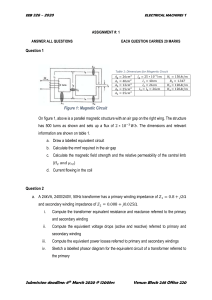
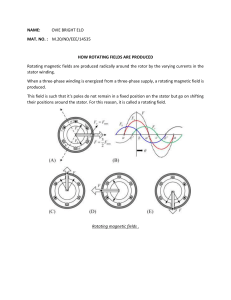
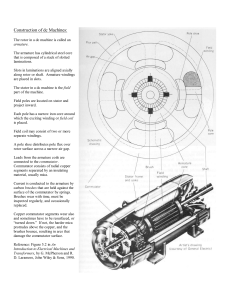
JAN LENARD CALLEJA BETMT-S-T-2A-T FUNCTION OF PARTS: DC Machine Field Core: is serves an essential function in generating and maintaining the magnetic field within the machine. Field Winding: is serves the primary function of generating the magnetic field that interacts with the armature winding to facilitate the conversion of electrical energy to mechanical energy or vice versa. Armature Core: the armature core in a DC machine provides mechanical support, completes the magnetic circuit, guides the magnetic field, reduces eddy current losses, and facilitates thermal dissipation. Armature Winding: The armature winding in a DC machine, whether it's a DC motor or generator, plays a vital role in the conversion of electrical energy to mechanical energy (in the case of a motor) or vice versa (in the case of a generator). Shaft: the shaft in a DC machine provides mechanical support, facilitates power transmission, connects to the rotor, enables speed regulation, and assists in cooling and heat dissipation. Bearing: The bearings in a DC machine, whether it's a DC motor or generator, serve essential functions related to the support, alignment, and smooth rotation of the machine's components. Field Rheostat: serves the primary function of controlling the field current and, consequently, the strength of the magnetic field produced by the field winding. Frame: the frame in a DC machine provides structural support, enclosure, and protection for internal components, completes the magnetic circuit, aids in heat dissipation, facilitates mounting and installation, and offers grounding capabilities. Commutator: the commutator in a DC machine facilitates current reversal, segmentation of the armature winding, commutation of the armature current, maintenance of torque production, and provides electrical connections between the rotating armature and the external circuit. Collector Brusher: the brushes in a DC machine provide electrical contact, facilitate current transfer, assist in commutation, contribute to cooling, and require periodic replacement due to wear. AC Machine Frame: The frame in a synchronous machine, whether it's a synchronous generator or synchronous motor, serves several important functions. Shaft: The shaft in a synchronous machine provides mechanical support, rotational stability, and a connection between the machine and the load or coupling system. Bearing: Bearings in a synchronous machine provide support, alignment, load distribution, reduced friction, stability, noise and vibration reduction, lubrication, cooling, and ease of maintenance. Slip Rings: Slip rings are more commonly found in other types of rotating electrical machines where they serve specific functions related to the rotor winding and electrical connections. Collector Brush: maintain electrical contact with the slip rings to allow electricity to flow from the rotor winding to the outside environment. Rotor Core: the rotor core in a synchronous machine provides a path for the magnetic flux, amplifies the magnetic field, offers mechanical support, facilitates heat dissipation, reduces eddy current losses, and provides electrical isolation in certain designs. Field Rheostat: the field rheostat in a synchronous machine provides control over the field excitation current, allowing for precise adjustment of the magnetic field strength. It plays a vital role in voltage regulation, power factor control, efficiency optimization, synchronization, and grid stability. Rotor Winding: the rotor winding in a synchronous machine is responsible for generating the magnetic field that interacts with the stator winding, enabling voltage generation or torque production. It facilitates synchronization, excitation control, cooling, mechanical support, electrical insulation, and serviceability. Stator Core: stator core is essential for the efficient and reliable operation of synchronous machines in various applications. Stator Winding: the stator winding in a synchronous machine plays a crucial role in voltage generation, magnetic field production, synchronization, voltage regulation, cooling, mechanical support, and electrical insulation. Commutator: The commutator assures that the generator's current always flows in a single direction.