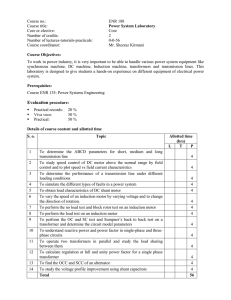
Lesson Plan Department: EEE Branch & Semester: B.E & EEE Course code & Title: 22EE303 & Electrical Machines I Unit Title: Induction Motor CO / Lesson No (GO): 4/1 1. Prerequisite(s): Electromagnetic material, Mutual Inductance, Three phase AC system 2. Topic: Three phase Induction motor - Construction - Types of rotor - Operation 3. General Objective (GO): To understand the construction and working of three phase induction motor 4. Specific Objectives (SO): SO1 – Infer the production of rotating field in a three phase induction motor by applying three phase ac supply (U/C) SO2 - Illustrate with a neat diagram about the constructional details of three phase induction motor. (U/C) SO3 – Compare the two types of rotor used in induction motor and its operation.(An/C) 5. Mapping Table: SO PO PO/PSO Competency PO/PSO Indicator SO1 1,2,4/ 14 1.1,1.2,1.3,1.4,2.1,2.2, 1.1.1,1.2.1,1.3.1,1.4.1,2.1.1,2.1.2,2.1.3. SO2 1,2,4/ 14 1.1,1.2,1.3,1.4,2.1/14.2 1.1.1,1.2.1,1.3.1,1.4.1,2.1.1,2.1.2,4.3.2/14.2.2. SO3 1,2,4/ 14 1.1,1.2,1.3,1.4,2.1 /14.2 1.1.1,1.2.1,1.3.1,1.4.1,2.1.1,2.1.2,2.1.3, 3.2/14.2.2. 6. Mind map and Summary: Summary: Very simple & extremely rugged Cost is low very & reliable In normal running condition, no brushes are needed Requires minimum maintenance Speed decreases with increase with increase in load Starting torque is somewhat inferior to d.c shunt motor Made up of this laminations of silicon steel to reduce hysteresis & eddy current Loss Squirrel cage rotor- Rotor bars are permanently short-circuited on themselves (ii) Phase -wound or wound rotor Rotor is wound for 3 phase Slip rings are mounted on the shaft with brushes Brushes are externally connected to a 3 phase star connected armature 7. Reference: [1] M.G.Say, Performance and Design of Alternating Current Machines, 3rd Edition, CBS Publisher, 2017. [2] D. P. Kothari and I. J. Nagrath, Electric Machines, Tata McGraw Hill Publishing Company Ltd, FourthEdition 2018. [3] Stephen J.Chapman, Electric Machinery Fundamentals, Tata McGraw Hill, New Delhi, 2018. [4] E. Fitzgerald, Charles Kingsley, Stephen.D.Umans, Electric Machinery, Tata McGraw Hill publishingCompany Ltd, New Delhi ,2015. Prepared by [Mr. A. Nandhakumar] Lesson Plan Department: EEE Branch & Semester: B.E & EEE Course code & Title: 22EE303 & Electrical Machines I Unit Title: Induction Motor CO / Lesson No (GO): 4/2 1. Prerequisite(s): Torque, Horse Power, Relationship between speed and torque, Slip 2. Topic: Torque equation and Torque - slip characteristics 3. General Objective (GO): Students will be able to understand the torque equation of induction motor and develop the torque speed characteristics 4. Specific Objectives (SO): SO1 – Formulate an expression for torque equation of three phase induction motor. (U/C) SO2 – Indicate the condition for maximum torque in a 3-phase induction motor (U/C) SO3 – Differentiate the characteristics of squirrel cage and slip ring induction motor.