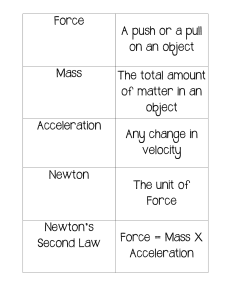
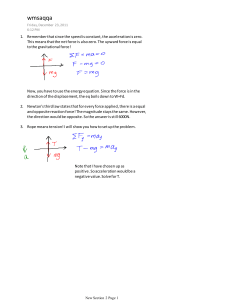
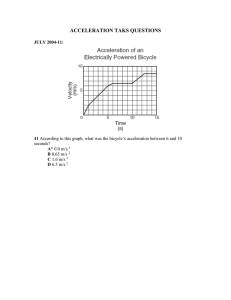
GRADE 1 to 12 DAILY LESSONLOG SCHOOL Jose C. Payumo Jr. Memorial High School TEACHER Mrs. Bliselda D. Bicaldo TEACHING DATES AND (Week 3) Sep. 12-15, 2023 TIME DAY 1 DAY 2 GRADE LEVEL 8 LEARNING AREA QUARTER SCIENCE FIRST QUARTER DAY 3 DAY 4 I. OBJECTIVES A. Content Standards The learner demonstrates understanding of Newton’s three laws of motion and uniform circular motion B. Performance Standards The learner shall be able to develop a writer plan and implement a “Newton’s Olympics”. C. Learning Competencies/Objectives II. CONTENT III. LEARNING RESOURCES A. References 1. Teacher’s Guide pages 2. Learner’s Materials pages 3. Textbook pages 4. Additional Materials from learningResource (LR) Portal Demonstrate how a body responds to changes in motion (S8FE-Ia-17) Law of Acceleration Demonstrate how a body responds to changes in motion (S8FE-Ia-17) Law of Acceleration Relate the Laws of Motion Demonstrate how a body to bodies in uniform responds to changes in circular motion motion.S8FE_Ib_18. (S8FE-Ia-17) Circular Motion and the Second Law of Motion Law of Interaction PP.13-16 PP.13-16 pp. 13-16 pp. 13-16 PP.16-17 PP.18-19 pp. 12-18 pp. 12-18 EASE Physics, Module 10. Lesson 3 EASE Physics, Module 10. Lesson 3 EASE Physics, Module 10. Lesson 3 EASE Physics, Module 10. Lesson 3 B. Other Learning Resources Lesson Guide G8 First EASE Physics. Module Quarter pp. 20 - 22 10.Lesson 3 Science and Technology IV: Physics Textbook. NISMED.2012. pp.292296 Lesson Guide G8 First Quarter pp. 23 - 25 EASE Physics. Module 10.Lesson 3 Science and Technology IV: Physics Textbook. NISMED.2012. pp.292-296 IV. PROCEDURES A. Reviewing previous lesson or presenting the new lesson B. Establishing a purpose for the lesson The teacher will show a video Prepare the materials Ask the students to restate the second law on the Law of Acceleration and whirl the bucket into a simple statement. https://www.youtube.com/ filled with water in front watch?v=EeT2yew0oDA of the students. Derivation of Formula: From the statement that acceleration is directly proportional to force at constant mass. Mathematically a= kF where nK = mass (eq. 1) Combining the two equations, we have a α F and a α 1/m Therefore a α F/m Mathematically, a= F/m where a= acceleration m= mass F= force What is the video all about? What is acceleration? Giving the same amount of push, which object was able to move, the skate board or the car? Why? What did you observe in the set-up? Where is the force coming from? What keeps the bucket swirling? Why is it that the water did not spill as you swirl the bucket? The teacher will show a video on the Law of Interaction https://www.youtube.com/ watch?v=TVAxASr0iUY What is the video all about? What is the Law of Interaction? What happens when two objects interact with each other? Differentiate action and reaction forces. C. Presenting examples/instances of the new lesson Give and discuss at least two examples of situation/problems on the Law of Acceleration 1. A huge stone is pushed with 30 N of force. If there is only 5N of friction and the stone’s mass is 88 kg. What is the acceleration of the table? 2. A car is being towed. If its mass is 1750 kg and it accelerated at 5m/s2, how much net force is involved? Group the students into 3 Group 1 Boy A pulling a 10kg load and Boy B pulling a 20kg load. Which among these boys require more force to pull and move the load? Why?(Boy B will require more force to accelerate the load, because force is directly proportional to the mass of an object) Group 2 Applying more force to an object with the same mass Which figure will have greater acceleration? Why? (The second figure with more force will have greater acceleration, because given the same mass, and greater force applied will make the object accelerate at a higher rate) Group 3 A3. A boy and a girl on the Swing Given the same amount of force, who will have a greater movement on the swing, the boy or the girl? Why? (The girl, because she has lesser mass and mass is inversely proportional to acceleration) See attached activity sheet Group the students into 3 and give the following situations: See attachment A1 A2 and A3 respectively. Let the students discuss among themselves the condition of the objects in the picture. How does the object react with the forces acting on each other in terms of magnitude and direction? Group 1 When you jump, See attachment A1. Group 2 A swimmer, See attachment A2. Group 3 While Walking, See attachment A3. D. Discussing new concepts and practicing new skills #1 Do the exercise in Lesson Guide G8 First Quarter pp 21 (choose items which will be solved individually/ in group) Let each group select a reporter to discuss