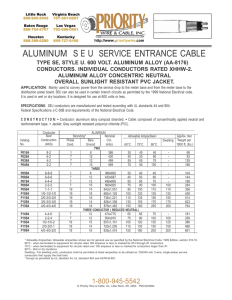
Reg no: 3878 Muhammad Akbar Abasyn University Passion to Design Futures LAB 08 SUBJECT: PGTD SUBMITTED BY: NAME: Muhammad Akbar ROLLNO: 3878 DEP: BEEE SEMESTER: 07 LAB INSTRUCTOR: Syed Mujtaba Ali Naqvi SUBMISSION DATE: 07/11/2022 PGTD Lab: 08 Muhammad Akbar Reg no: 3878 To study different types of Overhead Line Conductors & one line diagram Objective: To study materials of overhead line conductors. To study comparison of different materials. To analyze conductor properties. Theory: A conductor is one of the most important components of overhead lines. Selecting a proper type of conductor for overhead lines is as important as selecting economic conductor size and economic transmission voltage. A good conductor should have the following properties: high electrical conductivity high tensile strength in order to withstand mechanical stresses relatively lower cost without compromising much of other properties lower weight per unit volume Conductor Materials Copper was the preferred material for overhead conductors in earlier days, but, aluminum has replaced copper because of the much lower cost and lighter weight of the aluminum conductor compared with a copper conductor of the same resistance. Following are some materials that are considered to be good conductors. PGTD Copper: Copper has a high conductivity and greater tensile strength. So, copper in hard drawn stranded form is a great option for overhead lines. Copper has a high current density which means more current carrying capacity per unit crosssectional area. Therefore, copper conductors have relatively smaller crosssectional area. Also, copper is durable and has high scrap value. However, due to its higher cost and non-availability, copper is rarely used for overhead power lines. Aluminum: Aluminum has about 60% of the conductivity of copper; that means, for the same resistance, the diameter of an aluminum conductor is about 1.26 times than that of a copper conductor. However, an aluminum conductor has almost half the weight of an equivalent copper conductor. Also, tensile strength of aluminum is less than that of copper. Considering combined factors of cost, conductivity, tensile strength, weight etc., aluminum has an edge over copper. Therefore, aluminum is being widely used for overhead conductors. Cadmium-copper: Cadmium-copper alloys contain approximately 98 to 99% of copper and up to 1.5% of cadmium. Addition of about 1% of cadmium to copper Lab: 08 Muhammad Akbar Reg no: 3878 Increases the tensile strength by up to 50% and the conductivity is reduced only by about 15%. Therefore, cadmium-copper conductors can be useful for exceptionally long spans. However, due to high cost of cadmium, such conductors may be uneconomical in many cases. Other materials: There are many other metals and alloys that conduct electricity. Silver is more conductive than copper, but due to its high cost, it is not practical in most of the cases. Galvanized steel may also be used as a conductor. Although steel has very high tensile strength, steel conductors are not suitable for transmitting power efficiently due to the poor conductivity and high resistance of steel. High strength alloys such as phosphor-bronze may also be used sometimes at extreme conditions. Types Of Conductors As it is already mentioned above, aluminum conductors have an edge over copper conductors considering combined factors of cost, conductivity, tensile strength, weight etc. Aluminum conductors have completely replaced copper conductors in overhead power lines because of their lower cost and lower weight. Though an aluminum conductor has larger diameter than that of a copper conductor of same resistance, this is actually an advantage when 'Corona' is taken into consideration. Corona reduces considerably with increase in the conductor diameter. Following are four common types of overhead conductors used for overhead transmission and distribution to carry generated power from generating stations to the end users. Generally, all types of conductors are in stranded form in order to increase the flexibility. Solid wires, except for very small cross sectional area, are very difficult to handle and, also, they tend to crystallize at the point of support because of swinging in winds. 1. 2. 3. 