(An/C) 5. Mapping Table: SO PO PO/PSO Competency PO/PSO Indicator SO1 1,2,13 1.1,1.2,2.1,13.1 1.1.1,1.2.1,2.1.1,13.1.2 1,2,13 1.2,2.3,13.1 1.2.1,2.3.1,13.1.2 1,2,13 1.1,1.2,2.4,13.1 1.1.1,1.2.1,2.4.1,2.4.3,13.1.2 SO2 SO3 6. Mind map and Summary: T= 3/ws ×SE22 R2/R22 +SX22 Tst =3/2πns× E22R2/R22+X22 TORQU E EQUATI ON Starting torque Condition for maximum torque SX2=R2 Tm= kE22/2X2 T F.L/Tm= 2SfSm/Sm2+Sf2 Sf= Full load slip Summary: Torque Equation T α SE22 (R2/R22 +SX22) N-m N-m Starting torque Tst = (3/2πns)× Condition for maximum torque SX2=R2 Tm = kE22/2X2 Range S = 0 to S = Sm ---------- Low slip region ---------- Range S = Sm to S = 1 -------- High slip region ------------ T F.L/Tm = 2SfSm/Sm +Sf E2 R2/R2 +X22 2 2 Stable operation Unstable operation 7. Reference: [1] M.G.Say, Performance and Design of Alternating Current Machines, 3rd Edition, CBS Publisher, 2017. [2] D. P. Kothari and I. J. Nagrath, Electric Machines, Tata McGraw Hill Publishing Company Ltd, FourthEdition 2018. [3] Stephen J.Chapman, Electric Machinery Fundamentals, Tata McGraw Hill, New Delhi, 2018. [4] E. Fitzgerald, Charles Kingsley, Stephen.D.Umans, Electric Machinery, Tata McGraw Hill publishingCompany Ltd, New Delhi ,2015. Prepared by [Mr. A. Nandhakumar] Lesson Plan Department: EEE Branch & Semester: B.E & EEE Course code & Title: 22EE303 & Electrical Machines I Unit Title: DC Machines CO / Lesson No (GO): 4/3 1. Prerequisite(s): Power loss, slip, constant loss, variable loss 2. Topic: Equivalent circuit model 3. General Objective (GO): The student will be able to develop an equivalent circuit for induction motor 4. Specific Objectives (SO): SO1 – Classify the losses in three phase induction motor. (U/C) SO2 – Identify the losses computed in open circuit and blocked rotor test. (U/C) SO3 – Develop an equivalent circuit from the parameters obtained in the no load and blocked rotor test. (U/C) 5. Mapping Table: SO PO PO/PSO Competency PO/PSO Indicator SO1 1,2,14 1.1,1.2,2.1,14.1 1.1.1,1.2.1,2.1.1,14.1.2 SO2 1,2,13 1.2,2.3,13.1 1.2.1,2.3.1,13.1.2 1,2,13 1.1,1.2,2.4,13.1 1.1.1,1.2.1,2.4.1,2.4.3,13.1.2 SO3 6. Mind map and Summary: Summary: 7. Reference: Magnetizing component of core X0 = V1/Im Resistance R0 = V1/Ic Variable rotor resistance R2 = R2+ R2(1-s)/s Gross mechanical power developed Pg = 3 I2’2 Rl’ Pg is maxmimum when Rl’ = standstill impedance of the motor [1] M.G.Say, Performance and Design of Alternating Current Machines, 3rd Edition, CBS Publisher, 2017. [2] D. P. Kothari and I. J. Nagrath, Electric Machines, Tata McGraw Hill Publishing Company Ltd, FourthEdition 2018. [3] Stephen J.Chapman, Electric Machinery Fundamentals, Tata McGraw Hill, New Delhi, 2018. [4] E. Fitzgerald, Charles Kingsley, Stephen.D.Umans, Electric Machinery, Tata McGraw Hill publishingCompany Ltd, New Delhi ,2015. Prepared by [Mr. A. Nandhakumar] Lesson Plan Department: EEE Branch & Semester: B.E & EEE Course code & Title: 22EE303 & Electrical Machines I Unit Title: Induction Motor CO / Lesson No (GO): 4/4 1. Prerequisite(s): Magnetic fields, DC machine, Armature windings, Field system 2. Topic: Double field revolving theory. 3. General Objective (GO): To understand the principle of double field revolving theory and construction of single phase induction motor. 