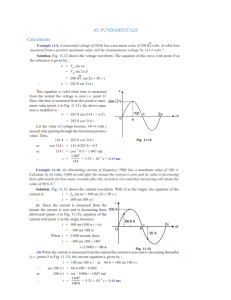
1 QUESTION 2(E). -57.45e-30V -57.45e-30V V+ D1 D4 Dbreak R1 I 0W 100 Dbreak W 438.5e-21V V1 VOFF = 0 VAMPL = 170 FREQ = 60 AC = 0 V+ 0V 438.5e-21V V- D3 D2 Dbreak L1 0W 10mH Dbreak 0V 0V V- 0 Figure 2.0: Circuit Diagram for a Full-Wave Rectifier with RL Load. 200 150 100 50 -0 -50 -100 -150 -200 0s V(V1:+,V1:-) 5ms V(R1:2,L1:1) 10ms -I(R1) AVG(W(R1)) 15ms AVG(-I(R1))*10 20ms 25ms 30ms 35ms 40ms 45ms Time Figure 2.1: Average Current Io waveform of a Full-wave Rectifier. 50ms 2 From the PSpice simulation shown below, the average current is given to be AVG(-I(R1)) *10 = 10.635A. If divided by 10, the Io will be 1.063A. This PSpice result is really close to my analytical result which is given to 1.08A, since PSpice result is usually peak, it is expected that that there would be a slight difference in my result. Figure 2.2: Average Current and the Power absorbed by the Resistor of a Full-wave Rectifier. The figure above shows the power across the resistor which is almost the same with my analytical result. This result is pretty close. Pr from the PSpice = 140watts Analytical result is given to be = 141watts 200 150 100 50 -0 -50 -100 -150 -200 0s V(D1:2,0) 5ms AVG(V(R1:2,0)) -I(R1) 10ms W(L1) V(D1:1,D4:1) 15ms V(D1:1,D4:1) 20ms 25ms Time Figure 2.3: Average Voltage Vo of a Full-wave Rectifier. 30ms 35ms 40ms 45ms 3 Figure 2.4: Average Voltage Vo of a Full-wave Rectifier. The PSpice result is really close to the analytical result for Vo. Vo is given as 108Volts while PSpice simulated result is given as 105volts Question 3 (E). L1 R1 25.94e-21W 72.00V 72.00V 50mH 5 D1 Dbreak W I D4 Dbreak 36.00V V1 VOFF = 0 VAMPL = 338 FREQ = 60 AC = 0 V+ 72.00V V+ 36.00V VI D3 72 D2 V2 -5.186nW I W Dbreak Dbreak 0V V- 0 Figure 3.0: Circuit Diagram for a Full-Wave Rectifier with RL Load. 4 2.8K 2.4K 2.0K 1.6K 1.2K 0.8K 0.4K 0 -0.4K 0s V(V1:+,V1:-) 5ms V(R1:2,0) I(R1) 10ms AVG(W(R1)) 15ms AVG(W(V2)) -I(V1) 20ms I(V2) 25ms 30ms 35ms 40ms 45ms 50ms Time Figure 3.2: Power across the DC circuit and the Power absorbed by the Resistor Waveform of a Full-wave Rectifier with RL Load. Figure 3.3: Power across the DC circuit and the Power absorbed by the Resistor Waveform of a Full-wave Rectifier with RL Load. In this simulation, power across the DC voltage source is found to be 1596watts, while the power across the resistor PR is found to be 2726watts 5 6 Question 5 (c). L1 0W -90.68e-30V 10mH V+ -90.68e-30V D1 D4 Dbreak R1 15 Dbreak -685.2e-21V V1 VOFF = 0 VAMPL = 170 FREQ = 60 AC = 0 V+ C1 10000u 0V -685.2e-21V V- D3 D2 Dbreak Dbreak 0V 0V V- 0 Figure 5.0: Circuit Diagram for a Full-Wave Rectifier with LC Filter. 200V 150V 100V 50V -0V -50V -100V -150V -200V 200ms V(D1:1,V1:-) 205ms AVG(V(R1:2,0)) 210ms 215ms 220ms 225ms 230ms 235ms 240ms 245ms 250ms Time Figure 5.1: Waveform of an Average Voltage Vo for a Full-Wave Rectifier with an LC Filter on 5ohms Resistor. 7 Figure 5.1: Average Voltage Vo for a Full-Wave Rectifier with an LC Filter on 5ohms Resistor. 200V 150V 100V 50V -0V -50V -100V -150V -200V 200ms V(D1:1,V1:-) 205ms AVG(V(R1:2,0)) 210ms 215ms 220ms 225ms 230ms 235ms 240ms 245ms 250ms Time Figure 5.1: Waveform of an Average Voltage Vo for a Full-Wave Rectifier with an LC Filter on 15ohms Resistor. 8 Figure 5.1: Average Voltage Vo for a Full-Wave Rectifier with an LC Filter on 15ohms Resistor.