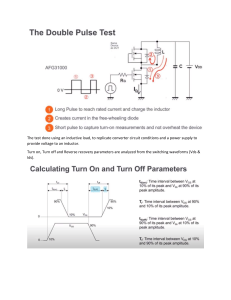
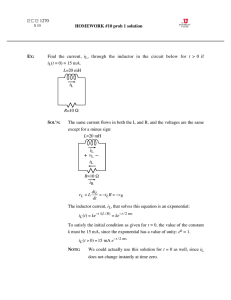
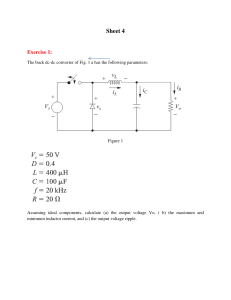
ELEC_E8412 Exercise#5 Power Electronics 12.11.2020 Problem 1: A buck converter has an input of 6 V and an output of 1.5 V. The load resistor is 3 Ω, the switching frequency is 400 kHz, L = 5 µH, and C =10 µF. Determine (a) the duty ratio (b) the average and peak inductor currents (c) the average source current, (d) the peak and average diode current. Solution: Part (a): 𝐷= 𝑉𝑜 1.5 = = 0.25 𝑉𝑖𝑛 6 Part (b): 𝐼𝑚𝑎𝑥 + 𝐼𝑚𝑖𝑛 𝑉𝑜 1.5 = = = 0.5 𝐴 2 𝑅 3 1 1−𝐷 1 1 − 0.25 ) = 1.5 ( + ) = 0.78 𝐴 = 𝑉𝑜 ( + 𝑅 2𝐿𝑓 3 2 ∗ 5 ∗ 10−6 ∗ 4 ∗ 105 ⟨𝑖𝐿 ⟩ = 𝐼𝑚𝑎𝑥 Part (c): ⟨𝑖𝑖𝑛 ⟩ =? 𝑉𝑖𝑛 . ⟨𝑖𝑖𝑛 ⟩ = 𝑉𝑜2 (𝐷 ∗ 𝑉𝑖𝑛 )2 = 𝑅 𝑅 ⟶ ⟨𝑖𝑖𝑛 ⟩ = 𝐷2 𝑉𝑖𝑛 (0.25)2 ∗ 6 = = 0.125 𝐴 𝑅 3 Part (d): Fig 5-5 b 𝐼𝐷_𝑚𝑎𝑥 = 𝐼𝑚𝑎𝑥 = 0.78 𝐴 ⟨𝑖𝐷 ⟩ = ⟨𝑖𝐿 ⟩ ∗ (1 − 𝐷) = 𝑉𝑜 1.5 ∗ (1 − 𝐷) = ∗ (1 − 0.25) = 0.375 𝐴 𝑅 3 1 Problem 2: A buck converter has an input of 50 V and an output of 25 V. The switching frequency is 100 kHz, and the output power to a load resistor is 125 W. Determine (a) the duty ratio (b) the value of inductance to limit the peak inductor current to 6.25 A. (c) the minimum inductor current Solution: 𝑅= 𝑉𝑜2 (25)2 = =5𝛺 𝑃𝑜𝑢𝑡 125 Part (a): 𝐷= 𝑉𝑜 25 = = 0.5 𝑉𝑖𝑛 50 Part (b): 1 1−𝐷 1 1 − 0.5 ) = 25 ( + ) 𝐼𝑚𝑎𝑥 = 𝑉𝑜 ( + 𝑅 2𝐿𝑓 5 2 ∗ 𝐿 ∗ 105 𝐼𝑚𝑎𝑥 = 6.25 𝐴 ⟶ 𝐿 = 50 µ𝐻 Part (c): 1 1−𝐷 1 1 − 0.5 ) = 25 ( − ) = 3.75 𝐴 𝐼𝑚𝑖𝑛 = 𝑉𝑜 ( − 𝑅 2𝐿𝑓 5 2 ∗ 50 ∗ 10−6 ∗ 105 Problem 3: A boost converter has the following parameters: Vin = 5 V, Vout = 20 V, and Pout = 40 W The minimum value of the inductor current must be at least 80% of the average inductor current. The switching frequency is 85 kHz. Determine the duty ratio and the minimum inductor value. 2 Solution: 𝐼𝑚𝑖𝑛 > 0.8 ⟨𝑖𝐿 ⟩ ⟶ 0.2 ⟨𝑖𝐿 ⟩ − ∆𝑖𝐿 > 0.8 ⟨𝑖𝐿 ⟩ 2 ⟶ 0.2⟨𝑖𝐿 ⟩ > ∆𝑖𝐿 2 𝑉𝑖𝑛 𝑉𝑖𝑛 𝐷𝑇 > 2 (1 − 𝐷) 𝑅 2𝐿 𝐷(1 − 𝐷)2 𝑅 𝐿> 0.4𝑓 D=? R=? 