the answers on the activity. Ask the students the following questions: Group 1. What is the relationship between mass and force? Mass is directly proportional to Force. An object with higher mass will require more force to accelerate an object. Group 2. What is the relationship between force and acceleration? (Force is directly proportional to Acceleration. The greater is the force applied, the higher is the rate of acceleration) Group 3. What is the relationship between mass and acceleration? (Mass is inversely proportional to Acceleration. Lesser mass will have higher rate of acceleration) When an object moves in a circle, it is really constantly changing direction. The object wants to travel in a straight line, but a force is pulling it towards the center of the circle. This force is called centripetal force. Let each group select a reporter to discuss the answers on the activity. Ask the students the following questions: Group 1 When you jump, See attachment A1. What are the forces present as you jump? (Your legs apply a force to the diving board, and the board applies an equal and opposite reaction force that propels you into the air.) Group 2 A swimmer, See attachment A2. What are the forces present that enables the swimmer to go forward? (A swimmer pushes the water backward by his/her hands and in return the water pushes the swimmer forwards, thus enabling him to go forward during swimming.) Group 3 While Walking, See attachment A3. What are the forces that allows a person to walk E. Discussing new concepts and practicing new skills #2 Presentation of the outcomes. Presentation of the outcomes. In circular motion, the whirling object accelerates not due to the change in its speed but to the change in the direction of its velocity. By Newton’s second law of motion, a net force must be acting on accelerating objects. In this case, the force comes from the rope/string pulls the object towards the center of its circular path. If you remove this force by either cutting or releasing the string, you will observe that the object will continue to move straight and fly off tangential to the path. This is the natural tendency of the object if there is no net force acting on it, according to on the surface or ground? (You push the floor or the surface you are walking on with your toes, And the surface pushes your legs up, helping you to lift your legs up.) Newton’s Third Law of Motion: Law of Interaction (Action-Reaction) “For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction.” Action-Reaction Forces Two forces are equal in size. Two forces are opposite to each other in terms of direction. Two forces have the same line of action. Action acts on one object, while reaction acts on another object. Force is a part of mutual action, an interaction, between one thing and another. For example, consider the interaction between the hammer and a nail. While the hammer exerts a force on the nail, the nail F. Developing mastery (Leads to Formative Assessment3) Discuss the answers in the exercise given. Newton’s Second Law Motion: Law of Acceleration The acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the magnitude of the net force acting on it and is inversely proportional to its mass. This statement actually pertains to Newton’s second law of motion or Law of Acceleration, because it is concerned with the relation of acceleration to mass and force. This can be expressed in equation form as: the First Law of Motion. But because of the net force from the string/rope, instead of going straight, the object accelerates inwards thereby covering a circular path. The object is said to be in uniform circular motion. The force pulling an object towards the center of a circle is called the centripetal force. Discuss the answers in the activity given. exerts a force on the hammer. In the interaction between the hammer and the nail, there is a pair of forces, one acting on the nail and the other acting on the hammer. Discuss the answers in the exercise given Acceleration = Net force/mass a = Fnet / mass G. Finding practical Engineers at the Two vehicles are stuck in a applications of concepts Johnson Space muddy place, a car and and skills in daily living Center must dump truck, the purok determine the net leader in your place ask for force needed for a help to remove the vehicles, rocket to achieve an which vehicle would you like acceleration of 70 to help considering your m/s2. If the mass of size and age? Why? (With the rocket is 45,000 my age and my capability, I kg, how much net will choose to help unstuck force must the rocket the car, because the car has develop. lesser mass compared to the dump truck, which means lesser mass needs lesser force to unstuck it.) H. Making generalizations Mathematically, second What is the Law of and