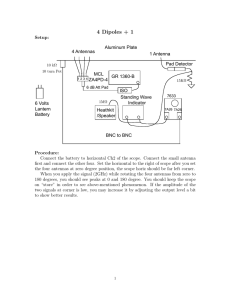
ANTENNA THEORY ANALYSIS AND DESIGN THIRD EDITION Constantine A. Balanis T WILEY INTERSCIENCE A JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC., PUBLICATION Contents Preface 1 Antennas 1.1 Introduction 1.2 Types of Antennas 1.3 Radiation Mechanism 1.4 Current Distribution on a Thin Wire Antenna 1.5 Historical Advancement 1.6 Multimedia References 2 Fundamental Parameters of Antennas 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 2.7 2.8 2.9 2.10 2.11 2.12 2.13 2.14 2.15 2.16 2.17 2.18 2.19 Introduction Radiation Pattern Radiation Power Density Radiation Intensity Banmwidth Directivity Numerical Techniques Antenna Efficiency Gain Beam Efficiency Bandwidth Polarization Input Impedance Antenna Radiation Efficiency Antenna Vector Effective Length and Equivalent Areas Maximum Directivity and Maximum Effective Area Friis Transmission Equation and Radar Range Equation Antenna Temperature Multimedia References Problems 1 1 4 7 17 20 24 24 27 27 27 38 40 42 44 58 64 65 69 70 70 80 85 87 92 94 104 108 112 114 VIII CONTENTS Radiation Integrals and Auxiliary Potential Functions 3 Introduction The Vector Potential A for an Electric Current Source J The Vector Potential F for a Magnetic Current Source M Electric and Magnetic Fields for Electric (J) and Magnetic (M) Current Sources 3.5 Solution of the Inhomogeneous Vector Potential Wave Equation 3.6 Far-Field Radiation 3.7 Duality Theorem 3.8 Reciprocity and Reaction Theorems References Problems 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 4 Linear Wire Antennas 4 .1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 4.6 4.7 4.8 4.9 4.10 5 Introduction Infinitesimal Dipole Small Dipole Region Separation Finite Length Dipole Half-Wavelength Dipole Linear Elements Near or on Infinite Perfect Conductors Ground Effects Computer Codes Multimedia References Problems Loop Antennas 5.1 Introduction 5.2 Small Circular Loop 5.3 Circular Loop of Constant Current 5.4 Circular Loop with Nonuniform Current 5.5 Ground and Earth Curvature Effects for Circular Loops 5.6 Polygonal Loop Antennas 5.7 Ferrite Loop 5.8 Mobile Communication Systems Applications 5.9 Multimedia References Problems 6 Arrays: Linear, Planar, and Circular 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 Introduction Two-Element Array N-Element Linear Array : Uniform Amplitude and Spacing N-Element Linear Array: Directivity 133 133 135 137 138 139 142 144 144 150 150 151 151 151 162 165 170 182 184 205 214 217 218 219 231 231 232 246 255 261 263 266 268 269 273 275 283 283 284 290 313 CONTENTS 6.5 6.6 6.7 6.8 6.9 6.10 6.11 6.12 6.13 Design Procedure N-Element Linear Array: Three-Dimensional Characteristics Rectangular-to-Polar Graphical Solution N-Element Linear Array: Uniform Spacing, Nonuniform Amplitude Superdirectivity Planar Array Design Considerations Circular Array Multimedia References Problems 7 Antenna Synthesis and Continuous Sources 7 .1 7.2 7.3 7.4 7.5 7.6 7.7 7.8 7 .9 7.10 7.11 Introduction Continuous Sources Schelkunoff Polynomial Method Fourier Transform Method Woodward-Lawson Method Taylor Line-Source (Tschebyscheff-Error) Taylor Line-Source (One-Parameter) Triangular, Cosine, and Cosine-Squared Amplitude Distributions Line-Source Phase Distributions Continuous Aperture Sources Multimedia References Problems 8 Integral Equations, Moment Method, and Self and Mutual Impedances 8.1 8.2 8.3 8.4 8.5 8.6 8.7 8.8 9 Introduction Integral Equation Method Finite Diameter Wires Moment Method Solution Self-Impedance Mutual Impedance Between Linear Elements Mutual Coupling in Arrays Multimedia