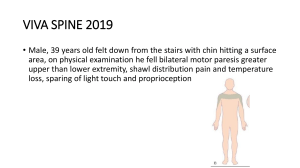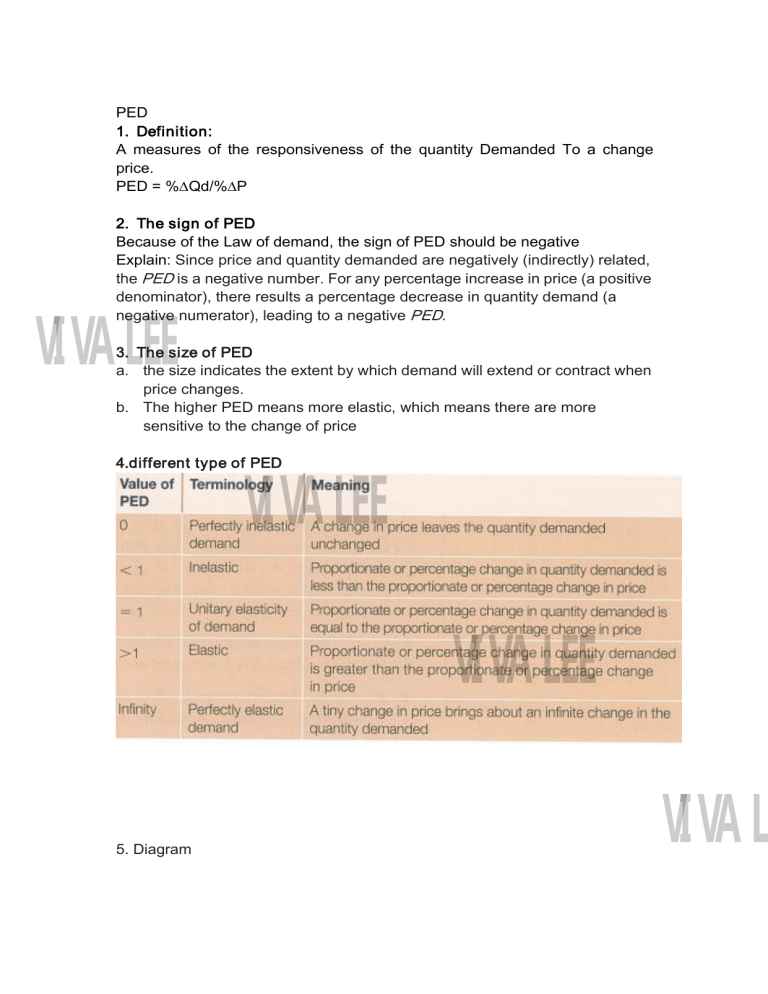
PED 1. Definition: A measures of the responsiveness of the quantity Demanded To a change price. PED = %∆Qd/%∆P 2. The sign of PED Because of the Law of demand, the sign of PED should be negative Explain: Since price and quantity demanded are negatively (indirectly) related, the PED is a negative number. For any percentage increase in price (a positive denominator), there results a percentage decrease in quantity demand (a negative numerator), leading to a negative PED. VIVA LEE 3. The size of PED a. the size indicates the extent by which demand will extend or contract when price changes. b. The higher PED means more elastic, which means there are more sensitive to the change of price 4.different type of PED VIVA LEE VIVA LEE 5. Diagram VIVA L VIVA LEE 6. Variable PED they should be used to refer to a portion of the demand curve that corresponds to a particular price or price range. VIVA LEE 7. Factors impacting PED a. number of substitutes Explain: Elastic: The more substitutes a good (or service) has, the more elastic is its demand. If the price of a good with many substitutes increases, consumers can switch to other substitute products, therefore resulting in a relatively large drop (large responsiveness) in quantity demanded VIVA LEE Inelastic: Consumers will be price sensitive as they can easily swap to alternative goods or services if the price rises. If there are no close substitutes then PED is likely to be inelastic; when prices rise consumers have no alternative but to pay the higher price or go without the product. b. proportion of income Explain; Inelastic:if a good or service has a very low price and is a small proportion of consumers' income, then PED tends to be inelastic. Because even if the price increases it won't take up much income, and therefore consumers are likely to continue buying the good. Consumers will not be sensitive as price change. VIVA L Elastic:if a good or service has a high proportion of consumers' income. then PED tends to be elastic. Because an increase in price will take up much income, and therefor consumers will be price sensitive,and are likely switch to buy close substitute. c. Time period Explain: Demand tends to be more elastic in the long run than in the short run. because consumers have time to adjust to price changes. For example, if the price of the product increases, consumers will have little choice but to pay the higher price and so PED is inelastic. However, over time consumers will be able to figure out more substitutes, so the demand for the product will become elastic in the long run. VIVA LEE 8. PED & Total Revenue Definition:Total revenue (TR) is the amount of money received by firms when they sell a good or service TR=P*Q Elastic: P ↑, TR↓; P↓,TR↑ Inelastic: P↑,TR↑ ; P↓, TR↓ Unit elastic: Price changes and TR remains unchanged VIVA LEE 9. Use of PED Producer: 1. producers got information from the size of PED (how consumer want the product) 2. how to set up the price to earn a higher TR. Government : Relationship between PED & indirect tax (CH3) VIVA LEE VIVA L XED: Definition: a measure of the responsiveness of Quantity demanded for one good to a change in the price of another good 2. the information of XED: 1 substitutes : (when the demand for one good and the price of the other good change in the same direction: when the price of one increases, the demand for the other also increases) The sign of XED: + The size of XED:Given two pairs of substitute goods, the larger the value of cross-price elasticity of demand, the greater the substitutability between two goods, and the larger the demand curve shift in the event of a price change. VIVA LEE VIVA LEE complement : (when the demand for one good and the price of the other good change in opposite directions: when the price of one good increases, the demand for the other falls. ) The sign of XED : The size of XED:The larger the absolute value of the negative cross-price elasticity of demand, the greater is the complementary between two goods, and the larger is the demand curve shift in the event of a price change. 