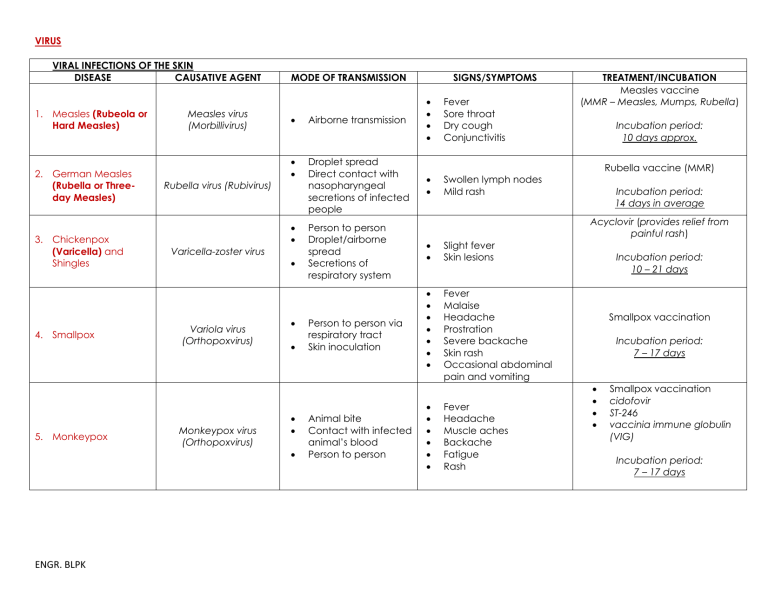
VIRUS VIRAL INFECTIONS OF THE SKIN DISEASE CAUSATIVE AGENT 1. Measles (Rubeola or Hard Measles) 2. German Measles (Rubella or Threeday Measles) 3. Chickenpox (Varicella) and Shingles 4. Smallpox 5. Monkeypox Measles virus (Morbillivirus) Rubella virus (Rubivirus) MODE OF TRANSMISSION Airborne transmission Droplet spread Direct contact with nasopharyngeal secretions of infected people Varicella-zoster virus Variola virus (Orthopoxvirus) Monkeypox virus (Orthopoxvirus) ENGR. BLPK SIGNS/SYMPTOMS Person to person Droplet/airborne spread Secretions of respiratory system Person to person via respiratory tract Skin inoculation Animal bite Contact with infected animal’s blood Person to person Fever Sore throat Dry cough Conjunctivitis Swollen lymph nodes Mild rash TREATMENT/INCUBATION Measles vaccine (MMR – Measles, Mumps, Rubella) Incubation period: 10 days approx. Rubella vaccine (MMR) Incubation period: 14 days in average Acyclovir (provides relief from painful rash) Slight fever Skin lesions Fever Malaise Headache Prostration Severe backache Skin rash Occasional abdominal pain and vomiting Fever Headache Muscle aches Backache Fatigue Rash Incubation period: 10 – 21 days Smallpox vaccination Incubation period: 7 – 17 days Smallpox vaccination cidofovir ST-246 vaccinia immune globulin (VIG) Incubation period: 7 – 17 days VIRAL INFECTIONS OF THE EYES DISEASE CAUSATIVE AGENT SIGNS/SYMPTOMS 6. Adenoviral conjunctivitis and keratoconjunctivitis 7. Haemorrhagic conjunctivitis MODE OF TRANSMISSION various types of adenoviruses Direct contact with eye secretions Adenoviruses Enteroviruses VIRAL INFECTIONS OF THE EARS DISEASE 8. Otitis Externa (External Otitis, Ear Canal Infection, Swimmer’s Ear) 9. Otitis Media (Middle Ear Infection) Direct or indirect contact with discharge from infected eyes CAUSATIVE AGENT Escherichia coli Pseudomonas aeruginosa Proteus vulgaris Staphylococcus aureus Measles virus Parainfluenza virus RSV (Respiratory Syncytial Virus) VIRAL INFECTIONS OF THE UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT DISEASE CAUSATIVE AGENT Inflammation of conjunctiva, edema of eyelids Blurred vision Direct or indirect contact with discharge from infected eyes MODE OF TRANSMISSION Contaminated swimming pool Not communicable MODE OF TRANSMISSION 10. Common Cold (Acute Viral Rhinitis, Acute Coryza) ENGR. BLPK Rhinovirus (family Picornaviridae) Coronavirus Reovirus Adenovirus Paramyxovirus Fomites Inhalation of airborne droplets TREATMENT/INCUBATION Cidofovir Incubation period: 7 – 10 days No specific treatment exists. Supportive care for symptoms must be provided SIGNS/SYMPTOMS Infection of ear canal with itching, pain, tenderness, redness, swelling, impaired hearing Common cold (most common in young children, 3months to 3 year of age) SIGNS/SYMPTOMS Infection of the lining of nose, sinuses, throat, and large airways Coryza (profuse discharge from nostrils) Sneezing, runny eyes Sore throat Chills Malaise (fatigue) Incubation period: 12 – 48 hours TREATMENT/INCUBATION Antibiotic ear drops Amoxicillin (dosage of 80 to 90 mg/kg/day) TREATMENT/INCUBATION Antiviral drugs Incubation period: 24 – 72 hours VIRAL INFECTIONS OF THE LOWER RESPIRATORY TRACT DISEASE CAUSATIVE AGENT Parainfluenza viruses RSV (major for early 11. Acute, febrile, infancy) viral respiratory Adenoviruses disease Rhinoviruses certain Coronaviruses Coxsackieviruses Echoviruses Five Hantaviruses: Sin Nombre 12. Hantavirus Bayou Pulmonary Black Creek Canal Syndrome (HPS) New York-1 Monongahela 13. Influenza 14. Avian Influenza (BirdFlu) 15. Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS) ENGR. BLPK Direct oral contact Droplets Indirectly by handkerchiefs, eating utensils, or other fomites Fecal-oral SIGNS/SYMPTOMS Fever One or more of the ff: Chills Headache General aching Malaise Anorexia Direct contact with infected rodents Inhaling rodent excreta Contaminated food and water Fever Muscular pain Cough Difficulty breathing Hypotension Airborne spread Direct contact Fever Chills Headache Aches Pain through the body Sore throat Cough Nasal discharge Avian influenza virus type A Direct or indirect contact with infected birds Fever Cough Sore throat Muscle aches SARS-associated coronavirus (SARS-CoV) Respiratory droplets Touching of mouth, nose, or eyes after touching a contaminated surface or object High fever Chills Headache Body ache Sometimes diarrhea Influenza viruses type A, B, and C 16. Sinusitis MODE OF TRANSMISSION Streptococcus pyogenes Streptococcus pneumoniae Person to person Inflammation of paranasal sinuses (adult disease) TREATMENT/INCUBATION Antiviral drug (ribavirin) Antiviral drug (ribavirin) Incubation period: 1 – 4 weeks Antiviral drug Incubation period: 2 days average Antiviral drug Incubation period: 2 - 5 days average Antibiotics Antiviral medications Chest therapy Incubation period: 2 – 7 days Antibiotic treatment (Amoxicillin-clavulanate) VIRAL INFECTIONS OF THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM DISEASE CAUSATIVE AGENT MODE OF TRANSMISSION SIGNS/SYMPTOMS Rapid weight loss Recurring fever or profuse night sweats Diarrhea that lasts for more than a week Sores of the mouth, anus, or genitals Diarrhea that lasts for more than a week Dry cough Memory loss Rapid weight loss Extreme fatigue Fever Sore throat Head and body aches Swollen lymph nodes in the neck and armpits 17. HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus) Type 1 & 2 HIV (Family Retroviridae) Direct sexual contact Sharing contaminated needles/syringes 18. AIDS (Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome) 19. Infectious Mononucleosis (Mono or Kissing Disease) 20. Mumps (Infectious Parotitis) (Latent stage of HIV disease) Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) also known as herpesvirus 4 Mumps virus (Family Paramyxoviridae VIRAL INFECTIONS OF THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM DISEASE CAUSATIVE AGENT Direct sexual contact Sharing contaminated needles/syringes Person to person Direct contact with saliva of an infected person Droplet spread Direct contact with the saliva of an infected person Lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (LCMV) Exposure to mouse urine Organ transplantation 22. Poliomyelitis (Polio or Infantile Paralysis) Polioviruses (Family Picornaviridae, “pico” = small) Fecal-oral Throat secretions ENGR. BLPK Rabies virus (Family Rhabdoviridae) Fever Swelling Tenderness of salivary glands MODE OF TRANSMISSION 21. Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis 23. Rabies Animal bite or inhalation SIGNS/SYMPTOMS Fever Malaise Suppressed appetite Muscle aches Nausea Headache Fever Malaise Headache Nausea Vomiting Mental depression Restlessness Headache TREATMENT/INCUBATION No treatment Incubation period: 2 – 4 weeks No treatment Ampicillin or amoxicillin Incubation period: 4 – 8 weeks Measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR) vaccine Incubation period: 7 days approx. TREATMENT/INCUBATION Anti-inflammatory drugs (corticosteroids) Incubation period: 1 – 2 weeks Polio vaccination Incubation period: 7 – 21 