Uploaded by
nielandrewmontevilla
Feedback Control Systems: Contactors & Circuit Breakers
advertisement

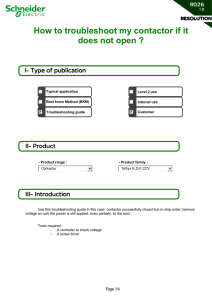
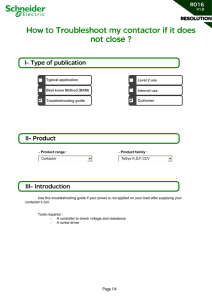
FEEDBACK CONTROL SYSTEM CANTOR, RANIEL REY P. BSEE4B 1. Show and Explain the internal parts of a contactor and its terminal designation. ❑ An electrical contactor is used in a wide range of situations where there is a need to switch power to a circuit repeatedly. Like relay switches, they are designed and built to perform this task over many thousands of cycles. ❑ An electrical contactor is used in a wide range of situations where there is a need to switch power to a circuit repeatedly. Like relay switches, they are designed and built to perform this task over many thousands of cycles. Contactor Wiring Diagram A common example of a contactor wiring diagram might look something like this. This example diagram would be for a three-pole contactor with one N.O. base contact. 1. Show and Explain the internal parts of a contactor and its terminal designation. What Do A1 and A2 Mean on a Contactor? A1 and A2 on a contactor typically refer to either end of the electromagnetic coil assembly. Most contactor manufacturers use A1 and A2 to designate the two terminals connecting electrical power to the contactor’s magnetic coil. What are 13 and 14 on a Contactor? 13 and 14 on a contactor also refer to common manufacturer designations. In this case, they are used to label the terminals on the normally open contacts in the device. A contactor is an electrical device that is widely used for switching circuits on and off. As such, electrical contactors form a subcategory of electromagnetic switches known as relays. 1. Show and Explain the internal parts of a contactor and its terminal designation. 1. Terminal bar - The terminal bar is a connection point at the input, output, or intermediate point of a device, or a point at which a voltage is to be applied. 2. Moving contact - Moving contact is the portion that moves physically under variable operating conditions. It moves after the energization or de-energization of the coil. 3. Fixed contact - Fixed contact is the stationary contact in a contactor. After the coil energization moving contacts touch the fixed contacts. 4. Operating coil - The coil is a long conductor or group of conductors wound into a tight helical package, often in several layers on a cylindrical form. 1. Show and Explain the internal parts of a contactor and its terminal designation. 5. Armature The armature connects the switching part to the mechanical action of the electromagnetic part. 6. Core The core is the body or form on which a coil is wound. It can be made of ferromagnetic or dielectric material. The properties depend on the application. 7. Coil terminals Coil terminals are the connection points that connect the energy to the magnetic coil. Many contactor manufacturers use the designations A1 and A2 for coil terminals. 8. Arc chute An Arc chute is a set of metal plates that are arranged in parallel and mutually insulated from each other, which can safely extinguish an electric arc inside the contactor. 9. Shading coil The shading coil is a coil used in a contactor to prevent chatter. 2. What is Modular Contactor Modular contactors are a group of devices - actuators, which allow for economical and safe control of the current flow in electrical installations. They are used, among others, in control systems for heating, lighting, ventilation and electric motor power supply systems. A modular contactor is a type of mechanical connector that is mounted on a rail in control cabinets. The design of the contactor consists of working contacts one or more pairs, a coil and an electromagnet. 3. What is the difference between DC and AC magnetic contactor • • DC and AC contactors operate on different principles. DC contactors use a magnetic field generated by the coil to move the contacts, while AC contactors rely on the magnetic field created by the alternating current to move the contacts. The structure of DC contactors and AC contactors is quite different. DC contactors typically have fewer poles and require a magnetic coil to operate the contacts, while AC contactors have more poles and operate through the magnetic field generated by the AC voltage. AC DC Basic Contactor Construction A contactor has three primary components: 1. The contacts are the current carrying part of the contactor. This includes power contacts, auxiliary contacts, and contact springs. 2. The electromagnet (or “coil”) provides the driving force to close the contacts. 3. The enclosure is a frame housing the contact and the electromagnet. Enclosures are made of insulating materials like Bakelite, Nylon 6, and thermosetting plastics to protect and insulate the contacts and to provide some measure of protection against personnel touching the contacts. Open-frame contactors may have a further enclosure to protect against dust, oil, explosion hazards and weather. Contactor Operation and Symbol Basically, a magnetic contactor works on the same principle as a relay, connecting and disconnecting electricity. The actuators are similar, this device uses a coil, which when an electrified coil creates a magnetic field. This magnetic field can control the contacts that exist in magnetic contactors. 