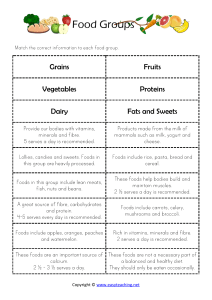
Nutrition Guide: Nutrients, Vitamins, Minerals & Diets
advertisement

NEMCC Associate Degree Nursing Nutrition Packet Nutrient Carbohydrates (4 kcalories/gram) Function Fuel, spare protein, prevent ketosis Proteins (4 kcalories/gram) Complete/incomplete Maintenance & growth, regulate body processes, immunity, energy Fats (9 kcalories/gram) LDL, HDL, cholesterol Terms: hydrogenation, Fuel reserve, organ protection, cell membrane structure, lubrication, insulation, fat soluble vitamins Fat Soluble Vitamins A, D, E, K Vitamin A. Preformed Provitamin A (carotene) Function Deficiency/Toxicity Excess intake above body’s need stored as fat Source of nitrogen for the body, excess protein excreted by the kidneys Excess above needs stored, in body triglycerides, essential fatty acid linoleic acid Deficiency/Toxicity Vision (rhodopsin), maintenance of skin & epithelium, normal bone growth, energy regulation Deficiency – xerophtalmia Excess – carotenemia Toxicity – HA, blurred, vision, Inc. ICP, pain in bones & joints, dry skin, poor appetite Vitamin D Normal Bone Mineralization Vitamin E Antioxidant, protects lung against pollution, stability of RBC membrane Deficiency – Rickets in children, osteomalacia in adults Most toxic of all vitamins, can lead to death from Ca+ deposit in brain, heart, kidney Deficiency – sterility Toxicity – supplemental dose of >600 mg/day for 1 year or longer Vitamin K Blood clotting, bone metabolism Deficiency – in newborn due to sterile bowel, Toxicity – Sources Fruits, cereal grain, vegetables Complete: meat, poultry, fish, eggs, milk. Incomplete: grains, vegetables, nuts, legumes, seeds. Saturated – Animal fats, solid at room temp., coconut, palmkernel oils. Polyunsaturated – corn oil, safflower oil, soybean oil. Monosaturated – olive & cannola Sources Sources: Preformedliver, kidney, egg yolk, butter, cream, milk & fortified milk products Provitamin – carrots, sweet potatoes, squash, apricots, cantaloupe, dark green leafy (broccoli, cabbage, etc.) Sunshine – manufactured in the skin, Fortified milk. Some health problems interfere with absorption. Sources: polyunsaturated fatty acids (vegetables oils, whole grains, wheat germ, milk, eggs, fish, meats, leafy vegetables Cheese, milk, green leafy vegetables. 1 NEMCC Associate Degree Nursing Nutrition Packet excess dose causes liver damage, bleeding, hemolysis of RBC’s, brain damage. Water Soluble Vitamins Vitamin C Function Wound and Fx healing, Antioxidant, Adrenal gland function, Fe+ absorption, Folic acid conversion Deficiency/Toxicity Sources Deficiency – Scurvy RDA – 60 mg/day. Abruptly stopping excessive intake will cause rebound scurvy Sources: citrus fruits, tomatoes, white potatoes, cabbage, broccoli, turnip greens, asparagus, berries, melons Thelma Rose Never Passes for B12 (Acronym for rest of the water soluble vitamins) Thiamin (B1) RDA Coenzyme in CHO Deficiency – Wernicke- Pork, wheat germ, increase with increased metabolism, metabolizes Korsakoff syndrome. brewer’s yeast, beef, CHO needs alcohol to energy, s/s – anorexia, liver, legumes, eggs, converts trytophan to indigestion, fish, enriched grains. niacin constipation, apathy, fatigue, muscle weakness, paralysis, muscle atrophy, ? cardiac failure/death. Riboflavin Coenzyme of protein Deficiency – Organ meats, milk, metabolism. ariboflavinosis s/s – whole or enriched lesions on lips & oral grains, legumes, cavity, seborrheic vegetables. dermatitis, scrotal or vulval skin changes, normocytic anemia, Need ↑ as protein need ↑. Niacin Coenzyme in production Deficiency: pellagra “ 3 Preformed in meat, Used to treat elevated of energy from glucose. D’s” – dermatitis, also peanuts, legumes, lipid levels Synthesis of fatty acids, diarrhea, dementia coffee body converts Toxicity causes tryptophan to niacin flushing, Pyridoxine (B6) Co-enzyme of amino Deficiency – unusual Pork & organ meats acids, converting Toxicity – megadoses best sources, otherstryptophan to niacin, of 2 – 6 grams. wheat germ, whole antibodies, coenzyme for grains. Not included in neurotransmitters enrichment. Folate ( folic acid) Formation of DNA, Deficiency – common. Liver, spinach, Body has a 2 – 4 month formation of HEME Results in impaired cell asparagus, broccoli, store division & protein kidney beans, beets, Alcohol, oral synthesis, impaired cabbage family, contraceptives, ASA, heme synthesis. oranges, cantaloupe. methotrexate interfere Toxicity – rare 2 NEMCC Associate Degree Nursing Nutrition Packet Vitamin B12 Stored in liver Pharmaceutical name: cyanocobalamin Precursor to use of folic acid in DNA replication, Essential for RBC manufacture, essential for synthesis & maintenance of myelin Minerals Calcium Function Muscle contractions and relaxation, catalyst in clotting, actives certain enzymes, manufacture of acetycholine Phosphorum Interrelated with Ca+ in function & food sources, component of bones, teeth, RNA & DNA, contained in ADP & ATP, phospholipids, pH buffer Maintain fld. Balance, transmission of electrochemical impulses, adrenals produce aldosterone which regulates level. 