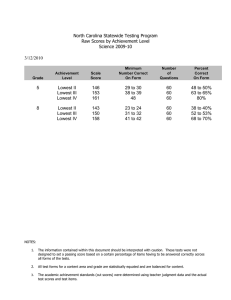
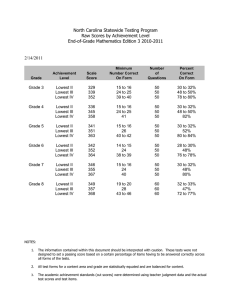
Psychological Assessment #BLEPP Source: Cohen & Swerdlik (2018), Kaplan & Saccuzzo (2018), Groth & Wright (2016), Psych Pearls - Ecological Momentary: “in the moment” evaluation of specific problems and related cognitive and Hellow, future RPm! behavioral variables at the very time and place that they occur Doubt is definitely going to eat you this review season. I - Collaborative: the assessor and assesee may work as just want you to know that it is very VALID to feel that “partners” from initial contact through final feedback way. But always remember to go back to the reason why - Therapeutic: therapeutic self-discovery and new you are doing this. understanding are encouraged - Dynamic: describe interactive approach to May this reviewer help you pass the boards like it did to psychological assessment that usually follows the me and to many people that I know <3 model: evaluation > intervention of some sort > evaluation o Psychological Test – device or procedure designed We will be remembered to measure variables related to psychology ▪ Content: subject matter Psychometric Properties and Principles (39) ▪ Format: form, plan, structure, arrangement, Psychometric Properties essential in Constructing, layout Selecting, Interpreting tests ▪ Item: a specific stimulus to which a person Psychological Testing - process of measuring responds overtly and this response is being psychology-related variables by means of devices or scored or evaluated procedures designed to obtain a sample of behavior ▪ Administration Procedures: one-to-one basis or - numerical in nature group administration - individual or by group ▪ Score: code or summary of statement, usually - administrators can be interchangeable without but not necessarily numerical in nature, but affecting the evaluation reflects an evaluation of performance on a test - requires technician-like skills in terms of ▪ Scoring: the process of assigning scores to administration and scoring performances - yield a test score or series of test score ▪ Cut-Score: reference point derived by judgement - minutes to few hours and used to divide a set of data into two or more Psychological Assessment - gathering and integration classification of psychology-related data for the purpose of making ▪ Psychometric Soundness: technical quality psychological evaluation ▪ Psychometrics: science of psychological - answers referral question thru the use of different measurement tools of evaluation ▪ Psychometrist or Psychometrician: refer to - individual professional who uses, analyzes, and interprets - assessor is the key to the process of selecting tests psychological data and/or other tools of evaluation - requires an educated selection of tools of evaluation, skill in evaluation, and thoughtful organization and integration of data - entails logical problem-solving that brings to bear many sources of data assigned to answer the referral question - Educational: evaluate abilities and skills relevant in school context - Retrospective: draw conclusions about psychological aspects of a person as they existed at some point in time prior to the assessment - Remote: subject is not in physical proximity to the person conducting the evaluation The reviewers I made are FREE :D instead of selling it, you can share the drive link to others :D Let’s help each other <3 See u soon, future RPms! - Aly Psychological Assessment #BLEPP Source: Cohen & Swerdlik (2018), Kaplan & Saccuzzo (2018), Groth & Wright (2016), Psych Pearls Ability or Maximal Performance Test – assess what Non-standardized/Unstructured – pursue relevant a person can do ideas in depth 1. Achievement Test – measurement of the previous Semi-Standardized/Focused – may probe further on learning specific number of questions - used to measure general knowledge in a specific Non-Directive – subject is allowed to express his period of time feelings without fear of disapproval - used to assess mastery ▪ Mental Status Examination: determines the - rely mostly on content validity mental status of the patient - fact-based or conceptual ▪ Intake Interview: determine why the client came 2. Aptitude – refers to the potential for learning or for assessment; chance to inform the client about acquiring a specific skill the policies, fees, and process involved - tends to focus on informal learning ▪ Social Case: biographical sketch of the client - rely mostly on predictive validity ▪ Employment Interview: determine whether the 3. Intelligence – refers to a person’s general potential candidate is suitable for hiring to solve problems, adapt to changing environments, ▪ Panel Interview (Board Interview): more than abstract thinking, and profit from experience one interviewer participates in the assessment Human Ability – considerable overlap of ▪ Motivational Interview: used by counselors and achievement, aptitude, and intelligence test clinicians to gather information about some problematic behavior, while simultaneously Typical Performance Test – measure usual or habitual thoughts, feelings, and behavior attempting to address it therapeutically - indicate how test takers think and act on a daily basis o Portfolio – samples of one’s ability and - use interval scales accomplishment - no right and wrong answers o Case History Data – refers to records, transcripts, and other accounts in written, pictorial, or other form Personality Test – measures individual dispositions that preserve archival information, official and and preferences informal accounts, and other data and items relevant - designed to identify characteristic to an assessee - measured ideographically or nomothetically ▪ Case study: a report or illustrative account 1. Structured Personality tests – provide statement, concerning a person or an event that was usually self-report, and require the subject to choose compiled on the basis of case history data between two or more alternative responses ▪ Groupthink: result of the varied forces that drive 2. Projective Personality Tests – unstructured, and the decision-makers to reach a consensus stimulus or response are ambiguous o Behavioral Observation – monitoring of actions of 3. Attitude Test – elicit personal beliefs and opinions others or oneself by visual or electronic means while 4. Interest Inventories – measures likes and dislikes recording quantitative and/or qualitative information as well as one’s personality orientation towards the regarding those actions world of work ▪ Naturalistic Observation: observe humans in Other Tests: natural setting 1. Speed Tests – the interest is the number of times a ▪ SORC Model: Stimulus, Organismic Valuables, test taker can answer correctly in a specific period Actual Response, Consequence 2. Power Tests – reflects the level of difficulty of items o Role Play – defined as acting an improvised or the test takers answer correctly partially improvised part in a stimulated situation 3. Values Inventory ▪ Role Play Test: assesses are directed to act as if 4. Trade Test they are in a particular situation 5. Neuropsychological Test o Other tools include computer, physiological devices 6. Norm-Referenced test (biofeedback devices) 7. Criterion-Referenced Tests Psychological Assessment Process o Interview – method of gathering information 1. Determining the Referral Question through direct communication involving reciprocal exchange 2. Acquiring Knowledge relating to the content of the problem Standardized/Structured – questions are prepared The reviewers I made are FREE :D instead of selling it, you can share the drive link to others :D Let’s help each other <3 See u soon, future RPms! - Aly Psychological Assessment #BLEPP Source: Cohen & Swerdlik (2018), Kaplan & Saccuzzo (2018), Groth & Wright (2016), Psych Pearls 3. Data collection 6. Test Sponsors – institutions or government who contract test developers for various testing services 4. Data Interpretation 7. Society o Hit Rate – accurately predicts success or failure o Profile – narrative description, graph, table. Or other o Test Battery – selection of tests and assessment representations of the extent to which a person has procedures typically composed of tests designed to demonstrated certain targeted characteristics as a measure different variables but having a common result of the administration or application of tools of objective assessment Assumptions about Psychological Testing and o Actuarial Assessment – an approach to evaluation Assessment characterized by the application of empirically Assumption 1: Psychological Traits and States Exist demonstrated statistical rules as determining factor o Trait – any distinguishable, relatively enduring in assessors’ judgement and actions way in which one individual varies from another o Mechanical Prediction – application of computer - Permit people predict the present from the past algorithms together with statistical rules and - Characteristic patterns of thinking, feeling, and probabilities to generate findings and behaving that generalize across similar situations, recommendations differ systematically between individuals, and remain Levels of Interpretation rather stable across time Level I – there is a minimal amount of any sort of - Psychological Trait – intelligence, specific interpretation intellectual abilities, cognitive style, adjustment, - minimal concern with intervening processes interests, attitudes, sexual orientation and preferences, - data are primarily treated in a sampling or correlate psychopathology, etc. way o States – distinguish one person from another but - no concern with underlying constructs are relatively less enduring - found in large-scale selection testing - Characteristic pattern of thinking, feeling, and - for psychometric approaches behaving in a concrete situation at a specific moment in time Level II - Identify those behaviors that can be controlled by a. Descriptive Generalizations manipulating the situation b. Hypothetical Construct: the assumption of an inner o Psychological Traits exists as construct state which goes logically beyond the description of - Construct: an informed, scientific concept developed visible behavior or constructed to explain a behavior, inferred from Level III – the effort to develop a coherent and overt behavior inclusive theory of the individual life or a “working - Overt Behavior: an observable action or the product image” of the patient of an observable action - the clinician attempts full scale exploration of the o Trait is not expected to be manifested in behavior individual’s personality, psychosocial situation, and 100% of the time developmental history o Whether a trait manifests itself in observable o Extra-Test Behavior – observations made by an behavior, and to what degree it manifests, is examiner regarding what the examinee does and how presumed to depend not only on the strength of the the examinee reacts during the course of testing that trait in the individual but also on the nature of the are indirectly related to the test’s specific content but action (situation-dependent) of possible significance to interpretation o Context within which behavior occurs also plays a Parties in Psychological Assessment role in helping us select appropriate trait terms for 1. Test Author/Developer – creates the tests or other observed behaviors methods of assessment o Definition of trait and state also refer to a way in 2. Test Publishers – they publish, market, sell, and which one individual varies from another control the distribution of tests o Assessors may make comparisons among people 3. Test Reviewers – prepare evaluative critiques based who, because of their membership in some group on the technical and practical aspects of the tests or for any number of other reasons, are decidedly 4. Test Users – uses the test of assessment not average 5. Test Takers – those who take the tests The reviewers I made are FREE :D instead of selling it, you can share the drive link to others :D Let’s help each other <3 See u soon, future RPms! - Aly Psychological Assessment #BLEPP Source: Cohen & Swerdlik (2018), Kaplan & Saccuzzo (2018), Groth & Wright (2016), Psych Pearls Assumption 2: Psychological Traits and States can o Despite best efforts of many professionals, be Quantified and Measured fairness-related questions and problems do o Once the trait, state or other construct has been occasionally rise defined to be measured, a test developer consider In al questions about tests with regards to fairness, it is the types of item content that would provide important to keep in mind that tests are tools ꟷthey can insight to it, to gauge the strength of that trait be used properly or improperly o Measuring traits and states means of a test entails Assumption 7: Testing and Assessment Benefit developing not only appropriate tests items but Society also appropriate ways to score the test and o Considering the many critical decisions that are interpret the results based on testing and assessment procedures, we o Cumulative Scoring – assumption that the more can readily appreciate the need for tests the testtaker responds in a particular direction Reliability keyed by the test manual as correct or consistent o Reliability – dependability or consistency of the with a particular trait, the higher that testtaker is instrument or scores obtained by the same person presumed to be on the targeted ability or trait when re-examined with the same test on different Assumption 3: Test-Rlated Behavior Predicts Nonoccasions, or with different sets of equivalent items Test-Related Behavior ▪ Test may be reliable in one context, but o The tasks in some tests mimics the actual unreliable in another behaviors that the test user is attempting to ▪ Estimate the range of possible random understand fluctuations that can be expected in an o Such tests only yield a sample of the behavior that individual’s score can be expected to be emitted under nontest ▪ Free from errors conditions ▪ More number of items = higher reliability Assumption 4: Test and Other Measurement ▪ Minimizing error Techniques have strengths and weaknesses ▪ Using only representative sample to obtain an o Competent test users understand and appreciate observed score the limitations of the test they use as well as how ▪ True score cannot be found those limitations might be compensated for by ▪ Reliability Coefficient: index of reliability, a data from other sources proportion that indicates the ratio between the true score variance on a test and the total Assumption 5: Various Sources of Error are part of variance the Assessment Process o Classical Test Theory (True Score Theory) – score o Error – refers to something that is more than on an ability tests is presumed to reflect not only the expected; it is component of the measurement testtaker’s true score on the ability being measured process but also the error ▪ Refers to a long-standing assumption that ▪ Error: refers to the component of the observed factors other than what a test attempts to test score that does not have to do with the measure will influence performance on the test testtaker’s ability ▪ Error Variance – the component of a test ▪ Errors of measurement are random score attributable to sources other than the trait or ability measured o Potential Sources of error variance: 1. Assessors 2. Measuring Instruments 3. Random errors such as luck o Classical Test Theory – each testtaker has true score on a test that would be obtained but for the action of measurement error Assumption 6: Testing and Assessment can be conducted in a Fair and Unbiased Manner The reviewers I made are FREE :D instead of selling it, you can share the drive link to others :D Let’s help each other <3 See u soon, future RPms! - Aly Psychological Assessment #BLEPP Source: Cohen & Swerdlik (2018), Kaplan & Saccuzzo (2018), Groth & Wright (2016), Psych Pearls When you average all the observed scores ▪ The greater the proportion of the total variance obtained over a period of time, then the result attributed to true variance, the more reliable the would be closest to the true score test ▪ The greater number of items, the higher the ▪ Error variance may increase or decrease a test reliability score by varying amounts, consistency of test ▪ Factors the contribute to consistency: stable score, and thus, the reliability can be affected attributes ▪ Factors that contribute to inconsistency: characteristics of the individual, test, or situation, which have nothing to do with the attribute being measured, but still affect the scores o Goals of Reliability: ✓ Estimate errors ✓ Devise techniques to improve testing and reduce errors o Variance – useful in describing sources of test score variability ▪ True Variance: variance from true differences Test-Retest Reliability ▪ Error Variance: variance from irrelevant random Error: Time Sampling sources - time sampling reliability Measurement Error – all of the factors associated - an estimate of reliability obtained by correlating with the process of measuring some variable, other pairs of scores from the same people on two different than the variable being measured administrations of the test - difference between the observed score and the true - appropriate when evaluating the reliability of a test score that purports to measure an enduring and stable - Positive: can increase one’s score attribute such as personality trait - Negative: decrease one’s score - established by comparing the scores obtained from - Sources of Error Variance: two successive measurements of the same individuals a. Item Sampling/Content Sampling: refer to variation and calculating a correlated between the two set of among items within a test as well as to variation scores among items between tests - the longer the time passes, the greater likelihood that - The extent to which testtaker’s score is affected by the reliability coefficient would be insignificant the content sampled on a test and by the way the - Carryover Effects: happened when the test-retest content is sampled is a source of error variance interval is short, wherein the second test is influenced b. Test Administration: testtaker’s motivation or by the first test because they remember or practiced attention, environment, etc. the previous test = inflated correlation/overestimation c. Test Scoring and Interpretation: may employ of reliability objective-type items amenable to computer scoring of - Practice Effect: scores on the second session are well-documented reliability higher due to their experience of the first session of Random Error – source of error in measuring a testing targeted variable caused by unpredictable fluctuations - Test Sophistication: items are remembered by the and inconsistencies of other variables in measurement test takers especially the difficult ones/items that we process (e.g., noise, temperature, weather) got highlight confused Systematic Error – source of error in a measuring a - Test