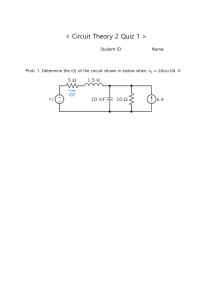
Topic 2: Resistivity and fundamentals of electricity Objectives: a. Define Resistivity b. Define ohm’s law c. Distinguish between DC and AC and their properties characteristic d. Describe the basic relationships of voltage, current and resistance in a series circuit e. Define ohm’s law Reference: 1.Electricity 1, Devices, Circuits and Materials ;4th edition by Thomas Kubala 2. Fundamental of Electric Circuit 6th edition by Charles K. Alexander and Mathew O. Sadiku 3. Basic Electronics, 2nd edition by Crob Note: Resistivity Problem Set ...Chapter 1 Resistances DC- for commercial uses such as flashlights and power supplies for electronic circuits BOARD WORK Use the White Board Example No. 2 2. rho= 10.4 Ωcm/ft L= 2 meters Dia=30 mil R? Temperature coefficient of resistance -Positive α all metals in their pure form have positive temperature coefficient. This means that R increases with temperature. -Change in resistance per unit resistance per degree change in temp. α= ΔR RO* Δt R or RT=RO(+(1+α(t-to)) Where : R or RT=Resistance at any temperature RO= Resistance at 0 degrees at 32 degree Farenheit to= Freezing point of H2O T= any temp. Example: A tungsten wire has a 14 ohms R at 20 degrees Celsius. Calculate its resistance at 120 degrees and the alpha(α) is 0.005 Given: RO= 14 ohms t= 120 degrees to= 20 degrees Solution: R or RT=RO(1+α(t-to)) =14(1+0.005(120-20) RT= 21 ohms Horsepower and Watts 1 Hp= 746 watts = 550ft lbs/sec Electric Energy Energy work is done whenever power is used at a definite time. Energy dispatched dependent on the amount of power applied as well as the time consumed performing certain task. Energy= power x time Unit: Watts*sec. = kWh Introduction Topic 1: Series and Parallel connection Presented by ENGR. ANDREW G. BITANCOR FACULTY DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Topic : Series and Parallel Connection Objectives: a. Define a series circuit and a parallel circuit connection b. Describe the current flow and the operational differences between series and parallel circuit c. Connect and draw the a series and parallel circuit Reference: 1.Electricity 1, Devices, Circuits and Materials ;4th edition by Thomas Kubala 2. Fundamental of Electric Circuit 6th edition by Charles K. Alexander and Mathew O. Sadiku 3. Basic Electronics, 2nd edition by Crob Series Circuit- is one of which devices are connected that there is one only one path for current to flow. Characteristic : 1. The voltage across the circuit is the sum of the voltages across each component Series Circuit- is one of which devices are connected that there is one only one path for current to flow. Characteristic : 1. The voltage across the circuit is the sum of the voltages across each component Series Circuit- is one of which devices are connected that there is one only one path for current to flow. Characteristic : 2.Current through each component is the same Series Circuit- is one of which devices are connected that there is one only one path for current to flow. Characteristic : 2.Current through each component is the same Series Circuit- is one of which devices are connected that there is one only one path for current to flow. Characteristic : 3.The resistance increases as each load is added Series Circuit- is one of which devices are connected that there is one only one path for current to flow. Characteristic : 3.The resistance increases as each load is added Series Circuit- is one of which devices are connected that there is one only one path for current to flow. Characteristic : 4.If there is a break at any point in the circuit it will break the flow of current Series Circuit- is one of which devices are connected that there is one only one path for current to flow. Characteristic : 4.If there is a break at any point in the circuit it will break the flow of current Application of Series Circuit Parallel Circuit- It has two or more path for current to flow Characteristic : 1. Voltage applied is the same across the branch terminal Parallel Circuit- It has two or more path for current to flow Characteristic : 1. Voltage applied is the same across the branch terminal Parallel Circuit- It has