abstractions about the law of motion can be Acceleration? expressed: lesson The acceleration of an object is directly A = F/m proportional to the F = ma magnitude of the net M = F/a force acting on it and is inversely proportional to its mass. Can you mention a particular fairground ride which demonstrate a uniform circular motion? What safety precautions should the ride owners consider to ensure the safety of their riders? Group the students into 3 Assign a picture for each group (See Attachment B,C,D), And let them answer the guide questions in the picture. Group 1 A bullet fired from a riffle Group 2 Boy stepping out from the boat Group 3 Bat hitting a baseball We say an object experienced uniform circular motion if it moves in a circle of constant radius To experience uniform circular motion, must the net force on the object be directed towards the center of the circle. For example, a person in a graviton ride experiences the normal force on his back, which is directed towards the center of the graviton. What is Newton’s third law of motion? Define. (Law of Interaction (ActionReaction) “For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction.”) Differentiate action and reaction forces. (Action acts on one object, while reaction acts on another object.) Explain Action-Reaction Forces (Two forces are equal in size, opposite to each other in terms of direction, and have the same line of action) I. Evaluating learning Direction: Solve problems involving the Law of acceleration then write the letter of the correct answer. 1. What is the mass of a truck if it produces a force of 14,000N while accelerating at a rate of 5 m/s2 ? A. 280 kg *B. 2800kg C. 70,000kg D. 7000kg 2. Which is the correct unit of acceleration? A. m/s *B. m/s2 C. kg.m/s D. kg.m/N 3. Suppose that a sled is accelerating at a rate of 2m/s2. If the net force is tripled and the mass is halved, what then is the new acceleration of the sled? A. decrease by half B. doubled *C. tripled D. quadrupled 4. Suppose a ball of mass 0.60 kg is hit with a force of 12 N. Its acceleration will be: *A. 20 m/s2 B. 40 m/s2 C. 10 m/s2 D. 20 m/s Give at least two examples of situation around you that the Law of Acceleration is applied. Explain in your own words ( 10 pts. ) If the object in uniform circular motion is accelerating towards the center of the circle, why does it remain a circular path at a constant radius and never get closer to the center of the circle? Direction: Read each sentence carefully and write the letter of the correct answer. 1. As a 500 N lady sits on the floor, the floor exerts a force on her equal to______________. A. 1000 N *B. 500 N C. 250 N D. 50 N 2. According to Newton's Third Law of Motion, when a hammer strikes and exerts a force on a nail, the nail A. creates a balanced force. B. disappears into the wood. C. moves at a constant speed. * D. exerts and equal and opposite force back on the hammer. 3. Pick the best example of Newton's Third Law in action. A. A rocket taking off from earth which pushes gases in one direction and the rocket in the other. *B. A rocket sitting on the ground preparing for take-off but it needs an outside force to overcome its inertia of a non-moving object. C. A rocket that is accelerating through space and exerts a great amount of force because its mass and acceleration is so large. D. Both b and c. 4. When a teacher stands at the front of the class, the force of gravity pulls her toward the ground. The ground pushes back with an equal and opposite force. 5. If the ball in question no. 4 is increased by 24 N, what is the increased in acceleration? A. 20 m/s2 B. 30 m/s2 *C. 4 0 m/s2 D. 50 m/s2 J. Additional activities for application or remediation Give additional information regarding: balance and un balance forces. SESSION 1 V. REMARKS VI. REFLECTION A. No. of learners who earned 80% in the evaluation B. No. of learners who require additional activities for remediation C. Did the remedial lessons work? No.of learners who have This is an example of which of Newton's Laws of Motion? A. Law of Inertia B. Law of Acceleration *C. Law of Interaction D. Law of Universal Gravitation 5. For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. This is a statement of A. Newton's First Law of Motion. B. Newton's Second Law of Motion. *C. Newton's Third Law of Motion. D. Newton's Law of Action. Design and implement an 1.Define centrifugal force Design and implement an experiment that will verify and differentiate it with experiment that will verify Newton’s Law of Motion the centripetal force. Newton’s Law of Motion. Does these two forces equal in magnitude? Do they have the same direction ? SESSION 2 SESSION 3 SESSION 4 ___ of Learners who earned 80% above _____of Learners who earned 80% above ___ of Learners who earned 80% above ___ of