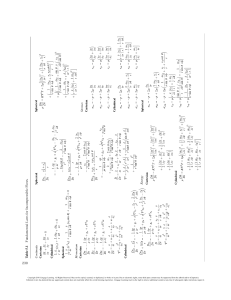
Statistics for Business and Economics (14e) Summary of Ch8, Ch9, and Ch10 • One Population: Ch8. Interval Estimation – σ Known and Unknown Ch9. Hypothesis Test – σ Known and Unknown • Two Population: Ch10. Interval Estimation & Hypothesis Test – σ Known and Unknown © 2020 Cengage. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part, except for use as permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website or school-approved learning management system for classroom use. 1 Statistics for Business and Economics (14e) Summary of Interval Estimation Procedures for a Population Mean © 2020 Cengage. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part, except for use as permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website or school-approved learning management system for classroom use. 2 Statistics for Business and Economics (14e) Summary of Forms for Null and Alternative Hypotheses • The equality part of the hypotheses always appears in the null hypothesis. • In general, a hypothesis test about the value of a population mean μ must take one of the following three forms (where μ0 is the hypothesized value of the population mean). © 2020 Cengage. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part, except for use as permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website or school-approved learning management system for classroom use. 3 Statistics for Business and Economics (14e) Steps of Hypothesis Testing Step 1. Develop the null and alternative hypotheses. Step 2. Specify the level of significance α. Step 3. Collect the sample data and compute the value of the test statistic. p-Value Approach When we can calculate z-score/-test statistics, find p-value (=area probability). Step 4. Use the value of the test statistic to compute the p-value. Step 5. Reject H0 if p-value ≤ α. Critical Value Approach when area probability (= p-value) is given, find the z-score value. Step 4. Use the level of significance α to determine the critical value and the rejection rule. Step 5. Use the value of the test statistic and the rejection rule to determine whether to reject H0. © 2020 Cengage. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part, except for use as permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website or school-approved learning management system for classroom use. 4 Statistics for Business and Economics (14e) One-Tailed Test : Step 5 Decision Rule 1: Reject 𝐻0 if p-value ≤ 𝜶. Null Hypothesis: 𝐻0 : 𝜇 ≥ 3 Alternative Hypothesis: 𝐻𝑎 : 𝜇 < 3 the p-value of .0038 resulted in the rejection of the null hypothesis Reject 𝐻0 because p-value, 0.0038 < 0.01. © 2020 Cengage. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part, except for use as permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website or school-approved learning management system for classroom use. 5 Statistics for Business and Economics (14e) One-Tailed Test : Step 5 Decision Rule 2: Reject 𝐻0 if 𝒛 ≤ 𝒛𝜶 . From Step 3, ҧ 𝑥−𝜇 z= 𝜎/ 𝑛 = 2.92−3 =-2.67 0.03 Reject H0 because z = −2.67 < zα = −2.33 𝒛𝟎.𝟎𝟏 © 2020 Cengage. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part, except for use as permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website or school-approved learning management system for classroom use. 6 Statistics for Business and Economics (14e) Two-Tailed Tests About a Population Mean: σ Known Critical Value Approach © 2020 Cengage. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part, except for use as permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website or school-approved learning management system for classroom use. 7 Statistics for Business and Economics (14e) © 2020 Cengage. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part, except for use as permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website or school-approved learning management system for classroom use. 8 Statistics for Business and Economics (14e) Estimating the Difference Between Two Population Means © 2020 Cengage. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part, except for use as permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website or school-approved learning management system for classroom use. 9 Statistics for Business and Economics (14e) Interval Estimation of μ1 – μ2 when σ1 and σ2 are Known Interval Estimate: Point Estimator ± Margin Error 𝛼 is the level of significance. © 2020 Cengage. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part, except for use as permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website or school-approved learning management system for classroom use. 10 Statistics for Business and Economics (14e) Hypothesis Tests About μ1 – μ2 when σ1 and σ2 are Known A hypothesis test about the value of the difference in two population means 𝜇1 −𝜇2 must take one of the following three forms (where D0 is the hypothesized difference in the population means). Test Statistic: © 2020 Cengage. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part, except for use as permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website or school-approved learning management system for classroom use. 11 Statistics for Business and Economics (14e) Interval Estimation of μ1 – μ2 when σ1 and σ2 are Unknown Interval Estimate © 2020 Cengage. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part, except for use as permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website or school-approved learning management system for classroom use. 12 Statistics for Business and Economics (14e) Hypothesis Tests About μ1 – μ2 when σ1 and σ2 are Unknown A hypothesis test about the value of the difference in two population means 𝜇1 −𝜇2 must take one of the following three forms (where D0 is the hypothesized difference in the population means). Test Statistic: with © 2020 Cengage. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part, except for use as permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website or school-approved learning management system for classroom use. 13 Statistics for Business and Economics (14e) © 2020 Cengage. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part, except for use as permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website or school-approved learning management system for classroom use. 14 Statistics for Business and Economics (14e) Chapter 13 - ANalysis Of VAriance (ANOVA) 1 - Analysis of Variance and the Completely Randomized Design 2 - Multiple Comparison Procedures • Fisher’s LSD © 2020 Cengage. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part, except for use as permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website or school-approved learning management system for classroom use. 15 Statistics for Business and Economics (14e) An Introduction to Experimental Design and Analysis of Variance • A factor is a variable that the experimenter has selected for investigation. • A treatment is a level of a factor. • Experimental units are the objects of interest in the experiment. • A completely randomized design is an experimental design in which the treatments are randomly assigned to the experimental units. © 2020 Cengage. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part, except for use as permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website or school-approved learning management system for classroom use. 16 Statistics for Business and Economics (14e) -------- Population k 𝜇𝑘 , 𝑛𝑘 , 𝜎𝑘 𝑥ҧ𝑘 , 𝑠𝑘 © 2020 Cengage. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part, except for use as permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website or school-approved learning management system for classroom use. 17 Statistics for Business and Economics (14e) Analysis of Variance: A Conceptual Overview • Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) can be used to test for the equality of three or more population means. • Data obtained from observational or experimental studies can be used for the analysis. • We want to use the sample results to test the following hypotheses: © 2020 Cengage. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part, except for use as permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website or school-approved learning management system for classroom use. 18 Statistics for Business and Economics (14e) Analysis of Variance: A Conceptual Overview • If 𝐻0 is rejected, we cannot conclude that all population means are different. • Rejecting 𝐻0 means that at least two population means have different values. • Assumptions for Analysis of Variance: 1. For each population, the response (dependent) variable is normally distributed. 2. The variance of the response variable, denoted σ2, is the same for all of the populations. 3. The observations must be independent. © 2020 Cengage. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part, except for use as permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website or school-approved learning management system for classroom use. 19 Statistics for Business and Economics (14e) © 2020 Cengage. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part, except for use as permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website or school-approved learning management system for classroom use. 20 Statistics for Business and Economics (14e) © 2020 Cengage. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part, except for use as permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website or school-approved learning management system for classroom use. 21 Statistics for Business and Economics (14e) ഥ = 60 𝒙 (ഥ 𝒙) (𝒔𝟐 ) (s) © 2020 Cengage. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part, except for use as permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website or school-approved learning management system for classroom use. 22 Statistics for Business and Economics (14e) Analysis of Variance: A Conceptual Overview • Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) can be used to test for the equality of three or more population means. • Data obtained from observational or experimental studies can be used for the analysis. • We want to use the sample results to test the following hypotheses: © 2020 Cengage. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part, except for use as permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website or school-approved learning management system for classroom use. 23 Statistics for Business and Economics (14e) Analysis of Variance: A Conceptual Overview © 2020 Cengage. