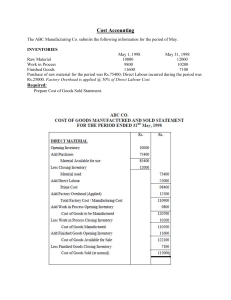
Self-Introduction e Name :- Shubham Yadav Topic :- Child Labour Class :- FYBMS Roll No :- 55 . . . . SOCIAL ISSUE :CHILD LABOUR We all Are Against Child Labour TABLE OF CONTENTS 01 Introduction Here you can describe the topic of the section 02 03 Statistic Here you can describe the topic of the section 04 Cause & Effect Preventation Here you can describe the topic of the section Here you can describe the topic of the section 01 INTRODUCTION . INTRODUCTION The term “child labour” is often defined as work that deprives children of their childhood, their potential and their dignity, and that is harmful to physical and mental development. It refers to work that: is mentally, physically, socially or morally dangerous and harmful to children WORK IN WHICH CHILDREN ARE MOST OFTEN INVOLVED Agriculture Services Industrial Agricultural field mostly in rural area Services in Shop & Resturants Most Comman child working in factories 02 Causes And Effect . Root Cause of child Labour ● Poverty ‘Poverty is certainly the greatest single force driving children into the workplace.’ When families cannot afford to meet their basic needs like food, water, education or health care, they have no choice but to send their children to work to supplement the household income. Poverty is considered as one of the most important causes of child labour as it is linked to other driving factors including: low literarcy and numeracy rates, lack of decent work opportunities, natural disasters and climate change, conflicts and mass displacement. Poverty and child labour form a vicious cycle, without tackling one, we cannot eradicate the other. ● Lack of access to quality Education The availability and quality of schooling is among the most important factors.’ School needs to be a welcoming environment, with appropriate class sizes, a curriculum designed for the local context, and affordable for rural communities. Getting children into school and out of harmful work is one thing but keeping them there a means creating quality education accessible for all. ● Poor access to decent work ‘Children who were involved in child labour often lack the basic educational grounding which would enable them to acquire skills and to improve their prospects for a decent adult working life.’ If young people cannot access work which is safe, with social protection, fair pay, equality for men and women and which provides a space for workers to express their opinions, they often have no choice but to do work which is hazardous. When children above the minimum working age are doing hazardous work, this is also considered child labour. ● Limited understanding of child labour ‘The view that work is good for the character-building and skill development of children.’ When families do not understand the dangers of child labour, and how these impact on the health, safety, well-being and future of their child, they are more likely to send their children to work. Some cultural beliefs and social norms can also be drivers of child labour. ● Natural Disaster & Climate Change ‘In rural areas, farmers who see their crops destroyed on account of climate changes have no other choice but to send their children out to work.’ ● Conflict Of Mass Migration ‘There is a strong correlation between child labour and situations of conflict and disaster’ According to the ILO children make up more than half of the total number of people displaced by war. These children are particularly vulnerable to forms of exploitation, including child labour, due to an increase in economic shocks, a breakdown of social support, education and basic services, and disruption of child protection services. The incidence of child labour in countries affected by conflict is almost twice as high as the global average. Children are also vulnerable to becoming involved in armed conflict, this is considered one of the Worst Forms of Child Labour. ● Fighting Child Labour SDG Goal 8.7 calls for the elimination of all forms of child labour by 2025. With 152 million children involved in child labour worldwide, we still have a long way to go. Programmes and policies which take into account the voices of the communities where child labour occurs, and the root causes, can advance real and sustainable progress in the fight against child labour. 03 STATISTIC . PREVALENCE OF CHILD LABOUR 72 M Africa 62 M South Asia mostly China & India 11 M Canada And Latin America CHILD LABOUR STATISTICS Paid work Unpaid work 55% 45% This is the Percentage child who are paid worker This is the percentage of child who are unpaid worker CHILD LABOUR STATISTICS Middle-income Countries This is is the statistics of the countries which having mid level of GDP Low-income Countries This is the statistics of the countries which having low level of GDP From this following graph we get to know that the lesser the country income the more is child labour GLOBAL ESTIMATES RESULTS AT A GLANCE Age range Employed children In child labour Hazardous work 5-14 144 066 120 453 37 841 15-17 120 362 47 503 47 503 Male 148 327 99 766 55 048 Female 116 100 68 190 30 296 Sex AGE STATISTICS 5-14 years old 15-17 years old Girls Boys This graph shows us a fact that during the age of 5-14 there is more involment of boys and after the age of 15 girl involment in child labour increases Jupiter is the biggest planet GENDER STATISTICS 37% Mercury is the smallest planet 63% Jupiter is the biggest planet 04 PREVENTATION . ● Spread Awareness If parents and communities are aware and alert, disruption in children’s education can be prevented and many of them will not get pushed into child labour. Lack of understanding on the part of parents creates situations where traffickers prey upon children and many trafficked children end up in child labour. Aware communities can comprehend and respond to children’s issues much more effectively Awareness also ensures that communities tap growth, education, employment, and enterprise opportunities and create a socially and economically developed society in which children suffer much less. NGOs like Save the Children use community events, sports, arts and theatre to educate communities about the importance of child rights in India. We also create income resources, educational resources, and help communities access information services – all with an aim to help children and their communities march ahead ● More stringent laws and effective implementation Policymaking is essential to bring in long-lasting social change, and advocating for better laws involves demonstrating how change can bring considerable benefit. NGOs conduct research and showcase findings regarding exploited children, and use case studies to establish how their work benefits children. Driving policy-level change requires relationships with several stakeholders – media, lawmakers, citizens, fellow civil society members and others. Many cases have been filed ● Sending More Child to school India has the world’s largest educational system, yet faces the hurdles of low literacy, due to low enrolment and lack of education infrastructure. Organisations like Save the Children execute several initiatives to boost children’s enrolment in schools. The organisation maps out-of-school children and those who are at risk of dropping out and ensures that they enter into the fold of education. ● Discouraging people to employ children in homes, shops, factories, etc Policymaking is essential to bring in long-lasting social change, and advocating for better laws involves demonstrating how change can bring considerable benefit. NGOs conduct research and showcase findings regarding exploited children, and use case studies to establish how their work benefits children. Driving policy-level change requires relationships with several stakeholders – media, lawmakers, citizens, fellow civil society members and others. Many cases have been filed under the recent Protection of Children Against Sexual Offences Act (2012) and I ● Sending More Child to school Save the Children also offers immediate aid to children involved in child labour, while also working for long-term societal change through policy change. The NGO works to ensure that existing policies are followed through with action. The NGO works with state and national level authorities, including Police departments of states to prevent child exploitation incidents.. “A child is meant to learn and not to earn.” —SOMEONE . THANKS CREDITS: This presentation template was created by Slidesgo, including icons by Flaticon, and infographics & images by Freepik. .