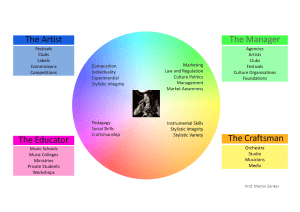
PLAN about the writer name, origin, his style about the title about the functional style (language, tone) mistic, ironic, romantic, humorous delicate humorous touch high-flown lofty language highly emotional tone wordplay unexpected ending about the genre of the story (novel) social, psychological, historical, detective, science fiction, documentary about the composition of the text types of narration (1st/3rd person) about the development of the plot the exposition, the setting, the climax and the denouement the theme about the personages’ characteristics main — secondary round (with changes) — flat (no learned lessons) about the stylistic devices Simile - a figure of speech comparing two unlike things, often introduced with the words "like", "as", or "than" (Same age, same background, but dumb as an ox) Hyperbole - is a figure of speech in which statements are exaggerated (I had taught her to think) Metaphor - a trope /or stylistic device/ in which a word or phrase is applied to an object or action to which it is not literally applicable but seems similar. For example, if you want to say that someone is very shy and frightened of things, you might say “you are a mouse” (I went back to my room with a heavy heart) Antithesis - a rhetorical or literary device in which an opposition or contrast of ideas is expressed (A nice enough fellow, you understand, but nothing upstairs) Irony - A stylistic device in which the word is used in the opposite meaning in the context. /”You are so brave” addressing it to a coward/ Parallelism - the use of successive verbal constructions in poetry or prose that correspond in grammatical structure, sound, meter, meaning, etc (Beautiful she was. Gracious she was. Intelligent she was not). Inversion - reversal of the usual or natural order words, used typically for rhetorical effect (Cool was I and logical).