝑎𝑙𝑡ℎ
Please write the program to input the respective value and print the score of player behavior
[7]: # read the input of user
kills = input('the number of kills is ')
assists = input('the number of assists is ')
deaths = input('the number of deaths is ')
# data type conversion
kills = int(kills)
deaths = int(deaths)
assists = int(assists)
3
# calculate the player behaviour
player_behaviour = (2 * kills) + (0.5 * assists) - (1.23 * deaths)
print('play bevaiour:' + str(player_behaviour))
the number of kills is 10
the number of assists is 2
the number of deaths is 5
play bevaiour:14.85
4