𝑉𝑜 20 1 = = → 𝐷 = 0.75 𝑉𝑖𝑛 5 1−𝐷 𝑃𝑜𝑢𝑡 𝑉𝑜2 (20)2 = 40 = = → 𝑅 = 10𝛺 𝑅 𝑅 𝐿 >13.79 µH Problem 4: A boost converter has parameter Vs =20 V, D =0.6, R =12.5 Ω, L=10 µH, C =40 µF, and the switching frequency is 200 kHz. Determine (a) the output voltage (b) the average, maximum, and minimum inductor currents. (c) the average current in the diode Assume ideal components. Solution: Part (a): 𝑉𝑜 = 𝑉𝑖𝑛 ∗ 1 1 = 20 ∗ = 50 𝑉 1−𝐷 1 − 0.6 Part (b): ⟨𝑖𝐿 ⟩ = 𝐼𝑚𝑎𝑥 + 𝐼𝑚𝑖𝑛 𝑉𝑖𝑛 20 = = = 10 𝐴 2 (1 − 𝐷)2 𝑅 (1 − 0.6)2 ∗ 12.5 3 𝐼𝑚𝑎𝑥 = 𝑉𝑖𝑛 𝑉𝑖𝑛 20 20 ∗ 0.6 + 𝐷𝑇 = + = 13 𝐴 (1 − 𝐷)2 𝑅 2𝐿 (1 − 0.6)2 ∗ 12.5 2 ∗ 10 ∗ 10−6 ∗ 2 ∗ 105 𝐼𝑚𝑖𝑛 = 𝑉𝑖𝑛 𝑉𝑖𝑛 20 20 ∗ 0.6 − 𝐷𝑇 = − =7𝐴 (1 − 𝐷)2 𝑅 2𝐿 (1 − 0.6)2 ∗ 12.5 2 ∗ 10 ∗ 10−6 ∗ 2 ∗ 105 Part (c): ⟨𝑖𝐷 ⟩ = ⟨𝑖𝐿 ⟩ ∗ (1 − 𝐷) = 10 ∗ (1 − 0.6) = 4 𝐴 𝑜𝑟 ⟨𝑖𝐷 ⟩ = 𝑉𝑜 50 = =4𝐴 𝑅 12.5 Problem 5: A buck-boost converter has the following parameters: Vin = 24 V, D= 0.65, R = 7.5 Ω, L = 50 μH, C = 200 μF, and switching frequency = 100 KHz. Determine (a) the output voltage, (b) the average, maximum, and minimum inductor currents. Solution: Part (a): 𝑉𝑜 𝐷 = , 𝐷 = 0.65, 𝑉𝑖𝑛 = 24 𝑉 𝑉𝑖𝑛 1 − 𝐷 → 𝑉𝑜 = 44.571 𝑉 Part (b): ⟨𝑖𝐿 ⟩ = 𝑉𝑖𝑛 𝐷 24 ∗ 0.65 = = 16.98 𝐴 (1 − 𝐷)2 𝑅 (1 − 0.65)2 ∗ 7.5 𝑉𝑖𝑛 𝐷𝑇 24 ∗ 0.65 = = 3.12 𝐴 𝐿 50 ∗ 10−6 ∗ 105 ∆𝑖𝐿 3.12 𝐼𝑚𝑎𝑥 = ⟨𝑖𝐿 ⟩ + = 16.98 + = 18.54 𝐴 2 2 ∆𝑖𝐿 3.12 𝐼𝑚𝑖𝑛 = ⟨𝑖𝐿 ⟩ − = 16.98 − = 15.42 𝐴 2 2 𝛥𝑖𝐿 = 4 Problem 6: A buck-boost converter has parameters Vs=12 V, D=0.6, R=10 Ω, L =10 µH, C =20 µF, and a switching frequency of 200 kHz. Determine (a) the output voltage (b) the average, maximum, and minimum inductor currents, and (c) the average value of input current. Solution: Part (a): 𝑉𝑜 = 𝑉𝑖𝑛 ∗ 𝐷 0.6 = 12 ∗ = 18 𝑉 1−𝐷 1 − 0.6 Part (b): ⟨𝑖𝐿 ⟩ = 𝑉𝑖𝑛 𝐷 12 ∗ 0.6 = = 4.5 𝐴 2 (1 − 𝐷) 𝑅 (1 − 0.6)2 ∗ 10 𝛥𝑖𝐿 = 𝑉𝑖𝑛 𝐷𝑇 12 ∗ 0.6 = = 3.6 𝐴 𝐿 10 ∗ 10−6 ∗ 2 ∗ 105 𝐼𝑚𝑎𝑥 = ⟨𝑖𝐿 ⟩ + ∆𝑖𝐿 3.6 = 4.5 + = 6.3 𝐴 2 2 𝐼𝑚𝑖𝑛 = ⟨𝑖𝐿 ⟩ − ∆𝑖𝐿 3.6 = 4.5 − = 2.7 𝐴 2 2 Part (c): ⟨𝑖𝑖𝑛 ⟩ =? 𝑉𝑖𝑛 . ⟨𝑖𝑖𝑛 ⟩ = 𝑉𝑜2 (𝐷 ∗ 𝑉𝑖𝑛 )2 = (1 − 𝐷)2 𝑅 𝑅 ⟶ ⟨𝑖𝑖𝑛 ⟩ = 5 𝐷2 ∗ 𝑉𝑖𝑛 (0.6)2 ∗ 12 = = 2.7 𝐴 (1 − 𝐷)2 𝑅 (1 − 0.6)2 ∗ 10