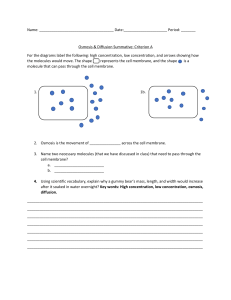
Describe the importance of diffusion of gases and solutes in living organisms Diffusion is important to living organisms because e it allows them to gain the useful substances they require to obtain energy and grow, and lets them get rid of waste products. Diffusion is important in gas exchange for respiration in animals and plants where oxygen and carbon dioxide easily diffuse into and out of cells through the permeable cell membrane. Oxygen, a waste product of photosynthesis diffuses out the same way, from a higher concentration in the leaf to a lower concentration in the air. Living organisms also rely on diffusion of solutes. A solute is a substance that has dissolved in a liquid, which is called a solvent. In organisms the solvent is always water. For example: the cytoplasm of all cells contains many solutes, these particles are free to move through the cytoplasm, so they diffuse spreading to all parts of the cytoplasm. The factors that influence diffusion Surface Area The greater the surface area (of the cell membrane separating the different regions), the faster the rate of diffusion. This is because there is more space for molecules to diffuse across the membrane. Temperature The higher the temperature, the more kinetic energy the particles will have, so they will move and mix more quickly Concentration Gradient The greater the difference in concentration on either side of the membrane, the faster movement across it will occur. This is because on the side with the higher concentration, more random collisions against the membrane will occur Distance The smaller the distance molecules have to travel the faster transport will occur, increasing the rate of diffusion. Investigating how surface area affects diffusion Investigating how temperature, concentration gradient or distance affect diffusion 3.2 Osmosis Osmosis is the net movement of water molecules from a region of higher water potential (dilute solution) to a region of lower water potential (concentration solution), through a partially permeable membrane. Water moves into and out of cells by osmosis through the cell membrane Investigate osmosis using materials such as dialysis tubing Plants are supported by the pressure of water inside the cells pressing outwards on the cell wall Explain the effects on plant cells of immersing them in solutions of different concentrations When plant cells are placed in a solution that has a higher water potential (dilute solution) than inside the cells (e.g. distilled water) then water moves into the plant cells via osmosis These water molecules push the cell membrane against the cell wall, increasing the turgor pressure in the cells which makes them turgid When plant cells are placed in a concentrated solution (with a lower water potential than inside the cells) water molecules will move out of the plant cells by osmosis, making them flaccid If plant cells become flaccid it can negatively affect the plant's ability to support itself If looked at underneath the microscope, the plant cells might be plasmolysed, meaning the cell membrane has pulled away from the cell wall Explain the importance of water potential and osmosis in uptake and loss of water by organisms