Wiseness: might inflate the abilities of test variable that is typically constant or proportionate to takers what is presumed to be the true values of the variable - test-retest with longer interval might be affected of being measured other extreme factors, thus, resulting to low - has consistent effect on the true score correlation - SD does not change, the mean does - lower correlation = poor reliability ▪ Reliability refers to the proportion of total variance attributed to true variance The reviewers I made are FREE :D instead of selling it, you can share the drive link to others :D Let’s help each other <3 See u soon, future RPms! - Aly ▪ Psychological Assessment #BLEPP Source: Cohen & Swerdlik (2018), Kaplan & Saccuzzo (2018), Groth & Wright (2016), Psych Pearls - Mortality: problems in absences in second session single trait (unifactorial) (just remove the first tests of the absents) - Heterogeneity: degree to which a test measures different factors (more than one factor/trait) - intelligence, motor test, traits, reaction time (stable - more homogenous = higher inter-item consistency traits) - KR-20: used for inter-item consistency of - Coefficient of Stability dichotomous items (intelligence tests, personality tests - statistical tool: Pearson R, Spearman Rho with yes or no options, multiple choice), unequal Parallel Forms/Alternate Forms Reliability variances, dichotomous scored Error: Item Sampling (Immediate), Item Sampling - KR-21: if all the items have the same degree of changes over time (delayed) difficulty (speed tests), equal variances, dichotomous - established when at least two different versions of scored the test yield almost the same scores - Cronbach’s Coefficient Alpha: used when two - has the most universal applicability halves of the test have unequal variances and on tests - Parallel Forms: each form of the test, the means, containing non-dichotomous items, unequal variances and the error variances, are EQUAL; same items, - Average Proportional Distance: measure used to different positionings/numberings evaluate internal consistencies of a test that focuses on - true score must be the same for two test the degree of differences that exists between item - Alternate Forms: simply different version of a test scores that has been constructed so as to be parallel Split-Half Reliability - test should contain the same number of items and the Error: Item sample: Nature of Split items should be expressed in the same form and - Split Half Reliability: obtained by correlating two should cover the same type of content; range and pairs of scores obtained from equivalent halves of a difficulty must also be equal single test administered ONCE - if there is a test leakage, use the form that is not - useful when it is impractical or undesirable to assess mostly administered reliability with two tests or to administer a test twice - Counterbalancing: technique to avoid carryover - cannot just divide the items in the middle because it effects for parallel forms, by using different sequence might spuriously raise or lower the reliability for groups (e.g., G1 – listen to song before counseling, coefficient, so just randomly assign items or assign G2 – counseling first, before listening to the song) odd-numbered items to one half and even-numbered - can be administered on the same day or different items to the other half time - Spearman-Brown Formula: allows a test developer - most rigorous and burdensome, since test developers of user to estimate internal consistency reliability create two forms of the test from a correlation of two halves of a test, if each half - main problem: difference between the two test had been the length of the whole test and have the - test scores may be affected by motivation, fatigue, or equal variances intervening events - Spearman-Brown Prophecy Formula: estimates how - means and the variances of the observed scores must many more items are needed in order to achieve the be equal for two forms target reliability - Statistical Tool: Pearson R or Spearman Rho - multiply the estimate to the original number of items Internal Consistency (Inter-Item Reliability) - Rulon’s Formula: counterpart of spearman-brown Error: Item Sampling Homogeneity formula, which is the ratio of the variance of - used when tests are administered once difference between the odd and even splits and the - consistency among items within the test variance of the total, combined odd-even, score - measures the internal consistency of the test which is - if the reliability of the original test is relatively low, the degree to which each item measures the same then developer could create new items, clarify test construct instructions, or simplifying the scoring rules - measurement for unstable traits - equal variances, dichotomous scored - if all items measure the same construct, then it has a - Statistical Tool: Pearson R or Spearman Rho good internal consistency Inter-Scorer Reliability - useful in assessing Homogeneity - Homogeneity: if a test contains items that measure a The reviewers I made are FREE :D instead of selling it, you can share the drive link to others :D Let’s help each other <3 See u soon, future RPms! - Aly Psychological Assessment #BLEPP Source: Cohen & Swerdlik (2018), Kaplan & Saccuzzo (2018), Groth & Wright (2016), Psych Pearls o Domain Sampling Theory – estimate the extent to Error: Scorer Differences which specific sources of variation under defined - the degree of agreement or consistency between two conditions are contributing to the test scores or more scorers with regard to a particular measure’ ▪ Considers problem created by using a limited - evaluated by calculating the percentage of times that number of items to represent a larger and more two individuals assign the same scores to the complicated construct performance of the examinees ▪ Test reliability is conceived of as an objective - a variation is to have two different examiners test the measure of how precisely the test score assesses same client using the same test and then to determine the domain from which the test draws a sample how close their scores or ratings of the person are ▪ Generalizability Theory: based on the idea that a - used for coding nonbehavioral behavior person’s test scores vary from testing to testing - observer differences because of the variables in the testing situations - Fleiss Kappa: determine the level between TWO or ▪ Universe: test situation MORE raters when the method of assessment is ▪ Facets: number of items in the test, amount of measured on CATEGORICAL SCALE review, and the purpose of test administration - Cohen’s Kappa: two raters only ▪ According to Generalizability Theory, given the - Krippendorff’s Alpha: two or more rater, based on exact same conditions of all the facets in the observed disagreement corrected for disagreement universe, the exact same test score should be expected by chance obtained (Universe score) o Tests designed to measure one factor (Homogenous) ▪ Decision Study: developers examine the are expected to have high degree of internal usefulness of test scores in helping the test user consistency and vice versa make decisions o Dynamic – trait, state, or ability presumed to be ever▪ Systematic Error changing as a function of situational and cognitive o Item Response Theory – the probability that a experience person with X ability will be able to perform at a o Static – barely changing or relatively unchanging level of Y in a test o Restriction of range or Restriction of variance – if ▪ Focus: item difficulty the variance of either variable in a correlational ▪ Latent-Trait Theory analysis is restricted by the sampling procedure used, ▪ a system of assumption about measurement and then the resulting correlation coefficient tends to be the extent to which item measures the trait lower ▪ The computer is used to focus on the range of o Power Tests – when time limit is long enough to item difficulty that helps assess an individual’s allow test takers to attempt all times ability level o Speed Tests – generally contains items of uniform ▪ If you got several easy items correct, the level of difficulty with time limit computer will them move to more difficult items ▪ Reliability should be based on performance from ▪ Difficulty: attribute of not being easily two independent testing periods using test-retest accomplished, solved, or comprehended and alternate-forms or split-half-reliability ▪ Discrimination: degree to which an item o Criterion-Referenced Tests – designed to provide differentiates among people with higher or lower an indication of where a testtaker stands with respect levels of the trait, ability etc. to some variable or criterion ▪ Dichotomous: can be answered with only one of ▪ As individual differences decrease, a traditional two alternative responses measure of reliability would also decrease, ▪ Polytomous: 3 or more alternative responses regardless of the stability of individual o Standard Error of Measurement – provide a performance measure of the precision of an observed test score o Classical Test Theory – everyone has a “true score” ▪ Standard deviation of errors as the basic measure on test of error ▪ True Score: genuinely reflects an individual’s ▪ Index of the amount of inconsistent or the amount ability level as measured by a particular test of the expected error in an individual’s score ▪ Random Error ▪ Allows to quantify the extent to which a test provide accurate scores The reviewers I made are FREE :D instead of selling it, you can share the drive link to others :D Let’s help each other <3 See u soon, future RPms! - Aly Psychological Assessment #BLEPP Source: Cohen & Swerdlik (2018), Kaplan & Saccuzzo (2018), Groth & Wright (2016), Psych Pearls Provides an estimate of the amount of error inherent in an observed score or measurement ▪ Higher reliability, lower SEM ▪ Used to estimate or infer the extent to which an observed score deviates from a true score ▪ Standard Error of a Score ▪ Confidence Interval: a range or band of test scores that is likely to contain true scores Standard Error of the Difference – can aid a test user in determining how large a difference should be before it is considered statistically significant Standard Error of Estimate – refers to the standard Validity error of the difference between the predicted and o Validity – a judgment or estimate of how well a test observed values measures what it supposed to measure Confidence Interval – a range of and of test score ▪ Evidence about the appropriateness of inferences that is likely to contain true score drawn from test scores ▪ Tells us the relative ability of the true score within ▪ Degree to which the measurement procedure the specified range and confidence level measures the variables to measure ▪ The larger the range, the higher the confidence ▪ Inferences – logical result or deduction If the reliability is low, you can increase the number ▪ May diminish as the culture or times change of items or use factor analysis and item analysis to ✓ Predicts future performance increase internal consistency ✓ Measures appropriate domain Reliability Estimates – nature of the test will often ✓ Measures appropriate characteristics determine the reliability metric o Validation – the process of gathering and evaluating a) Homogenous (unifactor) or heterogeneous evidence about validity (multifactor) o Validation Studies – yield insights regarding a b) Dynamic (unstable) or static (stable) particular population of testtakers as compared to the c) Range of scores is restricted or not norming sample described in a test manual d) Speed Test or Power Test o Internal Validity – degree of control among e) Criterion or non-Criterion variables in the study (increased through random Test Sensitivity – detects true positive assignment) Test Specificity – detects true negative o External Validity – generalizability of the research Base Rate – proportion of the population that results (increased through random selection) actually possess the characteristic of interest o Conceptual Validity – focuses on individual with Selection ratio – no. of hired candidates compared their unique histories and behaviors to the no. of applicants ▪ Means of evaluating and integrating test data so that the clinician’s conclusions make accurate statements about the examinee o Face Validity – a test appears to measure to the Four Possible Hit and Miss Outcomes person being tested than to what the test actually 1. True Positives (Sensitivity) – predict success measures that does occur Content Validity 2. True Negatives (Specificity) – predict failure - describes a judgement of how adequately a test that does occur samples behavior representative of the universe of 3. False Positive (Type 1) – success does not occur behavior that the test was designed to sample 4. False Negative (Type 2) – predicted failure but - representativeness and relevance of the assessment succeed instrument to the construct being measured - when the proportion of the material covered by the test approximates the proportion of material covered in the course ▪ o o o o o o o o o o The reviewers I made are FREE :D instead of selling it, you can share the drive link to others :D Let’s help each other <3 See u soon, future RPms! - Aly Psychological Assessment #BLEPP Source: Cohen & Swerdlik (2018), Kaplan & Saccuzzo (2018), Groth & Wright (2016), Psych Pearls - Test Blueprint: a plan regarding the types of criterion measure that is not explained by predictors information to be covered by the items, the no. of already in use; used to improve the domain items tapping each area of coverage, the organization Construct Validity (Umbrella Validity) of the items, and so forth - covers all types of validity - more logical than statistical - logical and statistical - concerned with the extent to which the test is - judgement about the appropriateness of inferences representative of defined body of content consisting drawn from test scores regarding individual standing the topics and processes on variable called construct - panel of experts can review the test items and rate - Construct: an informed, scientific idea developed or them in terms of how closely they match the objective hypothesized to describe or explain behavior; or domain specification unobservable, presupposed traits that may invoke to - examine if items are essential, useful and necessary describe test behavior or criterion performance - Construct underrepresentation: failure to capture - One way a test developer can improve the important components of a construct homogeneity of a test containing dichotomous items is - Construct-irrelevant variance: happens when scores by eliminating items that do not show significant are influenced by factors irrelevant to the construct correlation coefficients with total test scores - Lawshe: developed the formula of Content Validity - If it is an academic test and high scorers on the entire Ratio test for some reason tended to get that particular item wrong while low scorers got it right, then the item is obviously not a good one - Some constructs lend themselves more readily than others to predictions of change over time - Method of Contrasted Groups: demonstrate that - If the CVI is low, it is recommended to remove or scores on the test vary in a predictable way as a modify the items that have low CVR values to function of membership in a group improve the overall content validity of the test - If a test is a valid measure of a particular construct, - Zero CVR: exactly half of the experts rate the item as then the scores from the group of people who does not essential have that construct would have different test scores Criterion Validity than those who really possesses that construct - more statistical than logical - Convergent Evidence: if scores on the test - a judgement of how adequately a test score can be undergoing construct validation tend to highly used to infer an individual’s most probable standing correlated with another established, validated test that on some measure of interest – the measure of interest measures the same construct being criterion - Discriminant Evidence: a validity coefficient - Criterion: standard on which a judgement or showing little relationship between test scores and/or decision may be made other variables with which scores on the test being - Characteristics: relevant, valid, uncontaminated construct-validated should not be correlated - Criterion Contamination: occurs when the criterion - test is homogenous measure includes aspects of performance that are not - test score increases or decreases as a function of age, part of the job or when the measure is affected by passage of time, or experimental manipulation “construct-irrelevant” (Messick, 1989) factors that are - pretest-posttest differences not part of the criterion construct - scores differ from groups 1. Concurrent Validity: If the test scores obtained at - scores correlated with scores on other test in about the same time as the criterion measures are accordance to what is predicted obtained; economically efficient - Sensitivity: percentage of true positives 2. Predictive Validity: measures of the relationship - Specificity: percentage of true negatives between test scores and a criterion measure obtained o Multitrait-multimethod Matrix – useful for at a future time examining both convergent and discriminant validity - Incremental Validity: the degree to which an evidence additional predictor explains something about the ▪ Multitrait: two or more traits ▪ Multimethod: two or more methods The reviewers I made are FREE :D instead of selling it, you can share the drive link to others :D Let’s help each other <3 See u soon, future RPms! - Aly Psychological Assessment #BLEPP Source: Cohen & Swerdlik (2018), Kaplan & Saccuzzo (2018), Groth & Wright (2016), Psych Pearls The matrix or table that results from correlating distinct and potentially independent aspects of a variables within and between methods ratee’s behavior Factor Analysis – designed to identify factors or o Fairness – the extent to which a test is used in an specific variables that are typically attributes, impartial, just, and equitable way characteristics, or dimensions on which people may o Attempting to define the validity of the test will be differ futile if the test is NOT reliable ▪ Developed by Charles Spearman Utility ▪ Employed as data reduction method o Utility – usefulness or practical value of testing to ▪ Used to study the interrelationships among set of improve efficiency variables o Can tell us something about the practical value of the ▪ Identify the factor or factors in common between information derived from scores on the test test scores on subscales within a particular test o Helps us make better decisions ▪ Explanatory FA: estimating or extracting factors; o Higher criterion-related validity = higher utility deciding how many factors must be retained o One of the most basic