4. AAC : All Aluminum Conductor AAAC : All Aluminum Alloy Conductor ACSR : Aluminum Conductor, Steel Reinforced ACAR : Aluminum Conductor, Alloy Reinforced AAC : All Aluminium Conductor This type is sometimes also referred as ASC (Aluminum Stranded Conductor). It is made up of strands of EC grade or Electrical Conductor grade aluminum. AAC conductor has conductivity about 61% IACS (International Annealed Copper Standard). Despite having a good conductivity, because of its relatively poor strength, AAC has limited use in transmission and rural distribution lines. However, AAC can be seen in urban areas for distribution where spans are usually short but higher conductivity is required. AAAC : All Aluminium Alloy Conductor These conductors are made from aluminum alloy 6201 which is a high strength Aluminum-Magnesium-Silicon alloy. This alloy conductor offers good electrical conductivity (about 52.5% IACS) with better mechanical strength. Because of AAAC's PGTD Lab: 08 Muhammad Akbar Reg no: 3878 lighter weight as compared to ACSR of equal strength and current capacity, AAAC may be used for distribution purposes. However, it is not usually preferred for transmission. Also, AAAC conductors can be employed in coastal areas because of their excellent corrosion resistance. ACSR : Aluminium Conductor, Steel Reinforced ACSR consists of a solid or stranded steel core with one or more layers of high purity aluminum (aluminum 1350) wires wrapped in spiral. The core wires may be zinc coated (galvanized) steel or aluminum coated (aluminized) steel. Galvanization or aluminization coatings are thin and are applied to protect the steel from corrosion. The central steel core provides additional mechanical strength and, hence, sag is significantly less than all other aluminum conductors. ACSR conductors are available in a wide range of steel content - from 6% to 40%. ACSR with higher steel content is selected where higher mechanical strength is required, such as river crossing. ASCR conductors are very widely used for all transmission and distribution purposes. Aluminium Conductor, Alloy Reinforced ACAR conductor is formed by wrapping strands of high purity aluminum (aluminum 1350) on high strength Aluminum-Magnesium-Silicon alloy (6201 aluminum alloy) core. ACAR has better electrical as well as mechanical properties than equivalent ACSR conductors. ACAR conductors may be used in overhead transmission as well as distribution lines. Bundled Conductors PGTD Lab: 08 Muhammad Akbar Reg no: 3878 Transmission at extra high voltages (say above 220 kV) poses some problems such as significant corona loss and excessive interference with nearby communication lines when only one conductor per phase is used. This is because, at EHV level, the electric field gradient at the surface of a single conductor is high enough to ionize the surrounding air which causes corona loss and interference problems. The electric field gradient can be reduced significantly by employing two or more conductors per phase in close proximity. Two or more conductors per phase are connected at intervals by spacers and are called as bundled conductors. The image at right shows two conductors in bundled form per phase. Number of conductors in a bundled conductor is greater for higher voltages. PGTD Lab: 08 Muhammad Akbar Reg no: 3878 Questions Q#_01: What do you understand about cross sectional area of transmission line? Ans: If you cut directly and squarely across the width of a wire then you will look at the end and it looks like a circle. The area of that end is the cross section area, which is Pi x r^2. A larger cross section area results in lower resistance per foot when the type of wire is the same. Q#_02: What are the applications of a Hollow wire? Ans: The conductor that permits the flow of charges through a Central channel is referred to as a hollow conductor. In comparison to solid conductors, hollow conductors have a larger diameter. Our hollow conductors provide new possibilities to cool down electric motors. The internal cooling hole on the stator windings enables efficient thermal transfer out from the core - exactly from the source where the heat is generated. Q#_03: What is meant by stranded conductor? Stranded conductors are made of multiple small strands, which group together to make up a single conductor. It is more flexible than a solid conductor, but less durable. Q#_04: What are the examples of American homogenous and non homogenous standard? In North America bird names are used for the code words while animal names are used elsewhere. For instance in North America, Grosbeak is a 322.3 mm2 (636 kcmil) ACSR conductor with 26/7 Aluminum/Steel stranding whereas Egret is the same total aluminum size (322.3 mm2, 636 kcmil conductor) but with 30/19 Aluminum/Steel stranding. Although the number of aluminum strands is different between Grosbeak and Egret, differing sizes of the aluminum strands are used to offset the change in the number of strands such that the total amount of aluminum remains the same. PGTD Lab: 08 Muhammad Akbar Reg no: 3878 Conclusion In this lab we have studied about the different types of conductors. We have learnt the study of material of overhead line conductor, comparison of different materials and the different standards respectively. PGTD Lab: 08