two or more path for current to flow Characteristic : 2. Current is the sum of the branch circuit Parallel Circuit- It has two or more path for current to flow Characteristic : 3.The resistance decrease as the load increases Parallel Circuit- It has two or more path for current to flow Characteristic : 4.If one bulb is disconnected, it will not affect the other bulb Application of Parallel Application of Parallel Application of Parallel Application of Series Application:Christmas Light Topic 3: Series and Parallel Circuit Objectives: a. Explain the characteristics of series circuit b. Explain the characteristics of Parallel circuit c. Demonstrate a procedure for solving series and Parallel circuits Reference: 1.Electricity 1, Devices, Circuits and Materials ;4th edition by Thomas Kubala 2. Fundamental of Electric Circuit 6th edition by Charles K. Alexander and Mathew O. Sadiku 3. Basic Electronics, 2nd edition by Crob Series Circuit- is one of which devices are connected that there is one only one path for current to flow. Characteristic : 1. Voltage applied to a series circuit are distributed across the various components 2. The current is the same through out the circuit Series Circuit V1 V2 V3 Where: R Total Resistance I = I1 = I2 = I3 RT= R1+ R2 + R3 T= IT VT VT=V1+ V2+V3 T In Summary Series Circuit Parallel Circuit- It has one or more path for current to flow Characteristic : 1. Voltage applied is the same across the branch terminal 2. Current is the sum of the branch circuit Resistance Total 1/RT=1/R1+ 1/R2 RT= 1 1/R1+ 1/R2 Where: RT =total resistance R1 = resistance of resistor 1 R2 = resistance of resistor 2 R3 = resistance of resistor 3 Parallel Circuit VT IT I1 V1 I2 V2 1/RT= 1/R1+1/R2+R3 RT= 1 1 + 1+ 1 R1 R R Where: V3 V =V = V = V T 1 2 3 IT= I1+ I2 + I3 I3 In Summary Series Circuit Topic 4: Voltage Divider and Current Divider Objectives: a. Explain the characteristics of voltage divider theorem as applied in electric circuit b. Explain the characteristics of current divider theorem as applied in electric circuit c. Demonstrate a procedure for solving voltage divider and current divider circuits Reference: 1.Electricity 1, Devices, Circuits and Materials ;4th edition by Thomas Kubala 2. Fundamental of Electric Circuit 6th edition by Charles K. Alexander and Mathew O. Sadiku Current Divider Principle- Good for parallel circuit only IT VT I1 R1 I2 R2 Current Divider Principle- Good for parallel circuit only Where: IT VT I1 R1 RT = R1XR2 R1+ R2 Substitute RT to equation 1 I1 = IT R2 R1 + R2 I2 R2 VT=(IT)( RT) IT =I1 +I2 VT = V 1 + V 2 RT R1 R2 IT =I1 +I2 VT = V 1 = V 2 IT RT = I1 R1 = I2 R2 I1 = IT RT R1 I2 = IT RT R2 1 Voltage Divider Principle- Good for Where: series circuit only IT =I1 = I2 V1 V2 V3 VT = V1 = V2 = V2 RT R1 R2 R3 V1 = VT R1 IT VT RT V2 = VT R2 RT V3 = VT R3 RT Voltage Divider Principle- Good for series circuit only V1 IT V2 VT V3 Example 1 Two equal resistances draw 10A from 100V source while connected in series. How much current will they draw from the source if the resistances are connected in parallel. a. 10A b. 20A c. 30A d. 40A Example 1 Two equal resistances draw 10A from 100V source while connected in series. How much current will they draw from the source if the resistances are connected in parallel. Solution: R= V/I= 100/10= 10 ohm For two equal R, then 10/2= 5 ohm of each R -In parallel, two 5 ohm is equivalent to 2.5 ohm I= 100/2.5 = 40A RT=R1XR2= 5X5 = 25/10=2.5 R1+R2 5+5 1/RT=1/R1+ 1/R2 RT= 1 1/R1+ 1/R2 RT= 1 1/5+ 1/5 RT=2.5 ohm Example 2 A resistor of 4 resistance of 4 ohms is connected across a 120V supply. Another resistance of R ohms is connected across the same supply and the total current is 60 A. The value of R is. a. 2 b. 3 c. 4 d. 5 Example 3. What resistance must be connected across a 4-ohm resistor in order to give an equivalent resistance of 3 ohms. a. 8 b. 10 c. 12 d. None of these Example No.4 . If two incandescent bulbs rated 110 V, 25 W and 110V, 100W are in series and connected across 220V source. a. Both bulbs will give of their normal brightness b. The bulbs will divide the voltage source equally c. 25W watt bulb will be over voltage d. 100W watt bulb will be over voltage