2/3 in blood & extracellular fluids, 1/3 in bone 98% inside cells. Necessary for conduction of nerve impulses, contraction of muscles, maintain acid-base, conversion of glucose to glucogen Sodium Potassium Deficiency – stomach or intestinal disease, diet, inadequate intrinsic factor, ? due to surgery or heredity. S/S – numbness & tingling in hands & feet, RBC changes, moodiness, confusion, depression, delusion, overt psychosis. ? death. Deficiency/Toxicity Deficiency – osteoporosis, tetany, check Trousseau’s & Chvostek’s. Toxicity: due to excessive intake, hyperparathyroidism, Vit D poisoning, Deficiencyhyperparathyroidism where too much Ca+, along with phosphorus withdrawn from bone, Toxicity: unusual Deficiency not generally a problem unless vomiting, diarrhea, heavy sweating, kidney disease. Toxicity – problem with HTN, heart disease, kidney disease. Deficiency: due to diarrhea, vomiting, laxative abuse, alkalosis, proteincalorie malnutrition. Toxicity: can be fatal, usually due to DKA, kidney failure, adrenal insufficiency, severe dehydration, destruction of cells by Animals products – meat milk, eggs, cheese. Sources milk & milk products, sardines, canned fish such as salmon, beans, cauliflower, rhubarb, green leafy, beets, broccoli. High fiber or fat intake interferes in absorption. Widespread since essential part of plant & animal cells, animal protein best source, lean meats, nuts, legumes Table salt, milk & milk products, lots in processed foods (lunch meats, white bread, pickles, crackers, chips), butter, margarine Present in all plant & animal cells. Bananas, dried fruits, oranges, legumes, vegetables, nuts, meats. 3 NEMCC Associate Degree Nursing Nutrition Packet Magnesium 70% in bones, 30% in tissues & body flds. Nerve impulses, skeletal muscle relaxation, bone formation, holds Ca+ in teeth, activates enzymes for CHO, protein, fat metabolism Iron – when RBC’s destroyed, Fe+ stored, absorption increases with increased need. Heme iron in meat, fish & poultry, nonheme iron in plants (not as absorbable) HGB formation, myoglobin, enzymes for oxidation of glucose to energy, stored as ferritin in liver, spleen, bone marrow Iodine Synthesis of thyroid hormones burns, crushing injuries, severe infection Deficiency - ? due to protein-calories malabsorption , excessive vomiting, diarrhea, diuretic tx., malabsorption, chronic alcoholism. Impairs CNS muscular excitability, tetany, disorientation, convulsions, psychosis Toxicity: lethargy, sedation, hypotension, bradycardia, depression respirations, ? resp or cardiac arrest Deficiency – insufficient intake, excessive blood loss, malabsorption, lack of hydrochloric acid. Absorption affected by alcohol, high Ca+ intake, Vitamin C, MFP, decreased gastric acid. Toxicity: overdose in children, iron metabolism disorders, oversupply of hemosiderin, chronic alcoholism. Deficiency – goiter Toxicity – excess in American diet, may also cause goiter, skin lesions Widely distributed in foods since part of the chlorophyll molecule, green vegetables, legumes, shrimp, nuts, fruits. RDA 10 for men, 15 women Liver, meats, eggs, kidney beans, bran cereal with raisins, cream of wheat, lentils. Fortified table salt, saltwater fish, shellfish, seaweed. 4 NEMCC Associate Degree Nursing Nutrition Packet Diet Progression in the Hospital NPO Clear Liquid Full Liquid Pureed Soft Regular Nothing to eat or drink, nothing by mouth Broth, bouillon, coffee, tea, carbonated beverages, clear fruit juices, gelatin, popsicles all above plus smooth textured dairy products, custards, refined cooked cereals, vegetables juice, pureed vegetables, all fruit juices All above plus scrambled eggs, pureed meats, vegetables, fruits, mashed potatoes and gravy All above plus ground or finely diced meats, flaked fish, cottage cheese, cheese, rice, potatoes, pancakes, light breads, cooked vegetables, cooked or canned fruits, bananas, soups, peanut butter no restrictions on type or texture of food unless specified. Types of Vegetarian Diets Vegan Lactovegetarian Ovolactovegetarian Plant products only (deficient in B12), Need vitamin supplement Milk + vegetables (lacks iron & zinc) Milk, eggs and vegetables. Examples of Prescribed