elements in utility analysis is ▪ Confirmatory FA: researchers test the degree to financial cost of the selection device which a hypothetical model fits the actual data o Cost – disadvantages, losses, or expenses both ▪ Factor Loading: conveys info about the extent to economic and noneconomic terms which the factor determines the test score or o Benefit – profits, gains or advantages scores o The cost of test administration can be well worth it if ▪ can be used to obtain both convergent and the results is certain noneconomic benefits discriminant validity o Utility Analysis – family of techniques that entail a Cross-Validation – revalidation of the test to a cost-benefit analysis designed to yield information criterion based on another group different from the relevant to a decision about the usefulness and/or original group form which the test was validated practical value of a tool of assessment ▪ Validity Shrinkage: decrease in validity after o Expectancy table – provide an indication that a cross-validation testtaker will score within some interval of scores on ▪ Co-Validation: validation of more than one test a criterion measure – passing, acceptable, failing from the same group o Might indicate future behaviors, then if successful, ▪ Co-Norming: norming more than one test from the test is working as it should the same group o Taylor-Russel Tables – provide an estimate of the Bias – factor inherent in a test that systematically extent to which inclusion of a particular test in the prevents accurate, impartial measurement selection system will improve selection ▪ Prejudice, preferential treatment o Selection Ratio – numerical value that reflects the ▪ Prevention during test dev through a procedure relationship between the number of people to be called Estimated True Score Transformation hired and the number of people available to be hired Rating – numerical or verbal judgement that places a person or an attribute along a continuum identified by a scale of numerical or word descriptors known as Rating Scale o Base Rate – percentage of people hired under the ▪ Rating Error: intentional or unintentional misuse existing system for a particular position of the scale o One limitation of Taylor-Russel Tables is that the ▪ Leniency Error: rater is lenient in scoring relationship between the predictor (test) and criterion (Generosity Error) must be linear ▪ Severity Error: rater is strict in scoring o Naylor-Shine Tables – entails obtaining the ▪ Central Tendency Error: rater’s rating would tend difference between the means of the selected and to cluster in the middle of the rating scale unselected groups to derive an index of what the test ▪ One way to overcome rating errors is to use is adding to already established procedures rankings o Brogden-Cronbach-Gleser Formula – used to ▪ Halo Effect: tendency to give high score due to calculate the dollar amount of a utility gain resulting failure to discriminate among conceptually from the use of a particular selection instrument ▪ o o o o The reviewers I made are FREE :D instead of selling it, you can share the drive link to others :D Let’s help each other <3 See u soon, future RPms! - Aly Psychological Assessment #BLEPP Source: Cohen & Swerdlik (2018), Kaplan & Saccuzzo (2018), Groth & Wright (2016), Psych Pearls Utility Gain – estimate of the benefit of using a regarding the likelihood of offer acceptance, and the particular test distribution of applicant scores o Productivity Gains – an estimated increase in work o Discriminant Analysis – shed light on the output relationship between identified variables and two o High performing applicants may have been offered naturally occurring groups in other companies as well ▪ used by the researcher to analyze the research o The more complex the job, the more people differ on data when the criterion or the dependent variable how well or poorly they do that job is categorical and the predictor or the independent o Cut Score – reference point derived as a result of a variable is interval in nature judgement and used to divide a set of data into two ▪ enables the researcher to examine whether or more classifications significant differences exist among the groups, in terms of the predictor variables Relative Cut Score – reference point based on norm▪ identify two groups of people who represent two related considerations (norm-referenced), not fixed per distinct categories of some trait se Reason for accepting or rejecting instruments and Fixed Cut Scores – set with reference to a judgement tools based on Psychometric Properties concerning minimum level of proficiency required; Reliability e.g., Board Exams Multiple Cut Scores – refers to the use of two or more cut scores with reference to one predictor for the purpose of categorization Multiple Hurdle – multi-stage selection process, a cut score is in place for each predictor Compensatory Model of Selection – assumption that high scores on one attribute can compensate for lower scores o Angoff Method – setting fixed cut scores o Basic Research = 0.70 to 0.90 ▪ low interrater reliability o Clinical Setting = 0.90 to 0.95 ▪ requires expert judges to discuss the issues Validity involved in determining a pass mark and to evaluate the examination by using a well-defined and rational procedure o Known Groups Method – collection of data on the predictor of interest from group known to possess and not possess a trait of interest ▪ The determination of where to set cutoff score is inherently affected by the composition of contrasting groups o IRT-Based Methods – cut scores are typically set based on testtaker’s performance across all the items on the test ▪ Item-Mapping Method: arrangement of items in histogram, with each column containing items with deemed to be equivalent value ▪ Bookmark Method: expert places “bookmark” between the two pages that are deemed to separate testtakers who have acquired the minimal knowledge, skills, and/or abilities from those who are not o Method of Predictive Yield – took into account the number of positions to be filled, projections o The reviewers I made are FREE :D instead of selling it, you can share the drive link to others :D Let’s help each other <3 See u soon, future RPms! - Aly Psychological Assessment #BLEPP Item Difficulty Source: Cohen & Swerdlik (2018), Kaplan & Saccuzzo (2018), Groth & Wright (2016), Psych Pearls o 0 means 0% of the variance in the scores assigned by the scorers was attributed to true differences and 100% to error P-Value o P-Value ≤ ∞, reject null hypothesis o P-Value ≥ ∞, accept null hypothesis Item Discrimination The optimal boundary lines for the “upper” and “lower” areas of distribution of scores will demarcate the upper and lower 27% of distribution of scores ▪ 27% if normal ▪ 33% if platykurtic o 0.27/n, wherein n = no. of students Inter-Item Reliability Index o Interrater Reliability Coefficient Research Methods and Statistics (20) Statistics Applied in Research Studies on tests and Tests Development Measures of Central Tendency - statistics that indicates the average or midmost score between the extreme scores in a distribution - Goal: Identify the most typical or representative of entire group - Measures of Central Location Mean - the average of all the raw scores - Equal to the sum of the observations divided by the number of observations - Interval and ratio data (when normal distribution) - Point of least squares - Balance point for the distribution - susceptible to outliers Median – the middle score of the distribution - Ordinal, Interval, Ratio - for extreme scores, use median - Identical for sample and population - Also used when there has an unknown or undetermined score - Used in “open-ended” categories (e.g., 5 or more, more than 8, at least 10) The reviewers I made are FREE :D instead of selling it, you can share the drive link to others :D Let’s help each other <3 See u soon, future RPms! - Aly Psychological Assessment #BLEPP Source: Cohen & Swerdlik (2018), Kaplan & Saccuzzo (2018), Groth & Wright (2016), Psych Pearls - For ordinal data - equal to the square root - if the distribution is of the average squared skewed for ratio/interval deviations about the data, use median mean - Equal to the square root Mode - most frequently of the variance occurring score in the - Distance from the mean distribution - Bimodal Distribution: if Variance - equal to the arithmetic there are two scores that mean of the squares of occur with highest the differences between frequency the scores in a - Not commonly used distribution and their - Useful in analyses of mean qualitative or verbal - average squared nature deviation around the - For nominal scales, mean discrete variables Measures of Location - Value of the mode gives Percentile or Percentile - not linearly an indication of the shape Rank transformable, converged of the distribution as well at the middle and the as a measure of central outer ends show large tendency interval Measures of Spread or Variability – statistics that - expressed in terms of describe the amount of variation in a distribution the percentage of persons - gives idea of how well the measure of central in the standardization tendency represent the data sample who fall below a - large spread of values means large differences given score between individual scores - indicates the Range - equal to the difference individual’s relative between highest and the position in the lowest score standardization sample - Provides a quick but - essential in creating gross description of the normalized standardized spread of scores scores - When its value is based Quartile - dividing points between on extreme scores of the the four quarters in the distribution, the resulting distribution description of variation - Specific point may be understated or - Quarter: refers to an overstated interval Interquartile Range - difference between Q1 Decile/STEN - divide into 10 equal and Q2 parts Semi-Quartile Range - interquartile range - a measure of the divided by 2 asymmetry of the probability distribution of Standard Deviation - approximation of the a real-valued random average deviation around about its mean the mean - gives detail of how Correlation much above or below a Pearson R - interval/ratio + score to the mean interval/ratio The reviewers I made are FREE :D instead of selling it, you can share the drive link to others :D Let’s help each other <3 See u soon, future RPms! - Aly Psychological Assessment #BLEPP Source: Cohen & Swerdlik (2018), Kaplan & Saccuzzo (2018), Groth & Wright (2016), Psych Pearls - ordinal + ordinal ANOVA Mixed Design - 2 or more groups, measured more than 3 - artificial Dichotomous + times interval/ratio - e.g., Young Adults, Point Biserial - true dichotomous + Middle Adults, and Old interval/ratio Adults’ blood pressure is Phi Coefficient - nominal (true dic) + measured during nominal (true/artificial breakfast, lunch, and dic.) dinner Tetrachoric - Art. Dichotomous + Art. MANOVA - used to test the Dichotomous differences between the Kendall’s - 3 or more ordinal/rank means of multiple Rank Biserial - nominal + ordinal dependent variables Differences across two or more T-test Independent - two separate groups, independent groups (Unpaired T-test) random assignment Non-Parametric Tests - e.g., blood pressure of Mann Whitney U Test - t-test independent male and female grad Wilcoxon Signed Rank - t-test dependent students Test T-Test Dependent - one group, two scores Kruskal-Wallis H Test - one-way/two-way (Paired T-test) - e.g., blood pressure ANOVA before and after the Friedman Test - ANOVA repeated lecture of Grad students measures One-Way ANOVA - 3 or more groups, tested Lambda - for 2 groups of nominal once data - e.g., people in different Chi-Square socio-economic status Goodness of Fit - used to measure and the differences of differences and involves their salaries nominal data and only One-Way Repeated - 1 group, measured at one variable with 2 or Measures least 3 times more categories - e.g., measuring the Test of Independence - used to measure focus level of board correlation and involves reviewers during nominal data and two morning, afternoon, and variables with two or night sessions of review more categories Two-Way ANOVA - 3 or more groups, tested Regression – used when one wants to provide for 2 variables framework of prediction on the basis of one factor in - e.g., people in different order to predict the probable value of another factor socio-economic status and the differences of Linear Regression of Y - Y = a + bX their salaries and their on X - Used to predict the eating habits unknown value of variable Y when value of ANCOVA - used when you need to variable X is known control for an additional variable which may be Linear Regression of X - X = c + dY influencing the on Y - Used to predict the relationship between your unknown value of independent and variable X using the dependent variable known variable Y Spearman Rho Biserial The reviewers I made are FREE :D instead of selling it, you can share the drive link to others :D Let’s help each other <3 See u soon, future RPms! - Aly Psychological Assessment #BLEPP Source: Cohen & Swerdlik (2018), Kaplan & Saccuzzo (2018), Groth & Wright (2016), Psych Pearls Test for Normality – data are drawn from a - Entail lit reviews and experimentation, creation, population that has normal distribution revision, and deletion of preliminary items Kolmogorov-Smirnov More than 50 sample size II. Test Construction – stage in the process that entails writing test items, revisions, formatting, setting scoring Shapiro-Wilk Less than 50 sample size rules - it is not good to create an item that contains numerous ideas - Item Pool: reservoir or well from which the items will or will not be drawn for the final version of the test - Item Banks: relatively large and easily accessible collection of test questions - Computerized Adaptive Testing: refers to an interactive, computer administered test-taking process wherein items presented to the testtaker are based in part on the testtaker’s performance on previous items - The test administered may be different for each o True Dichotomy – dichotomy in which there are testtaker, depending on the test performance on the only fixed possible categories items presented o Artificial Dichotomy - dichotomy in which there are - Reduces floor and ceiling effects other possibilities in a certain category - Floor Effects: occurs when there is some lower limit o Levene’s Test – used to test if k samples have equal on a survey or questionnaire and a large percentage of variance respondents score near this lower limit (testtakers have ▪ P-Value > 0.05, variance not significantly low scores) different from each other (therefore, - Ceiling Effects: occurs when there is some upper limit homogenous) on a survey or questionnaire and a large percentage of ▪ P-Value < 0.05, there is significant difference respondents score near this upper limit (testtakers have between variance high scores) ▪ Less sensitive to departures from normality - Item Branching: ability of the computer to tailor the content and order of presentation of items on the basis of responses to previous items - Item Format: form, plan, structure, arrangement, and layout of individual test items o Bartlett’s Test – also used to test if k samples have - Dichotomous Format: offers two alternatives for each equal variance but much sensitive than Levene Test item Methods and Statistics used in Research Studies and - Polychotomous Format: each item has more than two Test Construction alternatives Test Development - Category Format: a format where respondents are o Test Development – an umbrella term for all that asked to rate a construct goes into the process of creating a test 1. Checklist – subject receives a longlist of adjectives I. Test Conceptualization – brainstorming of ideas and indicates whether each one if characteristic of about what kind of test a developer wants to publish himself or herself - stage wherein the ff. is determined: construct, goal, 2. Guttman Scale – items are arranged from weaker to user, taker, administration, format, response, benefits, stronger expressions of attitude, belief, or feelings costs, interpretation - Selected-Response Format: require testtakers to select - determines whether the test would be normresponse from a set of alternative responses referenced or criterion-referenced 1. Multiple Choice - Has three elements: stem - Pilot Work/Pilot Study/Pilot Research – preliminary (question), a correct option, and several incorrect research surrounding the creation of a prototype of the alternatives (distractors or foils), Should’ve one test correct answer, has grammatically parallel alternatives, - Attempts to determine how best to measure a targeted similar length, alternatives that fit grammatically with construct The reviewers I made are FREE :D instead of selling it, you can share the drive link to others :D Let’s help each other <3 See u soon, future RPms! - Aly Psychological Assessment #BLEPP Source: Cohen & Swerdlik (2018), Kaplan & Saccuzzo (2018), Groth & Wright (2016), Psych Pearls the stem, avoid ridiculous distractors, not excessively 2. Rank Order – respondents are presented with long, “all of the above”, “none of the above” (25%) several items simultaneously and asked to rank them in - Effective Distractors: a distractor that was chosen order or priority equally by both high and low performing groups that 3. Constant Sum – respondents are asked to allocate a enhances the consistency of test results constant sum of units, such as points, among set of - Good distractors has been chosen frequently by low stimulus objects with respect to some criterion scorers 4. Q-Sort Technique – sort object based on similarity - Ineffective Distractors: may hurt the reliability of the with respect to some criterion test because they are time consuming to read and can Non-Comparative Scales of Measurement limit the no. of good items 1. Continuous Rating – rate the objects by placing a - Cute Distractors: less likely to be chosen, may affect mark at the appropriate position on a continuous line the reliability of the test bec the testtakers may guess that runs from one extreme of the criterion variable to from the remaining options the other 2. Matching Item - Test taker is presented with two - e.g., Rating Guardians of the Galaxy as the best columns: Premises and Responses Marvel Movie of Phase 4 3. Binary Choice - Usually takes the form of a sentence 2. Itemized Rating – having numbers or brief that requires the testtaker to indicate whether the descriptions associated with each category statement is or is not a fact (50%) - e.g., 1 if your like the item the most, 2 if so-so, 3 if - Constructed-Response Format: requires testtakers to you hate it supply or to create the correct answer, not merely 3. Likert Scale – indicate their own attitudes by selecting it checking how strongly they agree or disagree with 1. Completion