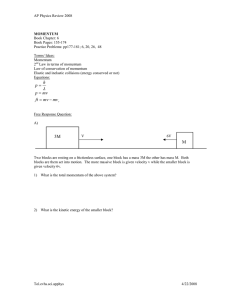
Model Answers 1a CIE AS Physics Topic Questions (a) Determine the velocity v of ball X before the collision: the known quantities: ASList Physics CIE Topic Questions 3.2 Linear Momentum Mass of X = 140 g& Conservation 3. Dynamics Mass of Y = 620 g Velocity of X before the collision = v Velocity of X after the collision = 0 Velocity of Y before the collision = 0 Velocity of Y after the collision = 0.8 m s−1 3.2 Linear Momentum & Conservation Use conservation of momentum to write an expression for v: Medium Easy Momentum before collision: m X v X + m Y v Y = 140v + 0 Momentum after collision: m X v X Hard + Answers m Y v Y = 0 + (620 × 0 . 8) Conservation of momentum: Momentum before collision = Momentum after collision 2 3 1 Conservation of momentum: 140v 1a Rearrange: v = = 620 × 0 . 8 [1 mark] 620 × 0 . 8 [1 mark] 140 v = 3.543 = 3.5 m s−1 [1 mark] 3 marks A ball X of mass 140 g travelling at constant velocity v collides head-on with a [Total: 3 marks] stationary ball Y of mass 620 g, as shown in Fig. 1.1. 1b (b) (i) Show that the collision in (a) is inelastic: List the known quantities: Mass of X = 140 g = 0.14 kg Mass of Y = 620 g = 0.62 kg Velocity of X before the collision = 3.5 m s−1 Velocity of X after the collision = 0 After the collision, ball X comes to a stop. Ball Y moves off in the same initial direction as X with a velocity of 0.8 m s−1. Model Answers Determine the velocity v of ball X before the collision. 1a (a) Determine the velocity v of ball X before the collision: List the quantities: How didknown you do? Mass of X = 140 g Mass of Y = 620 g Velocity of X before the collision = v Velocity of X after the collision = 0 Stuck? View related notes Velocity of Y before the collision = 0 Velocity of Y after the collision =View 0.8 mAnswer s−1 Use conservation of momentum to write an expression for v: Momentum before collision: m X v X 1b Momentum after collision: m v X X + m Y v Y = 140v + 0 + m Y v Y = 0 + (620 × 0 . 8) 4 marks Conservation of momentum: Momentum before collision = Momentum after (i) Show that the collision in (a) is inelastic. collision 140vin= × 0 . 8 [1 mark] Conservation momentum: (ii) Explainof why the collision (a)620 is inelastic. 620 × 0 . 8 Rearrange: v = [1 mark] 140 [3] [1] How vdid you do? = 3.543 = 3.5 m s−1 [1 mark] [Total: 3 marks] 1b Stuck? View related notes (b) View Answer (i) Show that the collision in (a) is inelastic: List the known quantities: Mass of X = 140 g = 0.14 kg 1c Mass of Y = 620 g = 0.62 kg Velocity of X before the collision = 3.5 m s−1 Velocity of X after the collision = 0 3 marks The balls are replaced by an aluminium sphere of mass 2.7 kg and a steel sphere 7.9 kg as shown in Fig. 1.2. ModelofAnswers The aluminium sphere has an initial velocity of 10.0 m s–1 when it collides with 1a stationary steel sphere. Immediately after the collision, the velocity of the the steel sphere is 5.1 m s–1. (a) Determine the velocity v of ball X before the collision: List the known quantities: Mass of X = 140 g Mass of Y = 620 g Velocity of X before the collision = v Velocity of X after the collision = 0 Velocity of Y before the collision = 0 Velocity of Y after the collision = 0.8 m s−1 Use conservation of momentum to write an expression for v: Momentum before collision: m X v X + m Y v Y = 140v + 0 Momentum after collision: v + m Y v sphere = 0 + (620 × 0 . 8) X X Y Calculate the velocity v of them aluminium immediately after the collision. Conservation of momentum: Momentum before collision = Momentum after collision HowConservation did you do? of momentum: 140v Rearrange: v = = 620 × 0 . 8 [1 mark] 620 × 0 . 