Diets* Carbohydrate (CHO) Counting High Fiber Lactose-Restricted Low Fat/Low cholesterol Low sodium Mechanical soft or edentulous Progressive May be the diet ordered for diabetics. Certain high carbohydrate food counts toward a total number of CHO for the day. Many older diabetics may still be on the numbered calorie ADA diets. Whole grains, raw vegetables, fruits with peel such as apples, etc. (need 25 g of fiber/day) Lactose the carbohydrate in milk, if lactase deficiency, causes bloating, loose stools, cramping. Teach to find other sources of vitamins A, D, calcium. Substitute poly- or mono-saturated fats for saturated fats, limit total fat intake to no more than 30% of total calories, limit cholesterol sources (eggs, milk, other animal products). Limit processed foods (lunch meats, vegetables canned with sodium), avoiding adding at table. Look for lower sodium items. For those without teeth. Begin with clear liquids and advance to regular as client tolerates. *Prescribed based on health status and diagnoses. Multiple diets may be prescribed (example: a progressive, low-fat diet). These are examples, there are many more prescribed diets, plus cultural and religious diets. 5 NEMCC Associate Degree Nursing Nutrition Packet Food and Nutrition Guidelines Food Group Grains Proteins Fruits Servings per Day/Meal Examples Serving Sizes Any food made from wheat, rice, oats, cornmeal, barley, or another cereal grain is a grain product. Bread, pasta, breakfast cereals, grits, and tortillas are examples of grain products. Foods such as popcorn, rice, and oatmeal are also included. Grains are divided into 2 subgroups: Whole Grains and Refined Grains. All foods made from seafood; meat, poultry, and eggs; beans, peas, and lentils; and nuts, seeds, and soy products are part of the Protein Foods Group. Beans, peas, and lentils are also part of the Vegetable Group. 1 slice of bread, 1 cup of readyto-eat cereal, or ½ cup of cooked rice/pasta/cereal is equal to 1 serving. 3 to 5 ounces/equivalent per day. Half of grains should be whole grains. In general, 1 ounce of meat, poultry or fish, ¼ cup cooked beans, 1 egg, 1 tablespoon of peanut butter, or ½ ounce of nuts or seeds can be considered as 1 ounceequivalent from the Protein Foods Group. 4 oz of protein (size of hand) is equal to 1 serving. Fruit the size of a 5 to 7 ounces/equivalent per day Any fruit or 100% fruit juice 1 ½ to 2 ½ cups per 6 NEMCC Associate Degree Nursing Nutrition Packet Vegetables Dairy counts as part of the Fruit Group. Fruits may be fresh, frozen, canned, or dried/dehydrated, and may be whole, cut-up, pureed, or cooked. tennis ball, 1 cup of fruit or 100% juice, or ½ cup of dried fruit is equal to 1 serving. Any vegetable or 100% vegetable juice counts as part of the Vegetable Group. Vegetables may be raw or cooked; fresh, frozen, canned, or dried/dehydrated; and may be whole, cut-up, or mashed. Based on their nutrient content, vegetables are organized into 5 subgroups: dark green; red and orange; beans, peas, and lentils; starchy; and other vegetables. Animal milk, soy milk, yogurt, natural cheeses. Low-fat or fatfree versions recommended. 1 cup of raw or cooked vegetables or 100% vegetable juice, 2 cups of raw, leafy salad greens is equal to 1 serving. Fats/Oils/Sweets Oils are fats that are liquid at room temperature (examples include fish oil, avocado oil, olive oil). Solid fats are solid at room temperature (examples include butter, lard, and shortening). day. Half of each plate should be fruits and vegetables. At least half of the recommended amount of fruit should come from whole fruit, rather than 100% fruit juice. 2 to 4 cups per day. Half of each plate should be fruits and vegetables. In general, 1 cup of milk, yogurt, or soy milk, or 1 ½ ounces of natural cheese can be considered as 1 serving from the Dairy Group. 2 to 3 servings per day Use sparingly Use sparingly 7 NEMCC Associate Degree Nursing Nutrition Packet How to Calculate BMI (page 1112 in Fundamentals book) 1. Calculate BMI with Imperial/English Measurements (lbs/ft/in): BMI = 703 x Body Weight (lbs) / [height(in)]2 Example: Pt weighs 130lbs and is 5 ft and 10 inches tall BMI = 703 x 130 / (70in)2 BMI = 91650/4900 BMI = 18.7 Or… 2. Calculate BMI with Metric System Measurements (kg/cm/m): BMI = Body weight (kg) / [height (m)]2 Example: Pt weighs 130lbs and is 5 ft and 10 inches tall BMI = 59 kg/(177.8cm)2 BMI = 59 kg/(1.778m)2 BMI = 59kg/3.16m BMI = 18.7 Important Conversions: • 1 kg = 2.2 lbs • 1 in = 2.54 cm • 100cm = 1 m BMI Categories: • <19.8 = underweight or low • 19.8 – 26.0 = normal • 26.0 – 29.0 = overweight or high • >29.0 = obese 8