Item - Requires the examinee to carefully worded statements that range from very provide a word or phrase that completes a sentence positive to very negative towards attitudinal object 2. Short-Answer - Should be written clearly enough - principle of measuring attitudes by asking people to that the testtaker can respond succinctly, with short respond to a series of statements about a topic, in terms answer of the extent to which they agree with them 3. Essay – allows creative integration and expression 4. Visual Analogue Scale – a 100-mm line that allows of the material subjects to express the magnitude of an experience or - Scaling: process of setting rules for assigning belief numbers in measurement 5. Semantic Differential Scale – derive respondent’s Primary Scales of Measurement attitude towards the given object by asking him to 1. Nominal - involve classification or categorization select an appropriate position on a scale between two based on one or more distinguishing characteristics bipolar opposites - Label and categorize observations but do not make 6. Staple Scale – developed to measure the direction any quantitative distinctions between observations and intensity of an attitude simultaneously - mode 7. Summative Scale – final score is obtained by 2. Ordinal - rank ordering on some characteristics is summing the ratings across all the items also permissible 8. Thurstone Scale – involves the collection of a - median variety of different statements about a phenomenon 3. Ratio - contains equal intervals, has no absolute zero which are ranked by an expert panel in order to develop point (even negative values have interpretation to it) the questionnaire - Zero value does not mean it represents none - allows multiple answers 4. Interval - - has true zero point (if the score is zero, 9. Ipsative Scale – the respondent must choose it means none/null) between two or more equally socially acceptable - Easiest to manipulate options Comparative Scales of Measurement III. Test Tryout - the test should be tried out on people 1. Paired Comparison - produces ordinal data by who are similar in critical respects to the people for presenting with pairs of two stimuli which they are whom the test was designed asked to compare - An informal rule of thumb should be no fewer than 5 - respondent is presented with two objects at a time and and preferably as many as 10 for each item (the more, asked to select one object according to some criterion the better) The reviewers I made are FREE :D instead of selling it, you can share the drive link to others :D Let’s help each other <3 See u soon, future RPms! - Aly Psychological Assessment #BLEPP Source: Cohen & Swerdlik (2018), Kaplan & Saccuzzo (2018), Groth & Wright (2016), Psych Pearls - Risk of using few subjects = phantom factors emerge - Item-Validity Index: designed to provide an indication - Should be executed under conditions as identical as of the degree to which a test is measure what it purports possible to measure - A good test item is one that answered correctly by high - The higher Item-Validity index, the greater the test’s scorers as a whole criterion-related validity - Empirical Criterion Keying: administering a large - Item-Discrimination Index: measure of item pool of test items to a sample of individuals who are discrimination; measure of the difference between the known to differ on the construct being measured proportion of high scorers answering an item correctly - Item Analysis: statistical procedure used to analyze and the proportion of low scorers answering the item items, evaluate test items correctly - Discriminability Analysis: employed to examine - Extreme Group Method: compares people who have correlation between each item and the total score of the done well with those who have done poorly test - Discrimination Index: difference between these - Item: suggest a sample of behavior of an individual proportion - Table of Specification: a blueprint of the test in terms - Point-Biserial Method: correlation between a of number of items per difficulty, topic importance, or dichotomous variable and continuous variable taxonomy - Guidelines for Item writing: Define clearly what to measure, generate item pool, avoid long items, keep the level of reading difficulty appropriate for those who will complete the test, avoid double-barreled items, consider making positive and negative worded items - Double-Barreled Items: items that convey more than one ideas at the same time - Item-Characteristic Curve: graphic representation of - Item Difficulty: defined by the number of people who item difficulty and discrimination get a particular item correct - Guessing: one that eluded any universally accepted - Item-Difficulty Index: calculating the proportion of solutions the total number of testtakers who answered the item - Item analyses taken under speed conditions yield correctly; The larger, the easier the item misleading or uninterpretable results - Item-Endorsement Index for personality testing, - Restrict item analysis on a speed test only to the items percentage of individual who endorsed an item in a completed by the testtaker personality test - Test developer ideally should administer the test to be - The optimal average item difficulty is approx. 50% item-analyzed with generous time limits to complete with items on the testing ranging in difficulty from the test about 30% to 80% - Optimal Difficulty Index Formula: [ (1+chance of getting it correct)/2 ] ➢ Multiple choice: 0.625 ➢ True or False (Binary): 0.75 ➢ Three choices: 0.665 ➢ Five choices: 0.6 Scoring Items/Scoring Models 1. Cumulative Model – testtaker obtains a measure of the level of the trait; thus, high scorers may suggest high level in the trait being measured - Omnibus Spiral Format: items in an ability are 2. Class Scoring/Category Scoring – testtaker arranged into increasing difficulty response earn credit toward placement in a particular - Item-Reliability Index: provides an indication of the class or category with other testtaker whose pattern of internal consistency of a test responses is similar in some way - The higher Item-Reliability index, the greater the test’s internal consistency The reviewers I made are FREE :D instead of selling it, you can share the drive link to others :D Let’s help each other <3 See u soon, future RPms! - Aly Psychological Assessment #BLEPP Source: Cohen & Swerdlik (2018), Kaplan & Saccuzzo (2018), Groth & Wright (2016), Psych Pearls ▪ Ceiling Effects: occurs when there is some upper 3. Ipsative Scoring – compares testtaker’s score on one scale within a test to another scale within that same test, limit on a survey or questionnaire and a large two unrelated constructs percentage of respondents score near this upper IV. Test Revision – characterize each item according to limit (testtakers have high scores) its strength and weaknesses ▪ Item Branching: ability of the computer to tailor - As revision proceeds, the advantage of writing a large the content and order of presentation of items on item pool becomes more apparent because some items the basis of responses to previous items were removed and must be replaced by the items in the ▪ Routing Test: subtest used to direct or route the item pool testtaker to a suitable level of items - Administer the revised test under standardized ▪ Item-Mapping Method: setting cut scores that conditions to a second appropriate sample of examinee entails a histographic representation of items and - Cross-Validation: revalidation of a test on a sample of expert judgments regarding item effectiveness testtakers other than those on who test performance was o Basal Level – the level of which a the minimum originally found to be a valid predictor of some criterion number of correct responses is obtained criterion; often results to validity shrinkage - Validity Shrinkage: decrease in item validities that o Computer Assisted Psychological Assessment – inevitably occurs after cross-validation standardized test administration is assured for - Co-validation: conducted on two or more test using testtakers and variation is kept to a minimum the same sample of testtakers ▪ Test content and length is tailored according to - Co-norming: creation of norms or the revision of the taker’s ability existing norms Statistics - Anchor Protocol: test protocol scored by highly o Measurement – the act of assigning numbers or authoritative scorer that is designed as a model for symbols to characteristics of things according to scoring and a mechanism for resolving scoring rules discrepancies Descriptive Statistics – methods used to provide - Scoring Drift: discrepancy between scoring in an concise description of a collection of quantitative anchor protocol and the scoring of another protocol information - Differential Item Functioning: item functions Inferential Statistics – method used to make differently in one group of testtakers known to have the inferences from observations of a small group of people same level of the underlying trait known as sample to a larger group of individuals - DIF Analysis: test developers scrutinize group by known as population group item response curves looking for DIF Items o Magnitude – the property of “moreness” - DIF Items: items that respondents from different o Equal Intervals – the difference between two points groups at the same level of underlying trait have at any place on the scale has the same meaning as the different probabilities of endorsing a function of their difference between two other points that differ by the group membership same number of scale units o Computerized Adaptive Testing – refers to an o Absolute 0 – when nothing of the property being interactive, computer administered test-taking measured exists process wherein items presented to the testtaker are o Scale – a set of numbers who properties model based in part on the testtaker’s performance on empirical properties of the objects to which the previous items numbers are assigned ▪ The test administered may be different for each Continuous Scale – takes on any value within the testtaker, depending on the test performance on range and the possible value within that range is infinite - used to measure a variable which can theoretically be the items presented divided ▪ Reduces floor and ceiling effects Discrete Scale – can be counted; has distinct, countable ▪ Floor Effects: occurs when there is some lower values limit on a survey or questionnaire and a large - used to measure a variable which cannot be percentage of respondents score near this lower theoretically be divided limit (testtakers have low scores) The reviewers I made are FREE :D instead of selling it, you can share the drive link to others :D Let’s help each other <3 See u soon, future RPms! - Aly Psychological Assessment #BLEPP Source: Cohen & Swerdlik (2018), Kaplan & Saccuzzo (2018), Groth & Wright (2016), Psych Pearls Error – refers to the collective influence of all the Median – the middle score of the distribution factors on a test score or measurement beyond those - Ordinal, Interval, Ratio specifically measured by the test or measurement - Useful in cases where relatively few scores fall at the ▪ Degree to which the test score/measurement may high end of the distribution or relatively few scores fall be wrong, considering other factors like state of at the low end of the distribution the testtaker, venue, test itself etc. - In other words, for extreme scores, use median ▪ Measurement with continuous scale always (skewed) involve with error - Identical for sample and population Four Levels of Scales of Measurement - Also used when there has an unknown or undetermined score Nominal – involve classification or categorization - Used in “open-ended” categories (e.g., 5 or more, based on one or more distinguishing characteristics more than 8, at least 10) - Label and categorize observations but do not make - For ordinal data any quantitative distinctions between observations - mode Mode – most frequently occurring score in the distribution Ordinal - rank ordering on some characteristics is also - Bimodal Distribution: if there are two scores that permissible occur with highest frequency - median - Not commonly used Interval - contains equal intervals, has no absolute zero - Useful in analyses of qualitative or verbal nature point (even negative values have interpretation to it) - For nominal scales, discrete variables - Zero value does not mean it represents none - Value of the mode gives an indication of the shape of Ratio - has true zero point (if the score is zero, it means the distribution as well as a measure of central tendency none/null) o Variability – an indication how scores in a - Easiest to manipulate distribution are scattered or dispersed o Distribution – defined as a set of test scores arrayed o Measures of Variability – statistics that describe the for recording or study amount of variation in a distribution o Raw Scores – straightforward, unmodified o Range – equal to the difference between highest and accounting of performance that is usually numerical the lowest score o Frequency Distribution – all scores are listed ▪ Provides a quick but gross description of the alongside the number of times each score occurred spread of scores o Independent Variable – being manipulated in the ▪ When its value is based on extreme scores of the study distribution, the resulting description of variation o Quasi-Independent Variable – nonmanipulated may be understated or overstated variable to designate groups o Quartile – dividing points between the four quarters ▪ Factor: for ANOVA in the distribution Post-Hoc Tests – used in ANOVA to determine which ▪ Specific point mean differences are significantly different ▪ Quarter: refers to an interval Tukey’s HSD test – allows the compute a single value ▪ Interquartile Range: measure of variability equal that determines the minimum difference between to the difference between Q3 and Q1 treatment means that is necessary for significance ▪ Semi-interquartile Range: equal to the o Measures of Central Tendency – statistics that interquartile range divided by 2 indicates the average or midmost score between the o Standard Deviation – equal to the square root of the extreme scores in a distribution average squared deviations about the mean ▪ Goal: Identify the most typical or representative ▪ Equal to the square root of the variance of entire group ▪ Variance: equal to the arithmetic mean of the Mean – the average of all the raw scores squares of the differences between the scores in a - Equal to the sum of the observations divided by the distribution and their mean number of observations ▪ Distance from the mean - Interval and ratio data (when normal distribution) o Normal Curve – also known as Gaussian Curve - Point of least squares o Bell-shaped, smooth, mathematically defined curve - Balance point for the distribution that is highest at its center The reviewers I made are FREE :D instead of selling it, you can share the drive link to others :D Let’s help each other <3 See u soon, future RPms! - Aly o Psychological Assessment #BLEPP o o Source: Cohen & Swerdlik (2018), Kaplan & Saccuzzo (2018), Groth & Wright (2016), Psych Pearls Asymptotically = approaches but never touches the axis Tail – 2 – 3 standard deviations above and below the mean ▪ Mean < Median < Mode Skewed is associated with abnormal, perhaps because the skewed distribution deviates from the symmetrical or so-called normal distribution o Kurtosis – steepness if a distribution in its center Platykurtic – relatively flat Leptokurtic – relatively peaked Mesokurtic – somewhere in the middle o Symmetrical Distribution – right side of the graph is mirror image of the left side ▪ Has only one mode and it is in the center of the distribution ▪ Mean = median = mode o Skewness – nature and extent to which symmetry is absent o Positive Skewed – few scores fall the high end of the distribution ▪ The exam is difficult ▪ More items that was easier would have been desirable in order to better discriminate at the lower end of the distribution of test scores o o ▪ Mean > Median > Mode Negative Skewed – when relatively few of the scores fall at the low end of the distribution ▪ The exam is easy ▪ More items of a higher level of difficulty would make it possible to better discriminate between scores at the upper end of the distribution ▪ High Kurtosis = high peak and fatter tails ▪ Lower Kurtosis = rounded peak and thinner tails o Standard Score – raw score that has been converted from one scale to another scale o Z-Scores – results from the conversion of a raw score into a number indicating how many SD units the raw score is below or above the mean of the distribution ▪ Identify and describe the exact location of each score in a distribution ▪ Standardize an entire distribution ▪ Zero plus or minus one scale ▪ Have negative values ▪ Requires that we know the value of the variance to compute the standard error o T-Scores – a scale with a mean set at 50 and a standard deviation set at 10 ▪ Fifty plus or minus 10 scale ▪ 5 standard deviations below the mean would be equal to a t-score of 0 ▪ Raw score that fell in the mean has T of 50 ▪ Raw score 5 standard deviations about the mean would be equal to a T of 100 ▪ No negative values ▪ Used when the population or variance is unknown The reviewers I made are FREE :D instead of selling it, you can share the drive link to others :D Let’s help each other <3 See u soon, future RPms! - Aly Psychological Assessment #BLEPP o o o o o o Source: Cohen & Swerdlik (2018), Kaplan & Saccuzzo (2018), Groth & Wright (2016), Psych Pearls Stanine – a method of scaling test scores on a nineo Directional Hypothesis Test or One-Tailed Test – point standard scale with a mean of five (5) and a statistical hypotheses specify either an increase or a standard deviation of two (2) decrease in the population mean Linear Transformation – one that retains a direct o T-Test – used to test hypotheses about an unknown numerical relationship to the original raw score population mean and variance Nonlinear Transformation – required when the ▪ Can be used in “before and after” type of research data under consideration are not normally distributed ▪ Sample must consist of independent Normalizing the distribution involves stretching the observationsꟷthat is, if there is not consistent, skewed curve into the shape of a normal curve and predictable relationship between the first creating a corresponding scale of standard scores, a observation and the second scale that is technically referred to as Normalized ▪ The population that is sampled must be normal Standard Score Scale ▪ If not normal distribution, use a large sample Generally preferrable to fine-tune the test according o Correlation Coefficient – number that provides us to difficulty or other relevant variables so that the with an index of the strength of the relationship resulting distribution will approximate the normal