References Problems Broadband Dipoles and Matching Techniques 9.1 9.2 9.3 9.4 Introduction Biconical Antenna Triangular Sheet, Bow-Tie, and Wire Simulation Cylindrical Dipole ix 318 320 322 324 345 349 362 365 369 370 371 385 385 386 388 393 399 406 410 417 418 419 423 423 424 433 433 434 442 450 458 468 478 491 491 494 497 497 500 506 508 X CONTENTS 10 9.5 Folded Dipole 9.6 Discone and Conical Skirt Monopole 9.7 Matching Techniques 9.8 Multimedia References Problems 515 521 523 541 542 543 Traveling Wave and Broadband Antennas 549 10.1 Introduction 10.2 Traveling Wave Antennas 10.3 Broadband Antennas 10.4 Multimedia References Problems 11 Frequency Independent Antennas, Antenna Miniaturization, and Fractal Antennas 11.1 Introduction 11.2 Theory 11.3 Equiangular Spiral Antennas 11.4 Log-Periodic Antennas 11.5 Fundamental Limits of Electrically Small Antennas 11.6 Fractal Antennas 11.7 Multimedia References Problems 12 13 549 549 566 600 600 602 611 611 612 614 619 637 641 648 648 650 Aperture Antennas 653 12.1 12.2 12.3 12.4 12.5 12.6 12.7 12.8 12.9 12.10 Introduction Field Equivalence Principle: Huygens' Principle Radiation Equations Directivity Rectangular Apertures Circular Apertures Design Considerations Babinet's Principle Fourier Transforms in Aperture Antenna Theory Ground Plane Edge Effects: The Geometrical Theory of Diffraction 12.11 Multimedia References Problems 653 653 660 662 663 683 692 697 701 Horn Antennas 739 13.1 Introduction 13.2 E-Plane Sectoral Horn 721 726 726 728 739 739 CONTENTS 13.3 13.4 13.5 13.6 13.7 13.8 13 .9 13.10 13.11 14 Microstrip Antennas 14.1 14.2 14.3 14.4 14.5 14.6 14.7 14.8 14.9 15 Introduction Rectangular Patch Circular Patch Quality Factor, Bandwidth, and Efficiency Input Impedance Coupling Circular Polarization Arrays and Feed Networks Multimedia References Problems Reflector Antennas 15.1 15.2 15.3 15.4 15.5 15.6 16 H-Plane Sectoral Horn Pyramidal Horn Conical Horn Corrugated Horn Aperture-Matched Horns Multimode Horns Dielectric-Loaded Horns Phase Center Multimedia References Problems Introduction Plane Reflector Corner Reflector Parabolic Reflector Spherical Reflector Multimedia References Problems A 755 769 783 785 792 794 797 799 802 802 805 811 811 816 843 852 855 856 859 865 872 872 876 883 883 883 884 893 934 936 937 939 Smart Antennas 945 16.1 Introduction 16.2 Smart-Antenna Analogy 16.3 Cellular Radio Systems Evolution 16.4 Signal Propagation 16 .5 Smart Antennas' Benefits 16.6 Smart Antennas' Drawbacks 16.7 Antenna 16.8 Antenna Beamforming 16.9 Mobile Ad hoc Networks (MANETs) 16.10 Smart-Antenna System Design, Simulation, and Results 945 946 947 954 957 958 958 962 977 982 Xii CONTENTS 16.11 Beamforming, Diversity Combining, Rayleigh-Fading, and Trellis-Coded Modulation 16.12 Other Geometries 16.13 Multimedia References Problems 990 993 994 995 999 Antenna Measurements 1001 17.1 17.2 17.3 17.4 17.5 17.6 17.7 17.8 17 .9 17.10 Introduction Antenna Ranges Radiation Patterns Gain Measurements Directivity Measurements Radiation Efficiency Impedance Measurements Current Measurements Polarization Measurements Scale Model Measurements References 1001 1003 1021 1028 1034 1036 1036 1038 1038 1044 1045 Appendix I: f (x ) = sin(x) 1049 Appendix II: A (x ) Appendix III: Cosine and Sine Integrals 1053 Appendix IV: Fresnel Integrals 1057 Appendix V: Bessel Functions 1063 Appendix VI : Identities 1075 Appendix VII: Vector Analysis 1079 Appendix VIII : Method of Stationary Phase 1089 Appendix IX: Television, Radio, Telephone, and Radar Frequency Spectrums 1095 17 Index _ I sin(Nx) N - 1, 3, 5,10, 20 N sin(x ) 1051 1099