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part, except for use as permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website or school-approved learning management system for classroom use. 24 Statistics for Business and Economics (14e) Analysis of Variance: A Conceptual Overview • If 𝐻0 is rejected, we canNOT conclude that all population means are different. © 2020 Cengage. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part, except for use as permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website or school-approved learning management system for classroom use. 25 Statistics for Business and Economics (14e) Analysis of Variance: A Conceptual Overview • If 𝐻0 is rejected, we canNOT conclude that all population means are different. • Rejecting 𝐻0 means that at least two population means have different values. © 2020 Cengage. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part, except for use as permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website or school-approved learning management system for classroom use. 26 Statistics for Business and Economics (14e) Analysis of Variance: A Conceptual Overview • If 𝐻0 is rejected, we canNOT conclude that all population means are different. • Rejecting 𝐻0 means that at least two population means have different values. • Assumptions for Analysis of Variance (i.i.d. = independent and identically distributed) 1. For each population, the response (dependent) variable is normally distributed. 2. The variance of the response variable, denoted σ2, is the same for all of the populations. 3. The observations must be independent. © 2020 Cengage. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part, except for use as permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website or school-approved learning management system for classroom use. 27 Statistics for Business and Economics (14e) Analysis of Variance: A Conceptual Overview Sampling distribution of 𝑥,ҧ given 𝐻0 is true (𝐻0 : 𝜇1 = 𝜇2 = 𝜇3 = 𝜇). © 2020 Cengage. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part, except for use as permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website or school-approved learning management system for classroom use. 28 Statistics for Business and Economics (14e) Analysis of Variance: A Conceptual Overview Sampling distribution of 𝑥,ҧ given 𝐻0 is false. 𝜇 © 2020 Cengage. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part, except for use as permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website or school-approved learning management system for classroom use. 29 Statistics for Business and Economics (14e) Analysis of Variance under the Completely Randomized Design Step 1. Calculate Between-Treatments Estimate of Population Variance (MSTR) Step 2. Calculate Within-Treatments Estimate of Population Variance (MSE) Step 3. Calculate Comparing the Variance Estimates: The F Test (= MSTR/MSE) Step 4. Build ANOVA Table Step 5. Test Hypothesis with p-value © 2020 Cengage. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part, except for use as permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website or school-approved learning management system for classroom use. 30 Statistics for Business and Economics (14e) Step 1. Between-Treatments Estimate of Population Variance σ2 The estimate of σ2 based on the variation of the sample means is called the mean square due to treatments and is denoted by MSTR. = 𝑆𝑆𝑇𝑅 𝑘−1 where Numerator is called the sum of squares due to treatments (SSTR), Denominator is the degrees of freedom associated with SSTR, and 𝑘 is the number of groups. © 2020 Cengage. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part, except for use as permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website or school-approved learning management system for classroom use. 31 Statistics for Business and Economics (14e) Step 1. Between-Treatments Estimate of Population Variance σ2 = © 2020 Cengage. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part, except for use as permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website or school-approved learning management system for classroom use. 𝑆𝑆𝑇𝑅 𝑘−1 32 Statistics for Business and Economics (14e) Step 1. Between-Treatments Estimate of Population Variance σ2 = 𝑆𝑆𝑇𝑅 𝑘−1 𝑘=3 𝑆𝑆𝑇𝑅 = 𝑛𝑗 𝑥𝑗ҧ − 𝑥Ӗ 2 𝑗=1 = 5 62 − 60 = 520 2 + 5 66 − 60 2 + 5 52 − 60 𝑆𝑆𝑇𝑅 520 𝑀𝑆𝑇𝑅 = = = 260 𝑘−1 3−1 © 2020 Cengage. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part, except for use as permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website or school-approved learning management system for classroom use. 33 2 Statistics for Business and Economics (14e) Step 2. Within-Treatments Estimate of Population Variance σ2 The estimate of σ2 based on the variation of the sample observations within each sample is called the mean square error and is denoted by MSE. = 𝑆𝑆𝐸 𝑛𝑇 −𝑘 where Numerator is called the sum of squares due to error (SSE), Denominator is the degrees of freedom associated with SSE, and 𝑛 𝑇 is total sample size of 𝑘 groups. © 2020 Cengage. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part, except for use as permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website or school-approved learning management system for classroom use. 34 Statistics for Business and Economics (14e) Step 2. Within-Treatments Estimate of Population Variance σ2 = © 2020 Cengage. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part, except for use as permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website or school-approved learning management system for classroom use. 