2 Unrelated Product (XED=0) Explain:If cross-price elasticity of demand is zero (XED = 0) or close to zero, this means that two products are unrelated or independent of each other. 3 VIVA LEE 3. Use of XED a. Substitute product Substitutes produced by a single business When a business produces a line of products that are similar to each other,it must consider the XED for these products when making decisions about prices. Since the two goods are substitutes To make a decision it must have information about: PED for Good A, so that it can determine whether a price cut will lower or raise total revenue from Good A XED for Good A and B; it is not enough to know that XED > 1 (that the two goods are substitutes). It is also important to know the degree of substitutability between them. If the value of XED is positive but low (low VIVA L substitutability), a percentage decrease in the price of Good A will produce only a small percentage drop in demand for Good B, so that the sales of good b would not be seriously affected. But if the value of XED is positive and high, a fall in the price of Good A will produce a large drop in demand for Good B. Increased sales of Good A would come at the expense of Good B sales and revenues .something that the company would probably want to avoid Substitutes produced by rival businesses A large XED would mean that if Good A (produce by own company)dropped its price, Good B (produced by rival businesses) would suffer a serious drop in sales, whereas a low XED would mean that Good B would not be seriously affected. Good A company would also want to know this XED in order to be able to predict the effect on Good A sales and revenues of any change in the price of Good B . VIVA LEE Substitutes and mergers between firms Businesses producing close substitutes with a high positive XED, might be interested in merging because that way they would eliminate the competition between them. b. Complementary goods a high absolute value of a (negative) XED means that lowering the price of one good can result in a large increase in demand and sales for the other Businesses producing strongly complementary goods often collaborate VIVA LEE VIVA LEE VIVA L Income elasticity of demand (YED): Definition: a measure of the responsiveness of demand to changes in income, and involves demand curve shifts. 2. Information of YED 1 VIVA LEE YED <0 :(Inferior good ) Explain: demand for the good and income move in opposite directions. For inferior good, as income increase, consumers will decrease their expenditure in Inferior good, as there are better choice. 2 YED > 0 (Normal good) Explain: when demand and income change in the same direction.For normal,good, as income increase, demand for normal good is gonna to increase. 3 VIVA LEE 0<YED<1: [Necessities good (income inelastic demand)] Definition: a percentage increase in income produces a smaller percentage increase in quantity demanded Necessities good means the Good or service (Such as foods, water, medical attention) that we cannot live without and will not likely cut back on even when times are tough. as income increases, people buy more necessities good but the proportion of income spent on necessities good increases more slowly than income. 