between two things curve o Correlation – an expression of the degree and STEN – standard to ten; divides a scale into 10 units direction of correspondence between two things ▪ + & - = direction ▪ Number anywhere to -1 to 1 = magnitude ▪ Positive – same direction, either both going up or both going down ▪ Negative – Inverse Direction, either DV is up and IV goes down or IV goes up and DV goes down ▪ 0 = no correlation Mean SD Z-Score 0 1 T-Score 50 10 Stanine 5 2 STEN 5.5 2 IQ 100 15 GRE or SAT 500 100 o Hypothesis Testing – statistical method that uses a sample data to evaluate a hypothesis about a population Alternative Hypothesis – states there is a change, difference, or relationships Null Hypothesis – no change, no difference, or no relationship o Alpha Level or Level of Significance – used to define concept of “very unlikely” in a hypothesis test o Critical Region – composed of extreme values that are very unlikely to be obtained if the null hypothesis is true o If sample data fall in the critical region, the null hypothesis is rejected o The alpha level for a hypothesis test is the probability that the test will lead to a Type I error Pearson r/Pearson Correlation Coefficient/Pearson Product-Moment Coefficient of Correlation – used when two variables being correlated are continuous and linear ▪ Devised by Karl Pearson ▪ Coefficient of Determination – an indication of how much variance is shared by the X- and Yvariables o Spearman Rho/Rank-Order Correlation Coefficient/Rank-Difference Correlation Coefficient – frequently used if the sample size is small and when both sets of measurement are in ordinal ▪ Developed by Charles Spearman o Outlier – extremely atypical point located at a relatively long distance from the rest of the coordinate points in a scatterplot o The reviewers I made are FREE :D instead of selling it, you can share the drive link to others :D Let’s help each other <3 See u soon, future RPms! - Aly Psychological Assessment #BLEPP Source: Cohen & Swerdlik (2018), Kaplan & Saccuzzo (2018), Groth & Wright (2016), Psych Pearls Regression Analysis – used for prediction Local Norms – provide normative information with ▪ Predict the values of a dependent or response respect to the local population’s performance on some variable based on values of at least one tests independent or explanatory variable o Age-Related Norms – certain tests have different ▪ Residual: the difference between an observed normative groups for age groups value of the response variable and the value of the o Tracking – tendency to stay at about the same level response variable predicted from the regression relative to one’s peers line Norm-Referenced Tests – compares each person with ▪ The Principle of Least Squares the norm ▪ Standard Error of Estimate: standard deviation of Criterion-Referenced Tests – describes specific types the residuals in regression analysis of skills, tasks, or knowledge that the test taker can ▪ Slope: determines how much the Y variable demonstrate changes when X is increased by 1 point Selection of Assessment Methods and Tools and Uses, o T-Test (Independent) – comparison or determining Benefits, and Limitations of Assessment tools and differences instruments (32) ▪ 2 different groups/independent samples + Identify appropriate assessment methods, tools (2) interval/ratio scales (continuous variables) 1. Test – measuring device or procedure Equal Variance – 2 groups are equal - Psychological Test: device or procedure designed to Unequal Variance – groups are unequal measure variables related to psychology o T-test (Dependent)/Paired Test – one groups Ability or Maximal Performance Test – assess what nominal (either matched or repeated measures) + 2 a person can do treatments a. Achievement Test – measurement of the previous o One-Way ANOVA – 3 or more IV, 1 DV comparison learning of differences b. Aptitude – refers to the potential for learning or o Two-Way ANOVA – 2 IV, 1 DV acquiring a specific skill o Critical Value – reject the null and accept the c. Intelligence – refers to a person’s general potential alternative if [ obtained value > critical value ] to solve problems, adapt to changing environments, o P-Value (Probability Value) – reject null and accept abstract thinking, and profit from experience alternative if [ p-value < alpha level ] Human Ability – considerable overlap of o Norms – refer to the performances by defined groups achievement, aptitude, and intelligence test on a particular test Typical Performance Test – measure usual or Percentiles – an expression of the percentage of people habitual thoughts, feelings, and behavior whose score on a tests or measure falls below a Personality Test – measures individual dispositions particular raw score and preferences Age Norms – average performance of different a. Structured Personality tests – provide statement, samples of testtakers who were at various ages at the usually self-report, and require the subject to choose time the test was administered between two or more alternative responses Grade Norms – developed by administering the test to b. Projective Personality Tests – unstructured, and representative samples of children over a range of the stimulus or response are ambiguous consecutive grade levels c. Attitude Test – elicit personal beliefs and opinions - Developmental Norms: developed on the basis of any d. Interest Inventories – measures likes and dislikes trait, ability, skill, or other characteristics that is as well as one’s personality orientation towards the presumed to develop, deteriorate, or otherwise be world of work affected by chronical age, school grade, or stage of life - Purpose: for evaluation, drawing conclusions of some aspects of the behavior of a person, therapy, National norms – derived from a normative sample decision-making that was nationally representative of the population at - Settings: Industrial, Clinical, Educational, the time the norming study was conducted Counseling, Business, Courts, Research Subgroup Norms – normative sample can be segmented by any criteria initially used in selecting subjects for the sample o The reviewers I made are FREE :D instead of selling it, you can share the drive link to others :D Let’s help each other <3 See u soon, future RPms! - Aly Psychological Assessment #BLEPP Source: Cohen & Swerdlik (2018), Kaplan & Saccuzzo (2018), Groth & Wright (2016), Psych Pearls - Population: Test Developers, Test Publishers, Test 6. Role Play – defined as acting an improvised or Reviewers, Test Users, Test Sponsors, Test Takers, partially improvised part in a simulated situation Society - Role Play Test: assesses are directed to act as if they Levels of Tests are in a particular situation 1. Level A – anyone under a direction of a supervisor - Purpose: Assessment and Evaluation or consultant - Settings: Industrial, Clinical 2. Level B – psychometricians and psychologists only - Population: Job Applicants, Children 3. Level C – psychologists only 7. Computers – using technology to assess an client, 2. Interview – method of gathering information thus, can serve as test administrators and very through direct communication involving reciprocal efficient test scorers exchange 8. Others: videos, biofeedback devices - can be structured, unstructured, semi-structured, or Intelligence Tests non-directive Stanford-Binet Intelligence Scale 5th Ed. (SB-5) - Mental Status Examination: determines the mental [C] status of the patient - 2-85 years old - Intake Interview: determine why the client came for - individually administered assessment; chance to inform the client about the - norm-referenced policies, fees, and process involved - age scale and point-scale format - Social Case: biographical sketch of the client - originally created to identify mentally disabled - Employment Interview: determine whether the children in Paris candidate is suitable for hiring - 1908 Scale introduced Age Scale format and Mental - Panel Interview (Board Interview): more than one Age interviewer participates in the assessment - 1916 scale significantly applied IQ concept - Motivational Interview: used by counselors and - Standard Scores: 100 (mean), 15 (SD) clinicians to gather information about some - Scaled Scores: 10 (mean), 3 (SD) problematic behavior, while simultaneously - co-normed with Bender-Gestalt and Woodcockattempting to address it therapeutically Johnson Tests - based on Cattell-Horn-Carroll Model of General Issues addressed by Structured Interviews: Intellectual Ability 1. Criterion Variance: amount of error caused by - no accommodations for PWDs vague guidelines for exclusion or inclusion in - 2 routing tests (task used to direct or route the different categories examinee to a particular level of questions) 2. Information Variance: variability in amount and - w/ teaching items, floor level, and ceiling level type of information derived from interviews with - provides behavioral observations during clients administration 3. Portfolio – samples of one’s ability and - First ed lacks representativeness of the accomplishment standardization sample - Purpose: Usually in industrial settings for evaluation - first test to introduce the concept of an alternate item of future performance - earlier versions employed Ratio IQ, which was 4. Case History Data – refers to records, transcripts, based on the concept of Mental Age and other accounts in written, pictorial, or other form - 1960 revision had consisted of single form and the that preserve archival information, official and use of Deviation IQ informal accounts, and other data and items relevant - Ratio IQ: testtaker’s mental age divided by chronical to an assessee age, multiplied by 100 5. Behavioral Observation – monitoring of actions of - Deviation IQ: reflects a comparison of the others or oneself by visual or electronic means while performance of the individual with the performance of recording quantitative and/or qualitative information others of the same age in the standardization sample regarding those actions - SB-4 had Point Scale, which was the test was - Naturalistic Observation: observe humans in natural organized into subtests by category of item, not by age setting The reviewers I made are FREE :D instead of selling it, you can share the drive link to others :D Let’s help each other <3 See u soon, future RPms! - Aly Psychological Assessment #BLEPP Source: Cohen & Swerdlik (2018), Kaplan & Saccuzzo (2018), Groth & Wright (2016), Psych Pearls at which most testtakers are presumed capable of responding in the way that is keyed as correct WAIS-IV Subtests: 1. Verbal Comprehension SB5 Scales: 2. Perceptual Reasoning 1. Verbal 3. Working Memory 2. Nonverbal 4. Processing Speed 3. Full Scale IQ (FSIQ) WISC-IV Subtests: SB5 Factors: 1. Verbal Comprehension 1. Fluid Reasoning (FR) 2. Visual Spatial 2. Knowledge (KN) 3. Fluid Reasoning 3. Qualitative Reasoning (QR) 4. Working Memory 4. Visual-Spatial Processing (VS) 5. Processing Speed 5. Working Memory (WM) Successive Five-Level Interpretative Procedures: Level I. Interpret the FSIQ Level II. Interpret index scores and CHC groupings Level III. Interpret subtest variability Level IV. Qualitative/Process Analysis Level V. Analysis Intrasubtest variability Wechsler Intelligence Scales (WAIS-IV, WPPSIIV, WISC-V) [C] - WAIS (16-90 years old), WPPSI (2-6 years old), WISC (6-11) - individually administered Raven’s Progressive Matrices (RPM) - norm-referenced [B] - Standard Scores: 100 (mean), 15 (SD) - 4-90 years old - Scaled Scores: 10 (mean), 3 (SD) - CPM, 5-11 years old; SPM, 6-16 yrs old & 17 yrs - addresses the weakness in Stanford-Binet old and older; APM, 12+ yrs old - could also assess functioning in people with brain - nonverbal test injury - used to measure general intelligence & abstract - evaluates patterns of brain dysfunction reasoning - measure abilities that are likely to be lowered by - multiple choice of abstract reasoning brain damage - group test - useful in assessment of Alzheimer’s Disease - IRT-Based - WAIS (1955), WAIS-R (1981), WAIS-III (1997), - Colored Progressive Matrices: Used to assess the WAIS-IV (2008) degree to which children and adults can think clearly, - the latest edition has updated norms, improved floor or the level to which their intellectual abilities have and ceilings, improved psychometric properties, deteriorated reduced testing time, and co-normed with Weschler - Standard Progressive Matrices: more difficult that Individual Achievement Test-II) CPM - time-honored verbal versus performance IQ was - Advanced Progressive Matrices: geared towards eliminated (they do not purely measure but typically adults and teenagers of advanced intelligence combine a number of different abilities) Culture Fair Intelligence Test (CFIT) - WISC (1949), WISC-R (1974), WISC-III (1991), [ B] WISC-IV (2003) The reviewers I made are FREE :D instead of selling it, you can share the drive link to others :D Let’s help each other <3 See u soon, future RPms! - Aly Psychological Assessment #BLEPP Source: Cohen & Swerdlik (2018), Kaplan & Saccuzzo (2018), Groth & Wright (2016), Psych Pearls - Nonverbal instrument to measure your analytical and - Multiple-aptitude battery that measures developed reasoning ability in the abstract and novel situations abilities and helps predict future academic and - Measures individual intelligence in a manner occupational success in the military designed to reduced, as much as possible, the Kaufman Assessment Battery for Children-II influence of culture (KABC-II) - Individual or by group - Alan & Nadeen Kaufman - Aids in the identification of learning problems and - 2 ½ yrs to 12 ½ yrs old helps in making more reliable and informed decisions - for assessing cognitive development in children in relation to the special education needs of children - evaluate preschoolers, minority, and children with Purdue Non-Language Test learning disabilities [B] - Joseph Tiffin, Alin Grubner & Kay Inaba Global Test Scores: - 13 yrs old and above 1. Sequential Processing Scales - Designed to measure mental ability, since it consists 2. Simultaneous Processing Scales entirely of geometric forms, assess the fluid 3. Achievement Scales intelligence 4. Mental Processing Composite - mainly abstract reasoning Differential Aptitude Scale – Fifth Edition (DAT- determine the underlying logic of pattern and devise V) a solution [B] - 5 designs, two parallel forms, 48 items - Harold G. Raven, John M. Oldfield, and John C. - Culture-fair Raven - Self-Administering - 14 to 65 years old Panukat ng Katalinuhang Pilipino (PKP) - assess an individual’s aptitudes across various - Aurora R. Palacio domains, including verbal reasoning, numerical - 16 yrs old and above ability, abstract reasoning, mechanical reasoning, - Basis for screening, classifying, and identifying space relations, spelling, language usage, and clerical needs that will enhance the learning process speed and accuracy - In business, it is utilized as predictors of - provide insights into an individual’s relative occupational achievement by gauging applicant’s strengths and weaknesses in these areas to guide ability and fitness for a particular job educational and career decisions - Essential for determining one’s capacity to handle - norm-referenced the challenges associated with certain degree General Aptitude Test Battery (GATB) programs - U.S. Employment Services - measures fluid, crystallized, and generalized - measure of wide range of aptitudes and is used in intelligence such areas as occupational selection, rehabilitation, and vocational counseling Subtests: 1. Vocabulary Aptitude Scores: 2. Analogy G – General Intelligence 3. Numerical Ability V – Verbal Aptitude 4. Nonverbal Ability N – Numerical Aptitude Wonderlic Personnel Test (WPT) S – Spatial Aptitude - Eldon Wonderlic P – Form Perception - Adults Q – Clerical-Perception - Assessing cognitive ability and problem-solving K – Motor Coordination aptitude of prospective employees F – Finger Dexterity - Multiple choice, answered in 12 minutes M – Manual Dexterity Armed Services Vocational Aptitude Battery California Verbal Learning Test (CVLT-II) (ASVAB) [C] - Most widely used aptitude test in US - 16 yrs old – 89 yrs old The reviewers I made are FREE :D instead of selling it, you can share the drive link to others :D Let’s help each other <3 See u soon, future RPms! - Aly Psychological Assessment #BLEPP Source: Cohen & Swerdlik (2018), Kaplan & Saccuzzo (2018), Groth & Wright (2016), Psych Pearls - measures episodic verbal learning and memory and - Louis Thurstone demonstrates sensitivity to a range of clinical - Adults conditions Four Job-Related Tasks assessed by TMA Test: Otis-Lennon Ability Test (OLSAT) 1. Adjusting to new situations [C] 2. Learning new skills quickly - Otis, A.S. & Lennon, R.T. 3. Understanding complex or subtle relationships - designed to assess general mental ability or 4. Thinking flexibly scholastic aptitude of pupils - identify gifted children Personality Tests Philippine Aptitude Classification Test (PACT) Minnesota Multiphasic Personality Inventory - Ma. Lourdes M. Franco (MMPI-2) - 14 yrs to 15 yrs old [C] - developed to measure student’s abilities and help - Starke Hathaway and J. Charnley McKinley students decide on the course they will take after high - 16 years old and older school - Multiphasic personality inventory intended for used - assumes that aptitudes are required in different with both clinical and normal populations to identify combinations and in varying degrees for successful sources of maladjustment and personal strengths performance in different post-secondary courses - Help in diagnosing mental health disorders, distinguishing normal from abnormal Flanagan Industrial Tests - elicits a wide range of self-descriptions scored to - Flanagan, J.C. give a quantitative measurement of an individual’s - used for personnel selection programs, based on level of emotional adjustment and attitude toward testidentified job elements taking - should be administered to someone with no guilt Job Elements feelings for creating a crime 1. Arithmetic - individual or by groups 2. Assembly - Original MMPI had 13 scales, whilst the latest ver 3. Components (MMPI-II) maintained the original 10 scales 4. Coordination - MMPI (1939), 5. Electronics - most important approach taken during construction 6. Expression of the MMPI was Empirical Criterion Keying 7. Ingenuity (development, selection, and scoring of items within 8. Inspection the scales was based on some external criterion of 9. Judgment and Comprehension reference) 10. Mathematics and Reasoning 11. Mechanics Clinical Scales: 12. Memory Patterns 1. Hypochondriasis (Hs) – present multiple, vague, 13. Planning and chronic physical problems 14. Precision 2. Depression (D) – depressed mood, low self-esteem, 15. Scales lethargy, and feelings of guilt 16. Tables 3. Hysteria (Hy) – develop physical symptoms in 17. Vocabulary reaction to stress and can be dependent, naïve, Watson Glaser Critical