4. Specific Objectives (SO): SO1 – Infer the concept of double field revolving theory. (U/C) SO2 – Illustrate the construction of single phase induction motor. (U/C) SO3 – Compare the single phase and three phase motor based on its operating principle. (U/C) 5. Mapping Table: SO PO SO1 1,2/ 14 1.2,1.3,1.4,2.1,2.2,2.4/14.2 1.2.1,1.3.1,1.4.1,2.1.3,2.1.1,2.2.2,2.4.4/14.1.1,14.2.2 SO2 1,2/ 14 1.2,1.3,1.4,2.2,2.4/14.2 1.2.1,1.3.1,1.4.1,2.1.3,2.2.2,2.4.4/14.1.1,14.2.2 1,2/ 14 1.2,1.3,1.4,2.1,2.2,2.4/14.2 1.2.1,1.3.1,1.4.1,2.1.3,2.1.1,2.2.2,2.4.4/14.1.1,14.2.2 SO3 PO/PSO Competency PO/PSO Indicator 6. Mind map and Summary: Summary: Both the stator and rotor components rotates in opposite direction. The resultant flux is zero and that is the instantaneous value of stator flux at the time of start. The net torque experienced by the rotor is zero. Induction motor is not a self-starting motor. 7. Reference: [1] M.G.Say, Performance and Design of Alternating Current Machines, 3rd Edition, CBS Publisher, 2017. [2] D. P. Kothari and I. J. Nagrath, Electric Machines, Tata McGraw Hill Publishing Company Ltd, FourthEdition 2018. [3] Stephen J.Chapman, Electric Machinery Fundamentals, Tata McGraw Hill, New Delhi, 2018. [4] E. Fitzgerald, Charles Kingsley, Stephen.D.Umans, Electric Machinery, Tata McGraw Hill publishingCompany Ltd, New Delhi ,2015. Prepared by [Mr. A. Nandhakumar] Lesson Plan Department: EEE Branch & Semester: B.E & EEE Course code & Title: 22EE303 & Electrical Machines I Unit Title: Induction motor CO / Lesson No (GO): 4/5 1. Prerequisite(s): Magnetic fields, self-starting, cross field, double field 2. Topic: Methods of starting induction motor. 3. General Objective (GO): To understand the working and characteristics of split phase, capacitor start and capacitor run single phase induction motor. 4. Specific Objectives (SO): SO1 – Interpret the functions auxiliary and starting winding in a single phase induction motor. (U/C) SO2 – Illustrate the operation of split phase motor. (U/C) SO3 – Compare the performance of a capacitor start and capacitor run induction motor. (An/C) 5. Mapping Table: SO PO SO1 1,2/ 14 1.2,1.3,1.4,2.1,2.2,2.4/14.2 1.2.1,1.3.1,1.4.1,2.1.3,2.1.1,2.2.2,2.4.4/14.1.1,14.2.2 SO2 1,2/ 14 1.2,1.3,1.4,2.2,2.4/14.2 1.2.1,1.3.1,1.4.1,2.1.3,2.2.2,2.4.4/14.1.1,14.2.2 1,2/ 14 1.2,1.3,1.4,2.1,2.2,2.4/14.2 1.2.1,1.3.1,1.4.1,2.1.3,2.1.1,2.2.2,2.4.4/14.1.1,14.2.2 SO3 PO/PSO Competency PO/PSO Indicator 6. Mind map and Summary: Summary: Split phase motor carries a series resistance in auxiliary winding Capacitor start improves the starting torque Capacitor start capacitor run improves the power factor. 7. Reference: [1] M.G.Say, Performance and Design of Alternating Current Machines, 3rd Edition, CBS Publisher, 2017. [2] D. P. Kothari and I. J. Nagrath, Electric Machines, Tata McGraw Hill Publishing Company Ltd, FourthEdition 2018. [3] Stephen J.Chapman, Electric Machinery Fundamentals, Tata McGraw Hill, New Delhi, 2018. [4] E. Fitzgerald, Charles Kingsley, Stephen.D.Umans, Electric Machinery, Tata McGraw Hill publishingCompany Ltd, New Delhi ,2015. Prepared by [Mr. A. Nandhakumar]