4 VIVA LEE YED > 1: [Luxuries good (income elastic demand)] Definition: a percentage increase in income produces a larger percentage increase in quantity demanded YED will change:What is a necessity and what is a luxury depends on income levels. For people with extremely low incomes, even food and certainly clothing can be luxuries. As income increases, certain items that used to be luxuries become necessities. VIVA L PES VIVA LEE Definition: is a measure of the responsiveness of the quantity of a good supplied to changes in its price. VIVA LEE VIVA LEE VIVA L Determinants of price elasticity of supply 1. Time period (Long term more elastic) The larger amount of time firms have to adjust their inputs increases, the larger the PES (more elastic). Explain: Firms have to adjust their input (resources) and the quantity supplied in response to changes in price. In the short time, even when price increase many firms cannot increase quantity supplied straightaway, so PES will be perfect inelastic in the immediate time period. After short time, firms will try to increase quantity supplied by producing more of the good or service or selling any stocks they have. Thus, quantity supplied will become relatively inelastic but not perfect inelastic. Over the long-run firms will have had a chance to change the scale of production and to expand in order to supply more of the good or service. Thins means that supply over the long run is elastic. VIVA LEE 2. The amount of stock (Inventories) or ability to store the stock (inventory) Firms that have an ability to store stocks are likely to have a higher PES for their products than firms that cannot store stocks. 这里的 stock 指的是存货 VIVA LEE Explain: If a firm has a large amount of stock and it is easy to store the finished product then it will be easier and quicker to increase the quantity supplied to the market if demand increases and prices rise. Therefore, supply will be elastic as firms can easily respond to a change in price. If a firm does not hold much stock because large items such as cars take up lots of storage space, or because the inventory is difficult to store, like many foods that perish or rot over time, then supply is likely to be inelastic, as firms can not easily respond to a change in price. (Only in short period. once stocks are released in the market and sold, other factors determining PES come into play. ) VIVA LEE VIVA L 3. Level of spare capacity The greater the spare (unused) capacity, the higher is PES (the more elastic the supply); the less the spare capacity, the smaller the PES (the less elastic the supply). Explain: If there is spare capacity in a factory, which means not all available space is being used or some machines are not being used all the time. So It is easier for the firm to quickly increase production and supply more products to the market, the supply will be elastic. If all the machines are being used and the factory has no space left to add more machines or workers, than the firms is at full capacity and cannot quickly increase supply. The supply will be inelastic. VIVA LEE 4. The mobility and cost of factors of production The more easily and quickly resources can be shifted out of one line of production and into another (where price is increasing), the greater the responsiveness of quantity supplied to changes in price, and hence the greater the PES Explain: The mobility of factors of production refers to how easily any of the FOP can be transferred to an alternative use. The more mobile the FOP are, and the cheaper it is to adopt or train them, then the more elastic the supply. The less mobile the FOP are, and the higher the cost to move them to alternative production, then the more inelastic supply will be. VIVA LEE VIVA LEE VIVA L VIVA LEE VIVA LEE VIVA LEE VIVA L PESinrelationtoprimarycommoditiesandmanufacturedproducts primarycommoditiesusuallyhavealowerPESthanmanufacturedproducts. 1.The main reason is the time needed for quantity supplied to respond to price changes (agriculturalgoods) 2.In the case of other primary products,such as oil,natural gas and minerals,time is needed VIVA LEE to make the necessary investments and to begin production.Because of the costs involved, firms do not respond quickly to price increases,and wait for a serious shortage(excess demand) in the commodity to arise before they take actions toi ncrease production. VIVA LEE VIVA LEE VIVA L