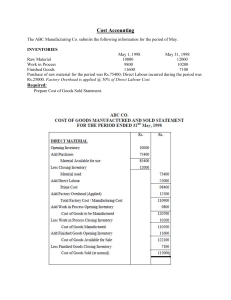
Notes for BUSINESS & ENTREPRENEURSHIP EDUCATION Grade 8 UNIT 3: Production Definition of Production Production is the process of using resources to manufacture goods or provide services. These goods and services are used to satisfy the needs and wants of consumers. Entrepreneurs are also known as Producers and Service providers. Entrepreneurs take initiative and decisions to carry out production in their enterprises. Some examples of production are: Production of shirts in a factory, the manufacturing of Chocolate in a business, Doctors providing health care services and so on. What is a production process? The Production process refers to the steps involved in turning inputs into outputs. INPUTS refer to resources or factors of production. These inputs are used to produce outputs Examples of INPUTS are : Land, Labour, Capital and Enterprise EXAMPLES OF PRODUCTION PROCESSES: In the production of table, the Input is the wood, the process is the cutting, polishing and assembling of different parts and the output is the table Similarly, in the production of dholl puri, the input consists of the ingredients like flour, water, salt and dholl, the process consists of mixing the dough and filling it with the dholl and the output is the dholl puri The types of production process There are 2 types of production process, namely 1. Labour intensive and 2. Capital intensive LABOUR INTENSIVE PRODUCTION PROCESS It is when the business uses more labour (workers) than capital (machinery, tools and equipment) in the production process Labour intensive production process is mainly used by: firms which find labour more productive than capital Page 1 of 5 small firms which find labour cheaper and more easily available than capital and enterprises providing services. EXAMPLES OF BUSINESSES USING LABOUR INTENSIVE PRODUCTION PROCESS 1. Law services 2. Banking services 3. Restaurant CAPITAL INTENSIVE PRODUCTION PROCESS It is when the business uses more capital (machinery, tools and equipment) than labour (workers) in the production process Capital intensive production process is mainly used by firms which: have complex production processes which cannot be carried out effectively by labour produce on large scale and find capital cheaper and more productive than labour EXAMPLES OF BUSINESSES USING CAPITAL INTENSIVE PRODUCTION PROCESS are 1. Newspaper printing 2. Juice production 3. Production of electricity There are different scales of production; namely 1. Small scale production and 2. Large scale production Small scale production refers to production carried out by small enterprises. They require a small amount of capital and They usually adopt labour intensive methods of production Such production is only appropriate if the enterprise sells its output to a small number of consumers. Moreover, the product should satisfy the consumer’s requirements. EXAMPLES OF BUSINESSES THAT UNDERTAKES SMALL SCALE PRODUCTION ARE: Corner shop Wedding dress maker Fruit seller and so on LARGE SCALE PRODUCTION Large scale production refers to mass production within a large enterprise. Page 2 of 5 They require less amount of labour and Usually uses capital intensive methods of production EXAMPLES OF BUSINESSES UNDERTAKING LARGE SCALE PRODUCTION ARE: Soft drink manufacturer Clothing manufacturer Biscuits manufacturer and so on The different methods of production Some businesses produce one item at a time while others produce in groups or on a larger scale. There are 3 methods of production. The first method of production is JOB PRODUCTION Job production is when enterprises produce one unit at a time. The product is made according to the customer’s tastes and preferences. Examples of job production are: 1. Hairdresser 2. Wedding Dress maker 3. Customised Birthday Cakes The second method of production is BATCH PRODUCTION It is when enterprises manufacture products stage by stage in different batches. Examples of batch production are: 1. Production of bread 2. Production of tables 3. Production of socks and so on The third method of production is FLOW PRODUCTION Flow production is when firms continuously produce standardised output in large quantities. Examples of flow production are: 1. Production of cars 2. Production of drugs 3. Production of crisps Technology in the production process What is technology? Technology is the methods and tools used to facilitate a process Technology facilitates production as many enterprises now use machineries and equipments in their manufacturing process Page 3 of 5 BENEFITS OF TECHNOLOGY IN THE PRODUCTION PROCESS The use of technology in enterprises brings many advantages like: 1. Higher quantity of output and 2. Better quality output are produced Some examples of the USE OF TECHNOLOGY IN THE PRODUCTION PROCESS are explained below. Long ago hunters used sticks to hunt while nowadays guns are more popular for hunting. Similarly, teaching was carried out using blackboards and chalks as compared digital boards which are increasingly being used. The USE OF TECHNOLOGY IN THE PRODUCTION PROCESS Nowadays, technology has evolved significantly. For example, in production process, businesses now use a lot of: 1. CAD –meaning Computer Aided Design 2. CAM –that is Computer Aided Manufacturing and 3. 3D printing EXAMPLES OF TECHNOLOGY IN THE PRODUCTION PROCESS are: The Use of robots in manufacturing The Use of machineries for different agricultural jobs Digital classroom and others IMPORTANCE OF TECHNOLOGY IN THE PRODUCTION PROCESS Technology allows producers to: 1. Produce high quality output 2. Produce more output 3. Produce output faster and 4. Produce variety of products SUSTAINABLE PRODUCTION Sustainable production is the production of output using processes and technology that protects the environment. Sustainable production is used for the following reasons: 1. 2. 3. 4. Reduce/Avoid pollution and other environmental problems Minimise wastage of scarce resources Make efficient use of resources Conserve resources for future generations Page 4 of 5 EXAMPLES OF SUSTAINABLE PRODUCTION 1. Sorting out wastes 2. Using energy saving devices 3. Composting 4. Using recycled and eco-friendly materials instead of plastic products 5. Using solar energy BENEFITS OF SUSTAINABLE PRODUCTION TO ENTERPRISES What are the advantages of sustainable production to businesses? It Attracts environment conscious consumers thus increasing sales 2. Low costs by using cheaper renewable energies 3. Improve health and safety of workers and customers and 4. Get Access to government incentives like for example, cheaper loans and lower taxes BENEFITS OF SUSTAINABLE PRODUCTION TO SOCIETY 1. Scarce resources are preserved for future generations 2. Improves quality of life of people 3. More output can be produced to satisfy people’s wants 4. A solution for environmental problems like global warming EXAMPLES OF BUSINESSES WHO HAVE ADOPTED SUSTAINABLE PRODUCTION Nestle Coca cola Company limited Apple Page 5 of 5