Learners who earned 80% above ___ of Learners who require additional ___ of Learners who require activities for remediation additional activities for remediation ___ of Learners who require additional activities for remediation ___ of Learners who require additional activities for remediation ___Yes ___No ____ of Learners who caught up the lesson ___Yes ___No ____ of Learners who caught up the lesson ___Yes ___No ____ of Learners who caught up the lesson ___Yes ___No ____ of Learners who caught up the lesson caught up with the lesson D. No. of learners who continue to require remediation E. Which of myT eaching strategies worked well? Why did these work F. What difficulties did I encounter whichmy principal or supervisor can help me solve G. What innovation or localized materialsdid I use/discover which I wish to ___ of Learners who continue to require remediation ___ of Learners who continue to require remediation ___ of Learners who continue to require remediation ___ of Learners who continue to require remediation Strategies used that work well: ___ Group collaboration ___ Games ___ Power Point Presentation ___ Answering preliminary activities/exercises ___ Discussion ___ Case Method ___ Think-Pair-Share (TPS) ___ Rereading of Paragraphs/ Poems/Stories ___ Differentiated Instruction ___ Role Playing/Drama ___ Discovery Method ___ Lecture Method Why? ___ Complete IMs ___ Availability of Materials ___ Pupils’ eagerness to learn ___ Group member’s Cooperation in doing their tasks __ Bullying among pupils __ Pupils’ behavior/attitude __ Colorful IMs __ Unavailable Technology Equipment (AVR/LCD) __ Science/ Computer/ Internet Lab __ Additional Clerical works __Reading Readiness __Lack of Interest of pupils Planned Innovations: __ Localized Videos __ Making use big books from views of the locality Strategies used that work well: ___ Group collaboration ___ Games ___ Power Point Presentation ___ Answering preliminary activities/exercises ___ Discussion ___ Case Method ___ Think-Pair-Share (TPS) ___ Rereading of Paragraphs/ Poems/Stories ___ Differentiated Instruction ___ Role Playing/Drama ___ Discovery Method ___ Lecture Method Why? ___ Complete IMs ___ Availability of Materials ___ Pupils’ eagerness to learn ___ Group member’s Cooperation in doing their tasks __ Bullying among pupils __ Pupils’ behavior/attitude __ Colorful IMs __ Unavailable Technology Equipment (AVR/LCD) __ Science/ Computer/ Internet Lab __ Additional Clerical works __Reading Readiness __Lack of Interest of pupils Planned Innovations: __ Localized Videos __ Making use big books from views of the locality Strategies used that work well: ___ Group collaboration ___ Games ___ Power Point Presentation ___ Answering preliminary activities/exercises ___ Discussion ___ Case Method ___ Think-Pair-Share (TPS) ___ Rereading of Paragraphs/ Poems/Stories ___ Differentiated Instruction ___ Role Playing/Drama ___ Discovery Method ___ Lecture Method Why? ___ Complete IMs ___ Availability of Materials ___ Pupils’ eagerness to learn ___ Group member’s Cooperation in doing their tasks __ Bullying among pupils __ Pupils’ behavior/attitude __ Colorful IMs __ Unavailable Technology Equipment (AVR/LCD) __ Science/ Computer/ Internet Lab __ Additional Clerical works __Reading Readiness __Lack of Interest of pupils Planned Innovations: __ Localized Videos __ Making use big books from views of the locality Strategies used that work well: ___ Group collaboration ___ Games ___ Power Point Presentation ___ Answering preliminary activities/exercises ___ Discussion ___ Case Method ___ Think-Pair-Share (TPS) ___ Rereading of Paragraphs/ Poems/Stories ___ Differentiated Instruction ___ Role Playing/Drama ___ Discovery Method ___ Lecture Method Why? ___ Complete IMs ___ Availability of Materials ___ Pupils’ eagerness to learn ___ Group member’s Cooperation in doing their tasks __ Bullying among pupils __ Pupils’ behavior/attitude __ Colorful IMs __ Unavailable Technology Equipment (AVR/LCD) __ Science/ Computer/ Internet Lab __ Additional Clerical works __Reading Readiness __Lack of Interest of pupils Planned Innovations: __ Localized Videos __ Making use big books from views of the locality share with other teachers? __ Recycling of plastics to be used as Instructional Materials __ local poetical composition __Fashcards __Pictures Prepared By: BLISELDA D. BICALDO Master Teacher I Noted: MENANDRO S. REYES Head Teacher III-Science Date signed: ___________ __ Recycling of plastics to be used as Instructional Materials __ local poetical composition __Fashcards __Pictures __ Recycling of plastics to be used as Instructional Materials __ local poetical composition __Fashcards __Pictures __ Recycling of plastics to be used as Instructional Materials __ local poetical composition __Fashcards __Pictures