Thinking Test (W-GCTA) infantile, and narcissistic - Goodwin Watson & Edward Glaser 4. Psychopathic Deviate (Pd) – associated with - 20 yrs old to 64 yrs old antisocial behavior - designed to assess a person’s critical thinking 5. Masculinity/Femininity (Mf) – interests more abilities and is widely used across legal practices traditionally viewed as feminine or masculine - assesses ability for critical thinking, creating 6. Paranoia (Pa) – suspicious, aloof, guarded, and conclusions, analyzing strong and weak arguments, overly sensitive recognizing assumptions, and evaluating arguments Thurstone Test of Mental Alertness (TMA) The reviewers I made are FREE :D instead of selling it, you can share the drive link to others :D Let’s help each other <3 See u soon, future RPms! - Aly Psychological Assessment #BLEPP Source: Cohen & Swerdlik (2018), Kaplan & Saccuzzo (2018), Groth & Wright (2016), Psych Pearls 7. Psychasthenia (Anxiety, Depression, OCD) (Pt) – - Very High = person is indiscriminately answering tense, anxious, ruminative, obsessive, phobic, and “true” to the items rigid 7. Variable Response Inconsistency (VRIN or VRIN): 8. Schizophrenia (Sc) – withdrawn, moody, and random true or false confused - expected to be answered in a consistent manner if 9. Hypomania or Mania (Ma) – sociable and the person is approaching the testing in a valid manner optimistic, though can be manipulative and grandiose - if a person answers in the opposite direction, then it 10. Social Introversion (Si) – introverted, withdrawn, indicates an inconsistent response and is, therefore, submissive, over-controlled, tense, inflexible (high scored as 1 raw score point on the VRIN Scale scorers) - High VRIN = indiscriminate responding, profile should be considered invalid and should not be Validity/Dissimulation scales: understand how interpreted genuine a test taker’s answers are 8. Infrequency-Psychopathology Scale (Fp): reveal 1. Lie Scale (L Scale): items that are somewhat intentional or unintentional over-reporting negative but apply to most people; assess the - High Fp = high probability of faking or exaggerating likelihood of the test taker to approach the instrument psychopathology, even among psychiatric patients with defensive mindset 9. Fake Bad Scale (FBS): “symptom validity scale” - High in L scale = faking good designed to detect intentional over-reporting of - Low in L Scale = frank and open regarding symptoms responses to items, can be sarcastic and cynical - detect personal injury claimants who were 2. Infrequency Scale (F Scale): reveal inconsistencies exaggerating their difficulties in answer patterns and could also indicate severe 10. Back Page Infrequency (Fb): reflects significant distress or psychopathology change in the testtaker’s approach to the latter part of - measures the extent to which a person answers in an the test atypical and deviant manner - identify a “fake bad” mode of responding for the last - High in F scale = faking bad, severe distress or 197 items psychopathology - High Fb = exaggeration of psychopathology - Moderate Scores = draw attention to distress as cry for help, may be rebellious, antisocial, curious, Higher-Order Scales psychologically sophisticated 1. Emotional/Internalizing Dysfunction (EID) - Low Scores = perceive the world as most other 2. Thought Dysfunction (THD) people do, possible denial of difficulties 3. Behavioral/Externalizing Dysfunction (BXD) 3. Superlative Self Presentation Scale (S Scale): a Personality Assessment Inventory (PAI) measure of defensiveness; Superlative Self- Leslie Morey Presentation to see if you intentionally distort answers - 18 to 89, PAI-A for 12-18 years old to look better (Social Desirability) - self-administered, paper-and-pencil/online test 4. Correction Scale (K Scale): reflection of the composed of 344 statements for which the respondent frankness of the testtaker’s self-report must choose who true each is for him or her - K Scale = reveals a person’s defensiveness around - assesses psychopathological syndromes and provide certain questions and traits; also faking good information relevant for clinical diagnosis, treatment - K scale sometimes used to correct scores on five planning, and screening for psychopathology clinical scales. The scores are statistically corrected - items for each scale were developed based on for an individual’s overwillingness or unwillingness to extensive reviews of both historical, conceptual admit deviance literature and contemporary, empirical literature, 5. “Cannot Say” (CNS or ?) Scale: measures how a focusing on the concepts that are central and core to person doesn’t answer a test item; number of items the concepts of each construct left unanswered - client might have difficulties with reading, Validity Scales: psychomotor retardation, or extreme defensiveness 1. Inconsistency (ICN) 6. True Response Inconsistency (TRIN): five true, then 2. Infrequency (INF) five false answers 3. Negative Impression (NIM) The reviewers I made are FREE :D instead of selling it, you can share the drive link to others :D Let’s help each other <3 See u soon, future RPms! - Aly Psychological Assessment #BLEPP Source: Cohen & Swerdlik (2018), Kaplan & Saccuzzo (2018), Groth & Wright (2016), Psych Pearls 4. Positive Impression (PIM) - Objective, forced-choice inventory for assessing the relative importance that an individual places on 15 Clinical Scales: personality variables 1. Somatic Complaints (SOM) - Useful in personal counselling and with non-clinical 2. Anxiety (ANX) adults 3. Anxiety-Related Disorders (ARD) - Individual 4. Depression (DEP) Guilford-Zimmerman Temperament Survey 5. Mania (MAN) (GZTS) 6. Paranoia (PAI) - J.P. Guilford & Wayne Zimmerman 7. Schizophrenia (SCZ) - 16 yrs and older 8. Borderline Features (BOR) - items are stated affirmatively rather than in question 9. Antisocial Features (ANT) form, using the 2nd person pronoun 10. Alcohol Problems (ALC) - factor analysis 11. Drug Problems (DRG) Personality Traits measured: Treatment Scales: 1. General Activity (G) 1. Aggression (AGG) 2. Restraint (R) 2. Suicidal Ideation (SUI) 3. Ascendance (A) 3. Stress (STR) 4. Sociability (S) 4. Nonsupport (NON) 5. Emotional Stability (E) 5, Treatment Rejection (RXR) 6. Objectivity (O) 7. Friendliness (F) Interpersonal Scales: 8. Thoughtfulness (T) 1. Dominance (DOM) 9. Personal Relations (P) 2. Warmth (WRM) 10. Masculinity (M) Myers-Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI) NEO Personality Inventory (NEO-PI-R) - Katherine Cook Briggs and Isabel Briggs Myers - Costa and McCrae - Self-report inventory designed to identify a person’s - 17 to 89 years old, NEO-PI-3 12 to 99 years old personality type, strengths, and preferences - Standard questionnaire measure of the Five Factor - Extraversion-Introversion Scale: where you prefer to Model, provides systematic assessment of emotional, focus your attention and energy, the outer world and interpersonal, experiential, attitudinal, and external events or your inner world of ideas and motivational styles experiences - gold standard for personality assessment - Sensing-Intuition Scale: how do you take inform, - Self-Administered you take in or focus on interpreting and adding - Brief Ver: NEO-FFI meaning on the information - T-scores - Thinking-Feeling Scale: how do you make decisions, logical or following what your heart says Neuroticism: - Judging-Perceiving Scale: how do you orient the - identifies individuals who are prone to psychological outer world? What is your style in dealing with the distress outer world – get things decided or stay open to new - measures the tendency toward emotional instability, info and options? turmoil, and general distress Edward’s Preference Personality Schedule (EPPS) - high = anxious, emotionally labile, quick to anger, [B] sad, impulsive, low self-worth - Adults - low = emotionally stable and secure, less prone to - Edwards, A. L. sadness - designed primarily as an instrument for research and - extremely low = less productive, no sense of urgency counselling purposes to provide quick and convenient 1. Anxiety (N1): measure proneness to becoming measures of a number of relatively normal personality tense, jittery, nervous, fearful variables 2. Angry Hostility (N2): tendency toward anger - based of Murray’s Need Theory bitterness, and resentment The reviewers I made are FREE :D instead of selling it, you can share the drive link to others :D Let’s help each other <3 See u soon, future RPms! - Aly Psychological Assessment #BLEPP Source: Cohen & Swerdlik (2018), Kaplan & Saccuzzo (2018), Groth & Wright (2016), Psych Pearls 3. Depression (N3): likelihood to experience the range 3. Feelings (O3): measures openness to one’s inner of depressive affects, including sadness, loneliness, emotional life, including both allowing oneself to feel hopelessness, helplessness, worthlessness, etc. deep emotions and valuing them as integral to the 4. Self-Consciousness (N4): measures discomfort with entire, full human experience social awkwardness 4. Actions (O4): measures the behavioral aspects of 5. Impulsiveness (N5): measures the degree to which openness, relating to trying novel and unknown individuals have difficulty resisting their urges activities, foods, and places 6. Vulnerability (N6): measures the degree to which 5. Ideas (O5): measure a cognitive aspect of openness, individuals feel capable or not of coping with stress related to intellectual curiosity 6. Values (O6): measure the willingness to re-examine Extraversion: one’s values of people with different worldviews, - quantity and intensity of energy directed different cultures, and a changing world, in general - measures the degree to which individuals are not only outgoing and sociable, but also assertive, upbeat, Agreeableness: warm, and friendly - the kind of interactions an individual prefers from - high = talkative, warm, and friendly, leaders, but can compassion to tough mindedness be quite socially dominant and aggressive - measures both attitudes about the trustworthiness - low = prefers to be on their own, reserved and general goodness of others and behaviors related 1. Warmth (E1): measures comfort with interpersonal to respecting, empathizing with, and deferring to intimacy and closeness others 2. Gregariousness (E2): measures the preference for - high = sympathetic, willing to help, cooperative, having other people around believes are others are generally decent and hones 3. Assertiveness (E3): tendency to make oneself heard - low = skeptical of others, expecting competition and and known in social situations challenge from people around them, sarcastic and 4. Activity (E4): measures the amount of energy and stubborn gusto with which individuals live their lives 1. Trust (A1): faith in the goodness of the human spirit 5. Excitement-Seeking (E5): measures the need for 2. Straightforwardness (A2): measures directness, and enjoyment in high-stimulating activities honesty, and genuineness 6. Positive Emotions (E6): tendency to experience 3. Altruism (A3): measure genuine concern for the positive emotions like happiness, joy, bliss, and love well-being of others 4. Compliance (A4): related to the way individuals Openness to Experience: react to conflict with others - active seeking and appreciation of experiences for 5. Modesty (A5): measures the outward-facing trait of their own sake humility, including beliefs about being better than or - encompasses many different personality traits that equal to others and whatever they would be likely to have been researched in the literature, including boast about their achievements imagination, curiosity, attunement toward personal 6. Tender-Mindedness (A6): measure sympathy and emotions, and preference for abstract thinking concern for others - high = intellectually and creatively curious, open to new ideas and to values and theories that may Conscientiousness: contradict or challenge their own - degree of organization, persistence, control, and - low = conservative and conventional, realistic and motivation in goal-directed behavior level-headed in solving problems - measures an array of traits related to both an 1. Fantasy (O1): how active one’s imagination is and orientation toward accomplishing things and the how much fantasy is used not as an escape from behavioral correlates of doing so successfully reality, but as a way to create, solve problems, and - high = motivated to achieve their goals, plans and even interact with the world organize well, extremely reliable but can also be 2. Aesthetics (O2): measures the interest in and moralistic and judgmental of both themselves and absorption by art, beauty, and even the inherent others beauty in nature The reviewers I made are FREE :D instead of selling it, you can share the drive link to others :D Let’s help each other <3 See u soon, future RPms! - Aly Psychological Assessment #BLEPP Source: Cohen & Swerdlik (2018), Kaplan & Saccuzzo (2018), Groth & Wright (2016), Psych Pearls - low = often unprepared and disorganized, do not E Dominance (does) think through potential consequences before acting, F Liveliness (life) not overly driven to succeed G Rule-Consciousness (really) 1. Competence (C1): measure the feeling that one is H Social Boldness (suck?) generally effective and capable to succeed in tasks and I Sensitivity (satisfy my) life in general L Vigilance (virgin) 2. Order (C2): measures preference for neatness, M Abstractedness (ass) tidiness, and orderliness N Privateness (putangina) 3. Dutifulness (C3): measures the degree to which 0 Apprehension (ay wow) individuals do things that they feel they should do Q1 Openness to change (oh) 4. Achievement Striving (C4): relates to an attitude of Q2 Self-Reliance (shit!) aspiration and striving to succeed in their goals Q3 Perfectionism (perfect) 5. Self-Discipline (C5): ability to actually follow Q4 Tension (timing!) through on a plan once it is set 6. Deliberation (C6): measures the degree to which Global Scales: individuals think and plan out carefully before acting 1. Extraversion 2. Anxiety Panukat ng Ugali at Pagkatao/Panukat ng 3. Tough-Mindedness Pagkataong Pilipino 4. Independence - 13 years and older 5. Self-Control - Indigenous personality test - Tap specific values, traits and behavioral dimensions Response Style Indices: related or meaningful to the study of Filipinos a. Impression Management – answering in socially desirable or undesirable way 1. Pagkamaalalahanin (Thoughtfulness) - sten score of 9 or 10 at or above the 95th percentile 2. Pagkamaayos (Organized) denotes Social Desirability 3. Pagkamadaldal (Social Curiosity) - a sten score of 1 or 2, or a score below the 5th 4. Pagkamagalang (Respectfulness) percentile means that the client has attempted to give a 5. Pagkamahinahon (Emotional Stability) socially unfavorable image 6. Pagkamalikhain (Creativity) b. Acquiescence – agree to questions regardless of the 7. Pagkamapagkumbaba (Humility) content 8. Pagkamapagsapalaran (Risk-Taking) - scores at or above 95th percentile 9. Pagkamadamdamin (Sensitiveness) - count each “true” 10. Pagkamasiyahin (Cheerfulness) - confused when completing the questionnaire 11. Pagkamasikap (Achievement-Oriented) c. Infrequency – detects unusual responses, responded 12. Pagkamasunurin (Obedience) randomly or indecisively 13. Pagkamatalino (Intelligence) - count “B or ?” response 14. Pagkamatapat (Honesty) - scores at or above 95th percentile 15. Pagkamatiyaga (Patience) - poor comprehension 16. Pagkamatulungin (Helpfulness) - trying to avoid making a wrong impression 17. Pagkamaunawain (Capacity for Understanding) 18. Pagkapalakaibigan (Sociability) Big Five Inventory-II (BFI-2) 19. Pagkaresponsable (Responsibility) - Soto & John - Assesses big 5 domains and 15 facets Sixteen Personality Factor Questionnaire (16PF) - for commercial purposes to researches and students - Raymond Cattell - constructed through factor analysis California Psychological Inventory (CPI-434) - Evaluates a personality on two levels of traits [C] - Harrison G. Gough Primary Scales: - 13 years old and older A Warmth (where) - create efficient and productive organizations, B Reasoning (r) promote teamwork, build leadership competencies, C Emotional Stability (everyone?) The reviewers I made are FREE :D instead of selling it, you can share the drive link to others :D Let’s help each other <3 See u soon, future RPms! - Aly Psychological Assessment #BLEPP Source: Cohen & Swerdlik (2018), Kaplan & Saccuzzo (2018), Groth & Wright (2016), Psych Pearls and find and develop employees who are destined for 5. Deviation success 6. Hypochondriasis - CPI-260, short form, 40-60 minutes 7. Impulse Expression - T-Scores 8. Interpersonal Problems 9. Persecutory Ideas Folk Scales: 10. Self-Depreciation 1. Capacity for Status 11. Social Introversion 2. Sociability 12. Thinking Disorder 3. Social Presence Projective Tests 4. Self-Acceptance Rorshcach Inkblot Test 5. Sense of Well-Being [C] 6. Responsibility - Hermann Rorschach 7. Socialization - 5 years and older 8. Self-Control - subjects look at 10 ambiguous inkblot images and 9. Tolerance describe what they see in each one 10. Good Impression - once used to diagnose mental illnesses like 11. Communality schizophrenia 12. Achievement via Conformance - Exner System: coding system used in this test 13. Achievement via Independence - Content: the name or class of objects used in the 14. Intellectual Efficiency patient’s responses 15. Psychological Mindedness 16. Femininity/Masculinity Independence Content: 17. Flexibility and Empathy 1. Nature Strong Campbell Interest Inventory (SCII) 2. Animal Feature - E.K. Strong 3. Whole Human - 15 years old and older 4. Human Feature - help individuals in identifying their work personality 5. Fictional/Mythical Human Detail by exploring their interests in six broad areas: 6. Sex RIASEC Thurstone Interest Schedule (TIS) Determinants: [A] 1. Form - Thurstone, L.L. 2. Movement - checklist by which a person can systematically 3. Color clarify his understanding of his vocational interest 4. Shading - designed as a counseling instrument to be used in 5. Pairs and Reflections situations in which the client-counselor relationship is such that straightforward and honest Location: 1. W – the whole inkblot was used to depict an image Basic Personality Inventory (BPI) 2. D – commonly described part of the blot was used [C] 3. Dd – an uncommonly described or unusual detail - Adults & Adolescents was used - Douglas Jackson 4. S – the white space in the background was used - self-report measure of general domain of psychopathology Thematic Apperception Test - 240 true/false items, 11 substantive clinical scales [C] and one critical item scale - Christiana Morgan and Henry Murray - 5 and above Dimensions: - 31 picture cards serve as stimuli for stories and 1. Alienation descriptions about relationships or social situations 2. Anxiety - popularly known as the picture interpretation 3. Denial technique because it