4. Submit the terminal allocation for ac magnetic contactor 13 and 14 are the terminals of the normally open auxiliary contacts. The terminals of the normally closed auxiliary contact are 21 and 22. A1 and A2 are the coil terminals of the contactor. A1 is the positive electrode and A2 is the negative electrode. What caused the contactor to fail or jam? • Overcurrent flows through the contacts. • Apply low or high voltage to the coil. • Dust, corrosion or vibration in the environment. • Wrong product selection. • Shortcircuits are caused by the electromotive force. • Transients and voltage fluctuations. • Ambient temperature. 5. What is earth leakage current Earth leakage current is not specifically defined in BS 7671:2018+A1:2020, it is referred to as protective conductor current. Protective conductor current is defined as an ‘electric current appearing in a protective conductor, such as leakage current or electric current resulting from an insulation fault.’ Leakage current is also defined as ‘electric current in an unwanted conductive path under normal operating conditions.’ Earth leakage current can exist through an insulation fault in cables or equipment, or it can occur under normal operating conditions in electronic equipment which use capacitors for filtering purposes in power supplies which can cause leakage to Earth when functioning. 5. What is earth leakage current Leakage Current is the residual flow of current through insulation after a high voltage has been applied for a period of time. Earth Leakage Current is the leakage current from all earthed parts of the product. The current flowing from the mains supply through or across insulation into the Protective Earth Conductor. 6. What is the difference between Miniature circuit breaker ( MCB) and Residual circuit breaker with over current ( RCBO) MCB stands for Miniature Circuit Breaker and RCBO stands for Residual Current Breaker with Overcurrent. MCB is used to protect against overload and short-circuit. But, RCBO is used to protect against earth leakage fault current with over-current also. Many do not know the exact meaning of earth leakage fault; let us understand it first. In a normal circuit, line and neutral currents will always be equal and balanced. But, whenever there is an earth leakage, as the leakage current flows through the earth, there will be an imbalance in both these currents as the line current will be higher than the neutral current. This difference in current is called residual current. 6. What is the difference between Miniature circuit breaker ( MCB) and Residual circuit breaker with over current ( RCBO) The major difference that separates both circuit breakers is that RCBO has the additional protection of earth leakage current. Basically, it majorly uses microcontrollers and it can also be said as a combination of MCB and RCCB. That is why; it is more useful than MCB; because MCB does not provide protection against the earth-leakage current. MCB is selected based on the load, maximum short-circuit current it can interrupt, and trip curve. RCBO too is selected on the basis of these three things; but apart from that, it also considers maximum leakage current. 6. What is the difference between Miniature circuit breaker ( MCB) and Residual circuit breaker with over current ( RCBO) Cost-wise, RCBO is costlier than MCB. MCB is used to protect lighting circuits, air conditioners, and other home appliances; but RCBO is used mainly to interrupt power to water heaters, power sockets, etc. where there is the possibility of electric shocks to humans. MCB does not provide protection against electric shocks to humans, but RCBO provides protection against electric shocks. This is because the role of RCBO is primarily to detect earth leakage and trip the circuit when detected. Earth leakage is dangerous for the human body. Typically, the human body can withstand a shock of 30mA. After this, it can lead to paralysis or even death for weaker human hearts. And, earth leakage current typically starts from 10mA and can go beyond 30mA. 6. What is the difference between Miniature circuit breaker ( MCB) and Residual circuit breaker with over current ( RCBO) The breaking capacity of RCBO is much higher than MCB (typically up to 10kA). Some RCBO’s also have indicators on them to show any earth fault trip. This feature is very helpful as it quickly aides the engineer in troubleshooting faults. Such a feature is not available in MCB’s. W i r i n g C o n n e c t i o n f M o o r t o 1 r W i r i n g C o n n e c t i o n f M o o r t o 1 r W i r i n g C o n n e c t i o n f M o o r t o 2 r W i r i n g C o n n e c t i o n f M o o r t o 2 r THANK YOU End of Presentation