8 [1 mark] 140 v =View 3.543related = 3.5 mnotes s−1 [1 mark] Stuck? [Total: 3 marks] View Answer 1b (b) 1d (i) Show that the collision in (a) is inelastic: List the known quantities: Verify that the collision in (c) is elastic. Mass of X = 140 g = 0.14 kg Mass of Y = 620 g = 0.62 kg of X before the collision = 3.5 m s−1 HowVelocity did you do? Velocity of X after the collision = 0 3 marks Model Answers Stuck? View related notes 1a View Answer (a) Determine the velocity v of ball X before the collision: List the known quantities: Mass of X = 140 g Did this page help you? Mass of Y = 620 g Velocity of X before the collision = v Velocity of X after the collision = 0 Velocity of Y before the collision = 0 Velocity of Y after the collision = 0.8 m s−1 Yes No Next question Use conservation of momentum to write an expression for v: YOUR PROGRESS before collision: m X v X CIE Momentum AS Physics + m Y v Y = 140v + 0 14%Momentum after collision: m X v X + m Y v Y = 0 + (620 × 0 . 8) Conservation of momentum: Momentum before collision = Momentum after collision 1. Physical Quantities & Units 16% Conservation of momentum: 140v = 620 × 0 . 8 [1 mark] 2. Kinematics Rearrange: v = 620 × 0 . 8 [1 mark] 140 37% v = 3.543 = 3.5 m s−1 [1 mark] 3. Dynamics [Total: 3 marks] 37% 1b 3.1 Newton's Laws of Motion (b) 36% (i) Show that the collision in (a) is inelastic: 3.2 Linear Momentum & Conservation List the known quantities: 39% Multiple Choice Mass of X = 140 g = 0.14 kg Mass of Y = 620 g = 0.62 kg Velocity of X before the collision = 3.5 m s−1 Velocity of X after the collision = 0 87% Structured Questions 0% Model Answers 4.1a Forces, Density & Pressure 45% (a) Determine the velocity v of ball X before the collision: List the known quantities: 5. Work, Energy & Power 0% Mass of X = 140 g Mass of Y = 620 g 6. Deformation Solidsthe collision = v Velocity of Xofbefore Velocity of X after the collision = 0 Velocity of Y before the collision = 0 Velocity of Y after the collision = 0.8 m s−1 7. Waves 0% 0% Use conservation of momentum to write an expression for v: Momentum before collision: m X v X 8. Superposition Momentum after collision: m X v X + m Y v Y = 140v + 0 0% + m Y v Y = 0 + (620 × 0 . 8) 9. Electricity 0% Conservation of momentum: Momentum before collision = Momentum after collision Conservation of momentum: 140v 10. D.C. Circuits Rearrange: v = = 620 × 0 . 8 [1 mark] 0% 620 × 0 . 8 [1 mark] 140 11. Particle Physics −1 v = 3.543 = 3.5 m s [1 mark] [Total: 3 marks] 1b (b) Resources Members (i) Show that the collision in (a) is inelastic: Join Launchpad List the known quantities: FAQ Account Mass of X = 140 g = 0.14 kg Support Log out Mass of Y = 620 g = 0.62 kg Velocity of X before the collision = 3.5 m s−1 Company Quick Links Velocity of X after the collision = 0 0% About us GCSE Revision Notes Contact ModelusAnswers IGCSE Revision Notes Jobs A Level Revision Notes Terms Biology 1a Privacy Chemistry (a) Determine the velocity v of ball X before the collision: Physics List the known quantities: Maths 2022 Advance Information Mass of X = 140 g Mass of Y = 620 g Velocity of X before the collision = v Velocity of X after the collision = 0 Velocity of Y before the collision = 0 Velocity of Y after the collision = 0.8 m s−1 Missing something? Tell us Use conservation of momentum to write an expression for v: © Copyright 2015-2023 Save My Exams Ltd. All Rights Reserved. Momentum before collision: m v + m Y v Y = 140v + 0 IBO was not involved in the production of,XandX does not endorse, the resources created by Save My Exams. Momentum after collision: m X v X + m Y v Y = 0 + (620 × 0 . 8) Conservation of momentum: Momentum before collision = Momentum after collision Conservation of momentum: 140v Rearrange: v = = 620 × 0 . 8 [1 mark] 620 × 0 . 8 [1 mark] 140 v = 3.543 = 3.5 m s−1 [1 mark] [Total: 3 marks] 1b (b) (i) Show that the collision in (a) is inelastic: List the known quantities: Mass of X = 140 g = 0.14 kg Mass of Y = 620 g = 0.62 kg Velocity of X before the collision = 3.5 m s−1 Velocity of X after the collision = 0