uses a standard series of 4. Depression The reviewers I made are FREE :D instead of selling it, you can share the drive link to others :D Let’s help each other <3 See u soon, future RPms! - Aly Psychological Assessment #BLEPP Source: Cohen & Swerdlik (2018), Kaplan & Saccuzzo (2018), Groth & Wright (2016), Psych Pearls provocative yet ambiguous pictures about which the - reveals the maturation level of visuomotor subject is asked to tell a story perceptions, which is associated with language ability - also modified African American testtakers and various functions of intelligence Children’s Apperception Test House-Tree-Person Test (HTP) - Bellak & Bellak - John Buck and Emmanuel Hammer - 3-10 years old - 3 years and up - based on the idea that animals engaged in various - measures aspects of a person’s personality through activities were useful in stimulating projective interpretation of drawings and responses to questions storytelling by children - can also be used to assess brain damage and general mental functioning Hand Test - measures the person’s psychological and emotional - Edward Wagner functioning - 5 years old and above - The house reflects the person’s experience of their - used to measure action tendencies, particularly immediate social world acting out and aggressive behavior, in adults and - The tree is a more direct expression of the person’s children emotional and psychological sense of self - 10 cards (1 blank) - The person is a more direct reflection of the person’s Apperceptive Personality Test (APT) sense of self - Holmstrom et. Al. Draw-A-Person Test (DAP) - attempt to address the criticisms of TAT - Florence Goodenough - introduced objectivity in scoring system - 4 to 10 years old - 8 cards include male and female of different ages - a projective drawing task that is often utilized in and minority group members psychological assessments of children - testtakers will respond to a series of multiple choice - Aspects such as the size of the head, placement of questions after storytelling the arms, and even things such as if teeth were drawn Word Association Test (WAT) or not are thought to reveal a range of personality - Rapaport et. Al. traits - presentation of a list of stimulus words, assessee - Helps people who have anxieties taking tests (no responds verbally or in writing the first thing that strict format) comes into their minds - Can assess people with communication problems Rotter Incomplete Sentences Blank (RISB) - Relatively culture free - Julian Rotter & Janet Rafferty - Allow for self-administration - Grade 9 to Adulthood Kinetic Family Drawing - most popular SCT - Burns & Kaufman SACK’s Sentence Completion Test (SSCT) - derived from Hulses’ FDT “doing something” - Joseph Sacks and Sidney Levy Controlled Oral Word Association Test (COWAT) - 12 years old and older - measures spontaneous production of words - asks respondents to complete 60 questions with the belonging to the same category or beginning with first thing that comes to mind across four areas: some designated letter Family, Sex, Interpersonal, Relationships and Self Clinical & Counseling Tests concept Millon Clinical Multiaxial Scale-IV (MCMI-IV) Bender-Gestalt Visual Motor Test Theodore Millon [B] - 18 years old and above - Lauretta Bender - standardized, self-report questionnaire that assesses a - 4 years and older wide range of information related to a client’s - consists of a series of durable template cards, each personality, emotional adjustment, and attitude toward displaying a unique figure, then they are asked to taking tests draw each figure as he or she observes it - for diagnosing and treatment of personality disorders - provides interpretative information about an - exaggeration of polarities results to maladaptive individual’s development and neuropsychological behavior functioning The reviewers I made are FREE :D instead of selling it, you can share the drive link to others :D Let’s help each other <3 See u soon, future RPms! - Aly Psychological Assessment #BLEPP Source: Cohen & Swerdlik (2018), Kaplan & Saccuzzo (2018), Groth & Wright (2016), Psych Pearls 2. Underreporting of Difficulties (Faking Good): low Validity/Modifying Indices: scores on Disclosure (X) and Debasement (Z), high 1. Invalidity (V) – person answers randomly score on Desirability (Y) 2. Inconsistency (W) – expected to be answered both 3. Fake Bad: high score on Disclosure (X) and high in same direction score in Debasement (Z) 3. Disclosure (X) – designed to measure whether a Beck Depression Inventory (BDI-II) client’s responses were open and revealing as opposed - Aaron Beck to defensive and secretive - 13 to 80 years old 4. Desirability (Y) – measure of defensive responding - 21-item self-report that taps Major Depressive 5. Debasement (Z) – extent to which a person is symptoms accdg. to the criteria in the DSM describing himself in negative, pathological terms - Beck’s Anxiety Inventory (BAI) MacAndrew Alcoholism Scale (MAC & MAC-R) Clinical Personality Patterns: - from MMPI-II 1. Schizoid - Personality & attitude variables thought to underlie 2. Avoidant alcoholism 3. Melancholic California Psychological Inventory (CPI-III) 4. Dependent - attempts to evaluate personality in normally adjusted 5. Histrionic individuals 6. Turbulent - has validity scales that determines faking bad and 7. Narcissistic faking good 8. Antisocial - interpersonal style and orientation, normative 9. Sadistic orientation and values, cognitive and intellectual 10. Compulsive function, and role and personal style 11. Negativistic - has special purpose scales, such as managerial 12. Masochistic potential, work orientation, creative temperament, leadership potential, amicability, law enforcement Severe Personality Pathology: orientation, tough-mindedness 1. Schizotypal Rosenberg Self-Esteem Scale 2. Borderline - measures global feelings of self-worth 3. Paranoid - 10-item, 4 point likert scale - used with adolescents Clinical Syndromes: Dispositional Resilience Scale (DRS) 1. Generalized Anxiety - measures psychological hardiness defined as the 2. Somatic Symptom ability to view stressful situations as meaningful, 3. Bipolar Spectrum changeable, and challenging 4. Persistent Depression Ego Resiliency Scale-Revised 5. Alcohol Use - measure ego resiliency or emotional intelligence 6. Drug Use HOPE Scale 7. Posttraumatic Stress - developed by Snyder - Agency: cognitive model with goal driven energy Severe Clinical Syndromes: - Pathway: capacity to contrast systems to meet goals 1. Schizophrenic Spectrum - good measure of hope for traumatized people 2. Major Depression - positively correlated with health psychological 3. Delusional adjustment, high achievement, good problem solving skills, and positive health-related outcomes Validity Indicators: Satisfaction with Life Scale (SWLS) 1. Random Responding: scores of one or more on the - overall assessment of life satisfaction as a cognitive three items of the MCMI-IV Invalidity scale (items judgmental process 49, 98, 160) Positive and Negative Affect Schedule (PANAS) The reviewers I made are FREE :D instead of selling it, you can share the drive link to others :D Let’s help each other <3 See u soon, future RPms! - Aly Psychological Assessment #BLEPP Source: Cohen & Swerdlik (2018), Kaplan & Saccuzzo (2018), Groth & Wright (2016), Psych Pearls - measure the level of positive and negative emotions a test taker has during the test administration 6 Categories: 1. Home Living Pictorial Self-Concept Scale for Children (PSC) 2. Community Living - Jack Joseph 3. Life-Long Learning - 3 yrs to 13 yrs old 4. Employment - Allows clinician to measure self-concept in children 5. Health and Safety as young as 3 6. Social Activities - Identifies children with negative self-appraisal put them at risk for academic and behavioral difficulties Self-Directed Search (SDS) - Let youngster respond using pictures rather than - career assessment and exploration tool that matches words your aspirations, activities, and talents to the career - Children are shown pairs of illustrations representing choices and educational opportunities that fit you best common self-appraisal situations and are asked to Eating Disorder Inventory (EDI-3) choose between a picture representing negative and - self-report measures of constructs shown to be positive self-concept clinically relevant in individuals with eating disorders - Can be used to evaluate psychological and educational interventions 12 Primary Scales Halstead-Reitan Neuropsychological Battery Drive for Thinness (HRNB) Bulimia - Ward Halstead & Ralph Reitan Body Dissatisfaction - 15 yrs old and older Low Self-Esteem - set of tests used to diagnose localize brain damage Personal Alienation by providing a comprehensive assessment of cognitive Interpersonal Insecurity functioning Interpersonal Alienation Interoceptive Deficits Five Core Subtests: Emotional Dysregulation 1. Category Test Perfectionism 2. Tactual Performance Test Asceticism 3. Seashore Rhythm Test Maturity Fears 4. Speech Sounds Perception Vineland Adaptive Behavior Scales (VABS-II) 5. Finger Tapping Test - leading instrument for supporting the diagnosis of intellectual and developmental disabilities Five Optional Subtests: 1. Trail Making Test Domains: 2. Reitan Indiana Aphasia Screening Test 1. Communication 3. Reitan-Klove Sensory Perceptual Examination 2. Daily Living Skills 4. Grip Strength Test 3. Socialization 5. Lateral Dominance Examination Neuropsychological Impairment Scale (NIS) Supplemental Scales: [C] 1. Motor Skills - William E. O’Donell et. Al. 2. Maladaptive Behaviors - 18 years old – 88 yrs old Kiddie Schedule of Affective Disorders and - self-report, observer report, and senior interview Schizophrenia-Present and Lifetime Version (K- identify neuropsychological symptoms and defiency SADS-PL) - produces one Global Measure of Impairment (GMI) - assesses hypomania, cyclothymia, and BD Supports Intensity Scale (SIS-A/SIS-C) - also combines dimensional and categorical - evaluates the support needed by an individual assessment approaches to diagnose current and past - focuses on the types and intensities of supports episodes of psychopathology in children and needed to enable an individual to lead a normal adolescents independent life Child Behavior Checklist (CBCL) The reviewers I made are FREE :D instead of selling it, you can share the drive link to others :D Let’s help each other <3 See u soon, future RPms! - Aly Psychological Assessment #BLEPP Source: Cohen & Swerdlik (2018), Kaplan & Saccuzzo (2018), Groth & Wright (2016), Psych Pearls - 6 yrs old to 18 yrs old - assesses the anxiety in children - Parent or other close relatives of the child complete - intended to provide an indicator of the number and the form regarding the behavior of the client severity of anxiety symptoms experienced by younger - 118 items regarding behavior problems children - Teacher’s Report Form and Youth Self-Report Form - can assist in identifying BD in children Subscales GAD Subscales: Social Anxiety Aggressive Behavior OCD Anxious/Depressed Physical Injury Fears Attention Problems Separation Anxiety Rule-Breaking Behavior Children’s Yale-Brown Obsessive-Compulsive Social-Problems Scale (CY-BOCS) Somatic Complaints - 6 yrs old to 17 yrs old Thought Problems - designed to rate the severity of OC symptoms in Withdrawn/Depressed children and adolescents Revised Child Anxiety and Depression Scale - clinician-rated (RCADS) Dimensional Yale-Brown Obsessive-Compulsive - 8 yrs old to 18 yrs old Scale (DY-BOCS) - 47-item, youth self-report questionnaire - assesses the presence and severity of obsessive - Revised Child Anxiety and Depression Scale – compulsive-symptoms Parent Version (RCADS-P) Children’s Obsessional Compulsive Inventory – Revised Self Report (ChOCI-R-S) Subscales: - 32-item self-report measure assessing the presence Anxiety Disorder and severity of obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD) Social Phobia in children and adolescents aged 7-17 years GAD Vineland Adaptive Behavior Scale (VABS) Panic Disorder [B] OCD - most popular measures of adaptive behavior in Low Mood children Screen for Child Anxiety Related Emotional - 0-90 years old Disorders (SCARED) Adaptive Behavior Assessment System (ABAS-III) - measure widely used to assess childhood anxiety - used to assess the functional skills necessary for the based on parent and child support daily living - Child and parent - 0-89 years old Spence Children’s Anxiety Scale (SCAS) 7-Minute Screen - 8 yrs old to 15 yrs old - identify patients with Alzheimer’s Disease - assess severity of anxiety symptoms in children Strengths and weaknesses of assessment tools (2) - Child and Parent Pros Cons Test Subscales: - can gather a sample of - In crisis situations when Separation Anxiety behavior objectively with relatively rapid decisions Social Phobia lesser bias need to be made, it can be OCD - flexible, can be verbal or impractical to take the Panic/Agoraphobia nonverbal time required to GAD administer and interpret Fears of Physical Injury tests Preschool Anxiety Scale (PAS) Interview - 2 ½ yrs old to 6 ½ yrs old - can take note of verbal - sometimes, due to - completed by parent/guardian and nonverbal cues negligence of interviewer The reviewers I made are FREE :D instead of selling it, you can share the drive link to others :D Let’s help each other <3 See u soon, future RPms! - Aly Psychological Assessment #BLEPP Source: Cohen & Swerdlik (2018), Kaplan & Saccuzzo (2018), Groth & Wright (2016), Psych Pearls - flexible and interviewee, it can know how their - expensive - time and cost effective miss out important colleagues think - inconvenient to assess in - both structured and information - group can discuss ways a real situation unstructured allows - interviewer’s effect on to potentially resolve the - While some employees clinicians to place a wider, the interviewee situation and participants will be comfortable role more meaningful context - various error such as leave with as much playing, they’re less adept - can also be used to help halo effect, primacy information as possible, at getting into the required predict future behaviors effect, etc. resulting in more efficient mood needed to actually interviews allow - interrater reliability handling of similar real- replicate a situation - clinicians to establish - interviewer bias life scenarios rapport and encourage Test Administration, Scoring, Interpretation and client self-exploration. Usage (20) Portfolio Detect Errors and impacts in Test Issues in Intelligence Testing - provides comprehensive - can be very demanding 1. Flynn Effect – progressive rise in intelligence score illustration of the client - time consuming that is expected to occur on a normed intelligence test which highlights the from the date when the test was first normed strengths and weaknesses ▪ Gradual increase in the general intelligence Observation among newborns - flexible - For private practitioners, ▪ Frog Pond Effect: theory that individuals - suitable for subjs that it is typically not practical evaluate themselves as worse when in a group of cannot be studied in lab or economically feasible high-performing individuals setting to spend hours out of the 2. Culture Bias of Testing - more realistic consulting room ▪ Bias In Testing: presence of systematic error in - affordable observing clients as they the measurement of certain factors - can detect patterns go about their daily lives ▪ Culture-Free: attempt to eliminate culture so - lack of scientific control, nature can be isolated ethical considerations, ▪ Impossible to develop bec culture is evident in its and potential for bias from influence since birth or an individual and the observers and subjects interaction between nature and nurture is - unable to draw causecumulative and not relative and-effect conclusions ▪ Culture Fair: minimize the influence of culture - lack of control with regard to various aspects of the evaluation - lack of validity procedures - observer bias ▪ Fair to all, fair to some cultures, fair only to one Case History culture - can fully show the - cannot be used to ▪ Culture Loading: the extent to which a test experience of the observer generalize a phenomenon incorporates the vocabulary concepts traditions, in the program knowledge etc. with particular culture - shed light on an Test Equivalence individual’s past and Linguistic: wording and content current adjustment as well - whether the test has been translated accurately as on the events and - Back-Translation: once translated to a certain circumstances that may language, it is translated back to the original language have contributed to any Conceptual: construct has the same meaning changes in adjustment - requires constructs to have the same meaning in Role Play various cultures - encourages individuals - may not be as useful as Metric: same psychometric feature across different to come together to find the real thing in all groups/culture solutions and to get to situations Errors: Reliability - time-consuming The reviewers I made are FREE :D instead of selling it, you can share the drive link to others :D Let’s help each other <3 See u soon, future RPms! - Aly Psychological Assessment #BLEPP Source: Cohen & Swerdlik (2018), Kaplan & Saccuzzo (2018), Groth & Wright (2016), Psych Pearls Classical Test Theory (True Score Theory) – score Error: Time Sampling on ability tests is presumed to reflect not only the - the longer the time passes, the greater likelihood that testtaker’s true score on the ability being measured the reliability coefficient would be insignificant but also the error - Carryover Effects: happened when the test-retest ▪ Error: refers to the component of the observed interval is short, wherein the second test is influenced test score that does not have to do with the by the first test because they remember or practiced the testtaker’s ability previous test = inflated correlation/overestimation of ▪ Errors of measurement are random reliability - Practice Effect: scores on the second session are higher due to their experience of the first session of testing - test-retest with longer interval might be affected of other extreme factors, thus, resulting to low correlation - target time for next administration: at least two weeks Parallel Forms/Alternate Forms Reliability Error: Item Sampling (Immediate), Item Sampling changes over time (delayed) - Counterbalancing: technique to avoid carryover ▪ The greater number of items, the higher the effects for parallel forms, by using different sequence reliability for groups ▪ Factors that contribute to inconsistency: - most rigorous and burdensome, since test developers characteristics of the individual, test, or situation, create two forms of the test which have nothing to do with the attribute being - main problem: difference between the two tests measured, but still affect the scores - test scores may be affected by motivation, fatigue, or o Error