𝑆𝑆𝐸 𝑛𝑇 −𝑘 35 Statistics for Business and Economics (14e) Step 2. Within-Treatments Estimate of Population Variance σ2 = 𝑆𝑆𝐸 𝑛𝑇 −𝑘 𝑘=3 𝑆𝑆𝐸 = 𝑛𝑗 − 1 𝑠𝑗2 𝑗=1 = 5 − 1 27.5 + 5 − 1 26.5 + 5 − 1 31 = 340 𝑆𝑆𝐸 340 𝑀𝑆𝐸 = = = 28.33 𝑛 𝑇 − 𝑘 15 − 3 © 2020 Cengage. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part, except for use as permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website or school-approved learning management system for classroom use. 36 Statistics for Business and Economics (14e) Step 3. Comparing the Variance Estimates: The F Test • If the null hypothesis is true and the ANOVA assumptions are valid, the sampling distribution of MSTR/MSE is an 𝐹 distribution with MSTR degrees of freedom equal to 𝑘 – 1 and MSE degrees of freedom equal to • If the means of the 𝑘 populations are not equal, the value of MSTR/MSE will be inflated because MSTR overestimates σ2. • Hence, we will reject 𝐻0 if the resulting value of MSTR/MSE appears to be too large to have been selected at random from the appropriate 𝐹 distribution. © 2020 Cengage. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part, except for use as permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website or school-approved learning management system for classroom use. 37 Statistics for Business and Economics (14e) Step 3. Comparing the Variance Estimates: The F Test • If the null hypothesis is true and the ANOVA assumptions are valid, the sampling distribution of MSTR/MSE is an 𝐹 distribution with MSTR degrees of freedom equal 𝑴𝑺𝑻𝑹 to 𝑘 – 1 and MSE degrees of freedom equal to ~𝑭𝒌−𝟏,𝒏𝑻 −𝒌 𝑴𝑺𝑬 • If the means of the 𝑘 populations are not equal, the value of MSTR/MSE will be inflated because MSTR overestimates σ2. • Hence, we will reject 𝐻0 if the resulting value of MSTR/MSE appears to be too large to have been selected at random from the appropriate 𝐹 distribution. © 2020 Cengage. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part, except for use as permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website or school-approved learning management system for classroom use. 38 Statistics for Business and Economics (14e) Step 3. Comparing the Variance Estimates: The F Test • If the null hypothesis is true and the ANOVA assumptions are valid, the sampling distribution of MSTR/MSE is an 𝐹 distribution with MSTR degrees of freedom equal 𝑴𝑺𝑻𝑹 to 𝑘 – 1 and MSE degrees of freedom equal to ~𝑭𝒌−𝟏,𝒏𝑻 −𝒌 𝑴𝑺𝑬 • If the means of the 𝑘 populations are not equal, the value of MSTR/MSE will be inflated because MSTR overestimates σ2. (MSTR is large) • Hence, we will reject 𝐻0 if the resulting value of MSTR/MSE appears to be too large to have been selected at random from the appropriate 𝐹 distribution. © 2020 Cengage. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part, except for use as permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website or school-approved learning management system for classroom use. 39 Statistics for Business and Economics (14e) Step 4. ANOVA Table for a Completely Randomized Design SST is partitioned into SSTR and SSE. SST’s degrees of freedom (df) are partitioned into SSTR’s df and SSE’s df. Source of Variation Sum of Squares Degrees of Freedom Mean Square F p-Value Treatments SSTR K minus 1 Begin equation. MSTR equals Start fraction, SSTR over k minus 1. End fraction. End equation. Begin fraction. MSTR over MSE. End fraction. empty cell Error SSE N subscript T baseline minus k Begin equation. MSE equals start fraction SSE over n subscript T baseline minus k end fraction. End equation. empty cell empty cell Total SST N subscript baseline minus 1 empty cell empty cell empty cell © 2020 Cengage. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part, except for use as permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website or school-approved learning management system for classroom use. 40 Statistics for Business and Economics (14e) © 2020 Cengage. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part, except for use as permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website or school-approved learning management system for classroom use. 41 Statistics for Business and Economics (14e) Step 5. Test for the Equality of 𝑘 Population Means © 2020 Cengage. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part, except for use as permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website or school-approved learning management system for classroom use. 42 Statistics for Business and Economics (14e) Step 5. Test for the Equality of 𝑘 Population Means © 2020 Cengage. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part, except for use as permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website or school-approved learning management system for classroom use. 43 Statistics for Business and Economics (14e) Step 5. Test for the Equality of 𝑘 Population Means Critical value approach © 2020 Cengage. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part, except for use as permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website or school-approved learning management system for classroom use. P-value approach 44 Statistics for Business and Economics (14e) P-value approach: © 2020 Cengage. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part, except for use as permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website or school-approved learning management system for classroom use. 45 Statistics for Business and Economics (14e) P-value approach: © 2020 Cengage. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part, except for use as permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website or school-approved learning management system for classroom use. 46 Statistics for Business and Economics (14e) Step 5. Comparing the Variance Estimates: The F Test Critical value approach: Sampling Distribution of MSTR/MSE © 2020 Cengage. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part, except for use as permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website or school-approved learning management system for classroom use. 47 Statistics for Business and Economics (14e) Step 5. Comparing the Variance Estimates: The F Test Critical value approach: Sampling Distribution of MSTR/MSE © 2020 Cengage. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part, except for use as permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website or school-approved learning management system for classroom use. 48 Statistics for Business and Economics (14e) Step 5. Comparing the Variance Estimates: The F Test Critical value approach: Sampling Distribution of MSTR/MSE if 𝐹 ≥ 𝐹𝛼 © 2020 Cengage. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part, except for use as permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website or school-approved learning management system for classroom use. 49 Statistics for Business and Economics (14e) © 2020 Cengage. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part, except for use as permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website or school-approved learning management system for classroom use. 50 Statistics for Business and Economics (14e) © 2020 Cengage. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part, except for use as permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website or school-approved learning management system for classroom use. 51 Statistics for Business and Economics (14e) Testing for the Equality of 𝑘 Population Means: A Completely Randomized Design AutoShine, Inc. is considering marketing a long- lasting car wax. Three different waxes (Type 1, Type 2, and Type 3) have been developed. In order to test the durability of these waxes, 5 new cars were waxed with Type 1, 5 with Type 2, and 5 with Type 3. Each car was then repeatedly run through an automatic carwash until the wax coating showed signs of deterioration. The number of times each car went through the carwash before its wax deteriorated is shown on the next slide. AutoShine, Inc. must decide which wax to market. Are the three waxes equally effective? Factor . . . Car wax Treatments . . . Type I, Type 2, Type 3 Experimental units . . . Cars Response variable . . . Number of washes © 2020 Cengage. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part, except for use as permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website or school-approved learning management system for classroom use. 52 Statistics for Business and Economics (14e) Testing for the Equality of 𝑘 Population Means: A Completely Randomized Design Wax Type 1 Wax Type 2 Wax Type 3 1 27 33 29 2 30 28 28 3 29 31 30 4 28 30 32 5 31 30 31 Sample Mean 29.0 30.4 30.0 Sample Variance 2.5 3.3 2.5 Observation © 2020 Cengage. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part, except for use as permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website or school-approved learning management system for classroom use. 53 Statistics for Business and Economics (14e) Testing for the Equality of 𝑘 Population Means: A Completely Randomized Design © 2020 Cengage. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part, except for use as permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website or school-approved learning management system for classroom use. 54 Statistics for Business and Economics (14e) Testing for the Equality of 𝑘 Population Means: A Completely Randomized Design Mean Square Between Treatments: (Because the sample sizes are all equal) Mean Square Error: © 2020 Cengage. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part, except for use as permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website or school-approved learning management system for classroom use. 55 Statistics for Business and Economics (14e) Testing for the Equality of 𝑘 Population Means: A Completely Randomized Design Rejection Rule: © 2020 Cengage. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part, except for use as permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website or school-approved learning management system for classroom use. 56 Statistics for Business and Economics (14e) Testing for the Equality of 𝑘 Population Means: A Completely Randomized Design Test Statistic: Conclusion: There is insufficient evidence to conclude that the mean number of washes for the three wax types are not all the same. © 2020 Cengage. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part, except for use as permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website or school-approved learning management system for classroom use. 57 Statistics for Business and Economics (14e) Testing for the Equality of 𝑘 Population Means: A Completely Randomized Design ANOVA Table Source of Variation Sum of Squares Degrees of Freedom Mean Squares F p-Value Treatments 5.2 2 2.60 0.939 0.42 Error 33.2 12 2.77 Total 38.4 14 © 2020 Cengage. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part, except for use as permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website or school-approved learning management system for classroom use. 58 Statistics for Business and Economics (14e) Testing for the Equality of 𝑘 Population Means: An Observational Study Example: Reed Manufacturing Janet Reed would like to know if there is any significant difference in the mean number of hours worked per week for the department managers at her three manufacturing plants (in Buffalo, Pittsburgh, and Detroit). An 𝐹 test will be conducted using α = 0.05. A simple random sample of five managers from each of the three plants was taken and the number of hours worked by each manager in the previous week is shown on the next slide. Factor . . . Manufacturing plant Treatments . . . Buffalo, Pittsburgh, Detroit Experimental units . . . Managers Response variable . . . Number of hours worked © 2020 Cengage. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part, except for use as permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website or school-approved learning management system for classroom use. 59 Statistics for Business and Economics (14e) Testing for the Equality of 𝑘 Population Means: An Observational Study Observation Plant 1 Buffalo Plant 2 Pittsburgh Plant 3 Detroit 1 48 73 51 2 54 63 63 3 57 66 61 4 54 64 54 5 62 74 56 55 68 57 26.0 26.5 24.5 Sample Mean Sample Variance © 2020 Cengage. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part, except for use as permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website or school-approved learning management system for classroom use. 60 Statistics for Business and Economics (14e) Testing for the Equality of 𝑘 Population Means: An Observational Study 1. Develop the hypotheses. © 2020 Cengage. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part, except for use as permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website or school-approved learning management system for classroom use. 61 Statistics for Business and Economics (14e) Testing for the Equality of 𝑘 Population Means: An Observational Study 2. Specify the level of significance. α = 0.05 3. Compute the value of the test statistic. © 2020 Cengage. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part, except for use as permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website or school-approved learning management system for classroom use. 62 Statistics for Business and Economics (14e) Testing for the Equality of 𝑘 Population Means: An Observational Study 3. Compute the value of the test statistic. © 2020 Cengage. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part, except for use as permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website or school-approved learning management system for classroom use. 63 Statistics for Business and Economics (14e) Testing for the Equality of 𝑘 Population Means: An Observational Study ANOVA Table Source of Variation Sum of Squares Degrees of Freedom Mean Square F p-Value Treatment 490 2 245 9.55 .0033 Error 308 12 25.667 EMPTY CELL EMPTY CELL Total 798 14 EMPTY CELL EMPTY CELL EMPTY CELL © 2020 Cengage. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part, except for use as permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website or school-approved learning management system for classroom use. 64 Statistics for Business and Economics (14e) Testing for the Equality of 𝑘 Population Means: An Observational Study p-value approach 4. Compute the p –value. With 2 numerator df and 12 denominator df, the p-value is 0.01 for 𝐹 = 6.93. Therefore, the p-value is less than 0.01 for 𝐹 = 9.55. 5. We can conclude that the mean number of hours worked per week by department managers is not the same at all 3 plants. © 2020 Cengage. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part, except for use as permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website or school-approved learning management system for classroom use. 65 Statistics for Business and Economics (14e) Testing for the Equality of 𝑘 Population Means: An Observational Study Critical Value Approach 4. Determine the critical value and rejection rule. 5. © 2020 Cengage. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part, except for use as permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website or school-approved learning management system for classroom use. 66 Statistics for Business and Economics (14e) © 2020 Cengage. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part, except for use as permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website or school-approved learning management system for classroom use. 67 Statistics for Business and Economics (14e) Multiple Comparison Procedures • Suppose that analysis of variance has provided statistical evidence to reject the null hypothesis of equal population means. • Fisher’s least significant difference (LSD) procedure can be used to determine where the differences occur. © 2020 Cengage. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part, except for use as permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website or school-approved learning management system for classroom use. 68 Statistics for Business and Economics (14e) (𝑥)ҧ ҧ 𝑥=60 • Do the means of population A and B differ ? • Do the means of population A and C differ ? • Do the means of population B and C differ ? © 2020 Cengage. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part, except for use as permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website or school-approved learning management system for classroom use. 69 Statistics for Business and Economics (14e) (𝑥)ҧ ҧ 𝑥=60 • Do the means of population A and B differ ? 𝐻0 : 𝜇𝐴 = 𝜇𝐵 𝑣𝑠 𝐻𝑎 : 𝜇𝐴 ≠ 𝜇𝐵 • Do the means of population A and C differ ? 𝐻0 : 𝜇𝐴 = 𝜇𝐶 𝑣𝑠 𝐻𝑎 : 𝜇𝐴 ≠ 𝜇𝐶 • Do the means of population B and C differ ? 𝐻0 : 𝜇𝐵 = 𝜇𝐶 𝑣𝑠 𝐻𝑎 : 𝜇𝐵 ≠ 𝜇𝐶 © 2020 Cengage. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part, except for use as permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website or school-approved learning management system for classroom use. 70 Statistics for Business and Economics (14e) Fisher’s LSD Procedure 1. Hypotheses: where i=A, B; j=B, C 2. Test Statistic: © 2020 Cengage. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part, except for use as permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website or school-approved learning management system for classroom use. 71 Statistics for Business and Economics (14e) Fisher’s LSD Procedure Chapter 10. Hypothesis Tests About μ1 – μ2 when σ1 and σ2 are Unknown 1. Hypotheses: where i=A, B; j=B, C 2. Test Statistic: © 2020 Cengage. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part, except for use as permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website or school-approved learning management system for classroom use. 72 Statistics for Business and Economics (14e) Fisher’s LSD Procedure Chapter 10. Hypothesis Tests About μ1 – μ2 when σ1 and σ2 are Unknown 1. Hypotheses: where i=A, B; j=B, C 2. Test Statistic: © 2020 Cengage. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part, except for use as permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website or school-approved learning management system for classroom use. 73 Statistics for Business and Economics (14e) Fisher’s LSD Procedure 3. Rejection Rule: 𝑛 𝑇 is the total number of sample; k is number of groups/methods/treatments. © 2020 Cengage. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part, except for use as permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website or school-approved learning management system for classroom use. 74 Statistics for Business and Economics (14e) Fisher’s LSD Procedure Based on the Test Statistic 𝑥ҧ𝑖 − 𝑥𝑗ҧ © 2020 Cengage. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part, except for use as permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website or school-approved learning management system for classroom use. 75 Statistics for Business and Economics (14e) Fisher’s LSD Procedure Based on the Test Statistic 𝑥ҧ𝑖 − 𝑥𝑗ҧ 1 5 1 5 = 2.179 28.33( + )≈ 7.304 © 2020 Cengage. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part, except for use as permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website or school-approved learning management system for classroom use. 76 Statistics for Business and Economics (14e) Fisher’s LSD Procedure Based on the Test Statistic 𝑥ҧ𝑖 − 𝑥𝑗ҧ 1. LSD for Treatments A and B • Hypothesis 1: 𝐻0 : 𝜇𝐴 = 𝜇𝐵 𝑣𝑠 𝐻𝑎 : 𝜇𝐴 ≠ 𝜇𝐵 • Rejection Rule: Reject 𝐻0 if 𝑥𝐴ҧ − 𝑥ҧ𝐵 ≥ 7.304 • Test Statistic: 𝑥𝐴ҧ − 𝑥ҧ𝐵 = 62 − 66 = 4 • Conclusion: The mean number of units produced at Treatment A is equal to the mean number produced at Treatment B. © 2020 Cengage. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part, except for use as permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website or school-approved learning management system for classroom use. 77 Statistics for Business and Economics (14e) Fisher’s LSD Procedure Based on the Test Statistic 𝑥ҧ𝑖 − 𝑥𝑗ҧ 2. LSD for Treatments A and C • Hypothesis 1: 𝐻0 : 𝜇𝐴 = 𝜇𝐶 𝑣𝑠 𝐻𝑎 : 𝜇𝐴 ≠ 𝜇𝐶 • Rejection Rule: Reject 𝐻0 if 𝑥𝐴ҧ − 𝑥ҧ𝐶 ≥ 7.304 • Test Statistic: 𝑥𝐴ҧ − 𝑥ҧ𝐶 = 62 − 52 = 10 • Conclusion: The mean number of units produced at Treatment A is not equal to the mean number produced at Treatment C. © 2020 Cengage. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part, except for use as permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website or school-approved learning management system for classroom use. 78 Statistics for Business and Economics (14e) Fisher’s LSD Procedure Based on the Test Statistic 𝑥ҧ𝑖 − 𝑥𝑗ҧ 3. LSD for Treatments B and C • Hypothesis 1: 𝐻0 : 𝜇𝐵 = 𝜇𝐶 𝑣𝑠 𝐻𝑎 : 𝜇𝐵 ≠ 𝜇𝐶 • Rejection Rule: Reject 𝐻0 if 𝑥ҧ𝐵 − 𝑥ҧ𝐶 ≥ 7.304 • Test Statistic: 𝑥ҧ𝐵 − 𝑥ҧ𝐶 = 66 − 52 = 14 • Conclusion: The mean number of units produced at Treatment B is not equal to the mean number produced at Treatment C. © 2020 Cengage. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part, except for use as permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website or school-approved learning management system for classroom use. 79 Statistics for Business and Economics (14e) © 2020 Cengage. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part, except for use as permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website or school-approved learning management system for classroom use. 80