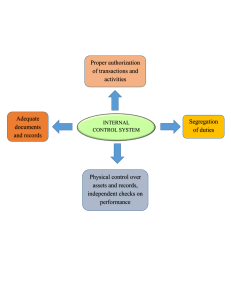
Overview of Internal Control LEARNING OBJECTIVES Understand the nature and purpose of internal control Define the internal control system Explain the elements of internal control INTERNAL CONTROL DEFINITION A process for assuring achievements of an organization’s objectives in operational effectiveness and efficiency, reliable financial reporting, and compliance with laws, regulations and policies. Designed and implemented to address identified business risk that threaten the achievement of any of these objectives. INTERNAL CONTROL SYSTEM DEFINITION Means policies and procedures ( internal controls) adopted by management of an entity to assist in achieving management’s objectives of ensuring ,as far as practicable , the orderly and efficiency of the business It provide direction that will increase efficiency and strengthen adherence to policies. INTERNAL CONTROL COSO ( Committee of Sponsoring Organization) , as a voluntary private sector initiative to sponsor the National commission of Fraudulent Financial Reporting. It has published two key reports laying down guidelines on the design of the internal control system. The COSO report views internal control as a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the achievements of three core objectives: Objectives 1. Effectiveness and efficiency of operations 2. Reliability of financial reporting 3. compliance with laws and regulations Elements of Internal Control Elements of Internal Control Control Environment Risk Assessment Information System & Business Process Control Activities Monitoring of Controls Communication and Enforcement of Integrity and Ethical Values Commitment to Competence Participation to those Charged with Governance Management’s Philosophy and Operating Style Organizational Structure Assignment of Authority and Responsibility Human Resource Policies and Procedures Company wide objectives consist of Infrastructure , software, people procedures and data Policies and procedures that help ensure management directives are carried out. Assessment of the quality of internal control over time Process level objectives Risk identification and Analysis Managing change Relevant to financial reporting objectives which includes accounting systems Performance review Information Processing control Quality of Information Physical control Effectiveness of communication On going monitoring Risk Assessment Process Process in Risk Management 1. Risk identification- risk that may influence the achievements of the company objectives and the success of the company strategies are pinpointed. 2. Risk Assessment – identified the risks that makes it possible to affects the impact of different risk factors on performance. Evaluation includes the probability of occurrence associated with risk factors. 3. Risk response- following the identification and assessment of the risk, management must act in order to implement risk management policies. Types of Internal Control Definition Examples Preventive Controls Designed to discourage errors or irregularities from occurring Segregation of duties Approval, Authorization and Verification Security of Assets Detective Controls Find errors or irregularities after they have occurred Review Performance Reconciliation Corrective Controls Target the correction of errors or irregularities as soon as they are detected Job rotation Quality improvement https://www.brainkart.com/article/Kinds-of-Internal-Control_37585/ Limitations of Internal Control 1. Judgement- Decisions must be made constrained by available time, information at hand and under pressure of getting a job done 2. Breakdowns- Employee’s may misunderstand instructions 3. Management override- High level personnel may be able to overrule controls for personal gain or advantage 4. Collusion- two or more individuals may work together to bypass control. Control Activities- are the policies and procedures that help ensures the management activities Performance Review Physical Control Management uses accounting and operating data to assess performance and then take corrective action Controls that encompass the physical security of asset, the authorization for access to computer programs and data files, and periodic counting and comparison. • comparing actual performance vs budget • Investigating performance indicators on operating or financial data • Reviewing functional or activity performance Example: employee ID cards, fences, cash registers, fire proof files and locks Computer related controls dealing with access privileges or established backup recovery procedures Control Activities- are the policies and procedures that help ensures the management activities Information Processing Control- Are policies and procedures designed to require authorization of transactions and to ensure the accuracy and completeness of transaction processing. Control Procedures Examples Proper authorization of transaction activities • example: List price approval, disposal of asset, expenses authorization, credit line approval Segregation of duties- requires that different individuals be assigned responsibility for different elements of related activities particularly those involving authorization, custody, or recordkeeping. • the same person who is responsible for an asset's recordkeeping should not be responsible for physical control of that asset. • One person orders good from suppliers and another person logs in the receiving goods Adequate documents and controls- use of adequate documents and records allow to obtain reasonable assurance that all valid transactions have been recorded • • • • Prenumbered : Official receipt Sales invoice Purchase order Control Activities- are the policies and procedures that help ensures the management activities Information Processing Control- Are policies and procedures designed to require authorization of transactions and to ensure the accuracy and completeness of transaction processing. Control Procedures Examples Access to Assets- establishment of physical barriers and appropriate policies • Inventories be kept in storeroom or warehouse • Instruments may be placed in a safe deposit box • Policies on the access to company resources and information Independent check performance- periodic counts of assets and comparing the counts to the balances in the general ledger account • Count of inventory vs inventory ledger • Bank reconciliation For each of the following , give an example of physical control the client can use to protect the asset or record Account Physical control Petty Cash Should be kept in locked in a fireproof safe Cash received by retail clerks Cash received by retail clerks should be entered into a cash register to record all cash received. Accounts receivable records Accounts receivable records should be stored in a locked, fireproof safe. If the records are computerized, adequate backup copies should be maintained and access to the master files should be restricted via passwords Raw material Inventory Raw material inventory should be retained in a locked storeroom with a reliable and employee controlling access. Perishable tools Perishable tools should be stored in a locked storeroom under control of a reliable employee. Manufacturing equipment should be kept in an area protected by burglar alarms and fire alarms and kept locked when not in use Marketable securities Marketable securities should be stored in a safety deposit vault. Case Study: The smallest branch of Super Fresh Cosmetics in Iloilo employs Mary Santos, the branch manager, and her sales assistant, Jane Reyes. The branch uses as bank account in Iloilo city to Pay expenses. The account is kept in the name of Super Fresh Cosmetics- Special account”. To pay expenses, checks must be signed by Mary Santos or by the treasurer of Super Fresh Cosmetics , Juan Dy. Mary receives the cancelled checks and bank statements. She reconciles the branch account herself and files cancelled checks and bank statements in her records. She also periodically prepares reports of cash disbursements and send them to the home office. Required: 1. List the weaknesses in internal control. 2. For each weakness, state the type of misstatements that is likely to result 3. How would you improve internal control Case Study: Role Identification: Mary Santos 1. Branch Manager 2. She is the signatory of the check 3. She receives the cancelled checks and bank statement 4. She do the reconciliation 5. She prepares the cash disbursement reports Weakness Misstatements that is likely to occur Recommendation to improve the internal control No segregation of duties • Mary Santos is the signatory and do the reporting • The bank statement and cancelled check is reconciled by the manager , where reconciliation should be made against the manger’s report of cash disbursement The manager may draw checks to herself for personal purpose and omit them from her list of cash disbursement of or inflate other reported disbursement amounts Have all cancelled checks and bank statement directly to the home office. Cash disbursement with all supporting documents should be submitted to the Head office and reconcile. Bank reconciliation should be done by the HO. ANNOUCEMENT Synchronous class next week, May 28 Case Study Presentation Worldcom Scandal Siemens Short quiz : Coverage: Chapter 13&14 Assignment: Individual Activity: Deadline: May 29th Activity: Internal Control Assessment Research and identify internal controls that are being implemented in the following business establishments. Give 3 each per establishments. 1. Department Store 2. Bank 3. Convenience store 4. Supermarket Internal