Variance – variance from irrelevant random intervening events sources - create a large set of questions that address the same Measurement Error – all of the factors associated construct then randomly divide the questions into two with the process of measuring some variable, other than sets the variable being measured Internal Consistency (Inter-Item Reliability) - difference between the observed score and the true Error: Item Sampling Homogeneity score Split-Half Reliability Positive: can increase one’s score Error: Item sample: Nature of Split - Negative: decrease one’s score Inter-Scorer Reliability - Sources of Error Variance: Error: Scorer Differences a. Item Sampling/Content Sampling o Standard Error of Measurement – provide a b. Test Administration measure of the precision of an observed test score c. Test Scoring and Interpretation ▪ Standard deviation of errors as the basic measure Random Error – source of error in measuring a of error targeted variable caused by unpredictable fluctuations ▪ Index of the amount of inconsistent or the amount and inconsistencies of other variables in measurement of the expected error in an individual’s score process (e.g., noise, temperature, weather) ▪ Allows to quantify the extent to which a test Systematic Error – source of error in a measuring a provide accurate scores variable that is typically constant or proportionate to ▪ Provides an estimate of the amount of error what is presumed to be the true values of the variable inherent in an observed score or measurement being measured ▪ Higher reliability, lower SEM - has consistent effect on the true score ▪ Used to estimate or infer the extent to which an - SD does not change, the mean does observed score deviates from a true score ▪ Error variance may increase or decrease a test ▪ Standard Error of a Score score by varying amounts, consistency of test ▪ Confidence Interval: a range or band of test score, and thus, the reliability can be affected scores that is likely to contain true scores Test-Retest Reliability o The reviewers I made are FREE :D instead of selling it, you can share the drive link to others :D Let’s help each other <3 See u soon, future RPms! - Aly Psychological Assessment #BLEPP Source: Cohen & Swerdlik (2018), Kaplan & Saccuzzo (2018), Groth & Wright (2016), Psych Pearls Standard Error of the Difference – can aid a test - Halo Effect: tendency to give high score due to failure user in determining how large a difference should be to discriminate among conceptually distinct and before it is considered statistically significant potentially independent aspects of a ratee’s behavior o Standard Error of Estimate – refers to the standard - snap judgement on the basis of positive trait error of the difference between the predicted and - Horn Effect: Opposite of Halo Effect observed values - One way to overcome rating errors is to use rankings o Four Possible Hit and Miss Outcomes 5. Fundamental Attribution Error – tendency to 1. True Positives (Sensitivity) – predict success explain someone’s behavior based on internal factors that does occur such as personality or disposition, and to underestimate 2. True Negatives (Specificity) – predict failure the influence the external factors have on another that does occur person’s behavior, blaming it on the situation 3. False Positive (Type 1) – success does not occur - Barnum Effect: people tend to accept vague 4. False Negative (Type 2) – predicted failure but personality descriptions as accurate descriptions of succeed themselves (Aunt Fanny Effect) o Bias – factor inherent in a test that systematically prevents accurate, impartial measurement ▪ Prejudice, preferential treatment ▪ Prevention during test dev through a procedure called Estimated True Score Transformation o Social Desirability – tendency to say good things about yourself or to mark items that you believe will be approved by the examiner Ethical Principles and Standards of Practice (19) o Assessment should only be conducted in the context of a clearly defined professional relationship, thus, nature, purpose, and conditions of the relationship must be discussed and agreed on Errors due to Behavioral Assessment o It is the examiner’s responsibility to recognize the 1. Reactivity – when evaluated, the behavior increases possible influences he or she may exert on the client - Hawthorne Effect and to optimize the level of rapport 2. Drift – moving away from what one has learned o It is particularly important to assess the degree of the going to idiosyncratic definitions of behavior client’s motivation and his or her overall level of - subjects should be retrained in a point of time anxiety - Contrast Effect: cognitive bias that distorts our ▪ There could be times that testing must be halted perception of something when we compare it to due to the client’s emotional state something else, by enhancing the differences between o The more the examiner likes the client, the more them likely he or she will be to score an ambiguous 3. Expectancies – tendency for results to be influenced response in a direction favorable to the client by what test administrators expect to find o If mistakes were made, they should do something to - Rosenthal/Pygmalion Effect: Test administrator’s correct or minimize the mistakes expected results influences the result of the test o If an ethical violation made by another psychologist - Golem Effect: negative expectations decreases one’s was witnessed, they should resolve the issue with performance informal resolution, as long as it does not violate any 4. Rating Errors – intentional or unintentional misuse confidentiality rights that may be involved of the scale o If informal resolution is not enough or appropriate, - Leniency Error: rater is lenient in scoring (Generosity referral to state or national committees on Error) professional ethics, state licensing boards, or the - Severity Error: rater is strict in scoring appropriate institutional authorities can be done. - Central Tendency Error: rater’s rating would tend to Still, confidentiality rights of the professional in cluster in the middle of the rating scale question must be kept. o The reviewers I made are FREE :D instead of selling it, you can share the drive link to others :D Let’s help each other <3 See u soon, future RPms! - Aly Psychological Assessment #BLEPP Source: Cohen & Swerdlik (2018), Kaplan & Saccuzzo (2018), Groth & Wright (2016), Psych Pearls Failure to cooperate in ethics investigation itself, is o Before recording voices or images, they must obtain an ethics violation, unless they request for deferment permission first from all persons involved or their of adjudication of an ethics complaint legal rep o Psychologists must file complaints responsibly by o Only discuss confidential information with persons checking facts about the allegations clearly concerned/involved with the matters o Psychologists DO NOT deny persons employment, o Disclosure is allowed with appropriate consent advancement, admissions, tenure or promotion based ▪ No consent is not allowed UNLESS mandated by solely upon their having made or their being the the law subject of an ethics complaint o No disclosure of confidential information that could ▪ Just because they are questioned by the ethics lead to the identification of a client unless they have committee or involved in an on-going ethics obtained prior consent or the disclosure cannot be investigation, they would be discriminated or avoided denied advancement ▪ Only disclose necessary information ▪ Unless the outcome of the proceedings are o Exemptions to disclosure: already considered ✓ If the client is disguised/identity is protected o Psychologists should do their services within the ✓ Has consent boundaries of their competence, which is based on ✓ Legally mandated the amount of training, education, experience, or o Psychologists can create public statements as long as consultation they had they would be responsible for it o When they are tasked to provide services to clients ▪ They cannot compensate employees of the media who are deprived with mental health services (e.g., in return for publicity in a news item communities far from the urban cities), however, ▪ Paid Advertisement must be clearly recognizable they were still not able to obtain the needed ▪ when they are commenting publicly via internet, competence for the job, they could still provide media, etc., they must ensure that their statement services AS LONG AS they make reasonable effort are based on their professional knowledge in to obtain the competence required, just to ensure that accord with appropriate psych literature and the services were not denied to those communities practice, consistent with ethics, and do not o During emergencies, psychologists provide services indicate that a professional relationship has been to individuals, even though they are yet to complete established with the recipient the competency/training needed just to ensure that o Must provide accurate information and obtain services were not denied. However, the services are approval prior to conducting the research discontinued once the appropriate services are o Informed consent is required, which include: available ✓ Purpose of the research o Any consent involves a clear explanation of what ✓ Duration and procedures procedures will occur, the relevance of the testing, ✓ Right to decline and withdraw and how the results will be used ✓ Consequences of declining or withdrawing ✓ Potential risks, discomfort, or adverse effects Privacy Confidentiality ✓ Benefits - actions of honoring an - refers to actions of ✓ Limits of confidentiality individual’s right to keeping documents, files, ✓ Incentives for participation control who has access for and other data away from ✓ Researcher’s contact information him/herself and how their people or entities that are o Permission for recording images or vices are needed information is shared not meant to see/hear unless the research consists of solely naturalistic publicly them observations in public places, or research designed - personal - relational includes deception - right - agreement ▪ Consent must be obtained during debriefing o Psychologists should discuss the limits of o Dispense or Omitting Informed consent only when: confidentiality, uses of the information that would be 1. Research would not create distress or harm generated from the services to the persons and ▪ Study of normal educational practices conducted organizations with whom they establish a scientific in an educational settings or professional relationships o The reviewers I made are FREE :D instead of selling it, you can share the drive link to others :D Let’s help each other <3 See u soon, future RPms! - Aly Psychological Assessment #BLEPP Source: Cohen & Swerdlik (2018), Kaplan & Saccuzzo (2018), Groth & Wright (2016), Psych Pearls Anonymous questionnaires, naturalistic ▪ Spatial Visualization observation, archival research ▪ Associative Memory ▪ Confidentiality is protected ▪ Perceptual Speed 2. Permitted by law ▪ Reasoning o Avoid offering excessive incentives for research o Cattell: Crystallized and Fluid Intelligence participation that could coerce participation o Spearman: Two-Factor Theory of Intelligence o DO not conduct study that involves deception unless ▪ General (g) Intelligence they have justified the use of deceptive techniques in ▪ Specific (s) Ability the study o Gardner: Theory of Multiple Intelligences ▪ Must be discussed as early as possible and not ▪ Visual-Spatial during the conclusion of data collection ▪ Linguistic-Verbal o They must give opportunity to the participants about ▪ Logical-Mathematical the nature, results, and conclusions of the research ▪ Body-Kinesthetic and make sure that there are no misconceptions about ▪ Musical the research ▪ Interpersonal o Must ensure the safety and minimize the discomfort, ▪ Intrapersonal infection, illness, and pain of animal subjects ▪ Naturalistic ▪ If so, procedures must be justified and be as Malingering – the deliberate feigning of an illness or minimal as possible disability to achieve a particular desired outcome ▪ During termination, they must do it rapidly and Faking Bad (Overreporting) - appear worse than minimize the pain actually is the case o Must no present portions of another’s work or data Faking Good (Underreporting) - attempt to appear as their own better than is actually the case ▪ Must take responsibility and credit, including - Intentional (Social Desirability) or Unintentional authorship credit, only for work they have (Impression Management) actually performed or to which they have Nay-Saying – answering question negatively of their substantially contributed content, which can distort results of surveys, ▪ Faculty advisors discuss publication credit with questionnaires, and similar instruments students as early as possible - Non-acquiescence o After publishing, they should not withhold data from Yea-Saying – answering question positively regardless other competent professionals who intends to of their content, which can distort the results of surveys reanalyze the data - Acquiescence ▪ Shared data must be used only for the declared Self-Deception – process of denying or rationalizing purpose away the relevance, significance, or importance of o RA 9258 – Guidance and Counseling Act of 2004 opposing evidence and logical argument o RA 9262 – Violence Against Women and Children o Jungian Typology: o RA 7610 – Child Abuse Extraverted Thinking – principle, idealistic, o RA 9165 – Comprehensive Dangerous Drugs Act of objective, rational 2002 Introverted Thinking – influenced by ideas, o RA 11469 – Bayanihan to Heal as One Act independent, often fearful of intimacy o RA 7277 – Magna Carta for Disabled Persons Extraverted Feeling – adaptive, relating well to the o RA 11210 – Expanded Maternity Leave Law external environment o RA 11650 – Inclusive Education Law Introverted Feeling – sympathetic, pleases others, o RA 10173 – Data Privacy Act may be dependent, reserved o House Bill 4982 – SOGIE Bill Extraverted Sensation – realistic, concrete, pleasant, o Art. 12 of Revised Penal Code – Insanity Plea and friendly Additional Information Introverted Sensation – calm, passive, restrained, o Thurstone: Seven Primary Mental Abilities controlled, and controlling ▪ Verbal Comprehension Extraverted Intuition – enterprising, outgoing, can be ▪ Word Fluency irresponsible ▪ Number Facility The reviewers I made are FREE :D instead of selling it, you can share the drive link to others :D Let’s help each other <3 See u soon, future RPms! - Aly ▪ Psychological Assessment #BLEPP Source: Cohen & Swerdlik (2018), Kaplan & Saccuzzo (2018), Groth & Wright (2016), Psych Pearls o Mental Status Exam – appropriate before Introverted Intuition – mystical, dreamer, and artist, assessment to determine the appropriateness of more can be obsessive formal psychological testing o Types of Interpretation: Appearance – client’s clothing, posture, gestures, Concrete – limited to the subtest and subscale scores speech, personal care/hygiene, and any unusual and does not draw conclusions beyond the scores physical features Mechanical – pattern of subscales; significant Relatedness – facial expressions, eye contact, activity difference between scores level, degree of cooperation, notable physical Individualized – interpreting the results in the context characteristics, and attentiveness of the larger picture Speech/Language – often proxies for their thought o 16 PF Factors processes, as they relate to the primary mode of Global Factors Cont. Primary Factors communicating thoughts to the outside world Extraversion (4) Warmth - help clinicians determine the possibility of poor or Liveliness exceptional cognitive functioning, focus, and Social Boldness confusion and possible thought disorder Privateness - evaluating how well individuals understand language, Self-Reliance as evidenced by responding appropriately to directions Independence (4) Dominance and conversations (receptive language) Social Boldness Affect/Mood (Feeling) – client might be cold or warm, Vigilance distant or close, labile, or have flat affect Openness to Change - Mood: dominant emotion reported during the Tough-Mindedness Warmth interview (6) Sensitivity - Affect: client’s outwardly projected range of emotions Abstractedness Thought Process Openness to Change Thought Content – can be coherent, spontaneous, and Self-Control (4) Liveliness comprehensible or may contain unusual features Rule-Consciousness Memory Abstractedness Attention/Concentration Perfectionism Alertness/Orientation – they know who they are, Anxiety (5) Emotional Stability where they are, and when current and past events have Vigilance occurred or are occurring Apprehension - Sensorium: refers to how intact their physical sensory Tension processes are to receiving and integrating information o Interpretation of Assessment Information: (hearing, smell, vision, and touch and might range from Intuitive Approach – no identifiable basis, based on being clouded to clear) feelings and instincts, and have no empirical Judgment/Planning – vary how they provide for explanation themselves, evaluate risks, and make plans Authoritative Approach – based on experts or wellInsight – why they believe they were referred for known psychologists evaluation and, in a wider context, they attitudes Empirical/Conceptual – derived from researches towards their cultures o Function of Tests: o Types of Decisions made through Psychological Additive Function – measuring different domains to Tests: broaden understanding of the person being examined Individual – testtakers use their scores to make Confirmatory Function – two or more measures of decisions about themselves the same domain are placed in a test battery to Institutional – made by another entity about a person’s strengthen initial impressions score Complementary Function – multiple measures of the Comparative – made by comparing the test scores of same dome yield different rather than confirmatory a number of people to see who has the best score results Absolute – decisions made by other by looking who has the minimum score needed to qualify The reviewers I made are FREE :D instead of selling it, you can share the drive link to others :D Let’s help each other <3 See u soon, future RPms! - Aly Psychological Assessment #BLEPP Source: Cohen & Swerdlik (2018), Kaplan & Saccuzzo (2018), Groth & Wright (2016), Psych Pearls end Congratulations for reaching the end of this reviewer! <3 Remember to take rest if you need to and be less harsh to yourself. Reward yourself, you deserve it. You can never learn everything but at least you still did learn something. Progress is progress. The most important thing is you will get there! Claim that license! Congratulations, Future RPm! The reviewers I made are FREE :D instead of selling it, you can share the drive link to others :D Let’s help each other <3 See u soon, future RPms! - Aly