days MMR vaccine Incubation period: 3 – 8 weeks 24. West Nile Virus Encephalitis West Nile virus VIRAL SEXUALLY TRANSMITTED DISEASES DISEASE CAUSATIVE AGENT Mosquito bites MODE OF TRANSMISSION 25. Genital Herpes (Anogenital herpes viral infections) 26. Genital Warts (Genital papillomatosis, Condyloma acuminatum) HSV-1 (cold sores) occasional HSV-2 (genital herpes) - common 70 types of Human papilloma virus(HPV) Sexual contact through breaks in skin or mucous membranes or from mother to neonate (during birth) 27. Hepatitis B Hepatitis B virus (HBV) ENGR. BLPK Direct sexual contact or oral-genital, oralanal, or anal-genital Mother-to-fetus (during pregnancy) Mother-to-neonate (during birth) Sexual contact Sharing needles, syringes Mother-to-baby (during birth) Fever Paralysis Salivation No symptoms in most people (8 out of 10) Febrile illness (fever) in some people (1 out of 5) SIGNS/SYMPTOMS Lesion Latency-Associated Transcript (LAT) Fever Women: lesions in vulva, cervix, legs, buttocks Men: lesions in penis, anus, rectum Tiny, soft, moist, pink, or red swellings (like small cauliflowers) Grows in penis for men Grows in vaginal wall, vulva, cervix in women Grows in anus for both men and women who engage in anal sex Over-the-counter pain relievers can be used to reduce and relieve some symptoms Fever Fatigue Loss of appetite Nausea Vomiting Abdominal pain Dark urine Joint pain Clay-colored bowel movements Incubation period: 2 - 14 days TREATMENT/INCUBATION Antiviral medications Incubation period: 2 - 12 days, 4 days average Applying cream, lotion or chemical to the warts Destroying the tissue of the warts by freezing, heating or removing them (physical ablation) Incubation period: 2 weeks to 8 months Antiviral agents: lamivudine adefovir tenofovir entecavir Incubation period: 1.5 - 6 months, 4 months average OTHER VIRAL DISEASES DISEASE CAUSATIVE AGENT 28. Chikungunya Chikungunya Virus Aedis aegypti Aedis albopictus MODE OF TRANSMISSION SIGNS/SYMPTOMS Mosquito bite Mother-to-child (rarely) High fever Severe headache Severe pain behind the eyes Joint pain Muscle and bone pain Rash Mild bleeding dengue Virus 29. Dengue 30. Leptospirosis ENGR. BLPK Aedis aegypti Leptospira interrogans Mosquito bite Spread through urine of infected animals like: Cattle Pigs Horses Dogs Rodents Wild animals Fever Joint pain Headache Muscle pain Joint swelling or rash High fever Headache Chills Muscle aches Vomiting Jaundice (yellow skin and eyes) Red eyes Abdominal pain Diarrhea rash TREATMENT/INCUBATION No vaccine Treatment: Get plenty of rest Drink fluids to prevent dehydration Incubation period: 3 - 7 days No specific medication analgesics (pain relievers) acetaminophen Incubation period: 2 - 7 days Oral antibiotics such as: doxycycline penicillin Intravenous antibiotics Incubation period: 4 – 19 days, 9 – 10 days average BACTERIA NOTE: sp. – single species, spp. – more than one species BACTERIAL INFECTION OF THE SKIN DISEASE 1. Acne 2. Anthrax (Woolsorter’s Disease) 3. Gas Gangrene (Clostridial Myonecrosis) ENGR. BLPK CAUSATIVE AGENT Propionibacterium acnes Bacillus anthracis Clostridium perfringens and some other Clostridium spp. STAINING REACTION GP BACILLI GP BACILLUS GP BACILLI MODE OF TRANSMISSION Not transmittable Entry of endospores through breaks in skin Inhalation of spores Ingestion of bacteria in contaminated meat Soil containing clostridial spores enters an open wound SIGNS/SYMPTOMS Pores become clogged with dried sebum, flaked skin, and bacteria which leads to the formation of blackheads and whiteheads (acne pimples) Cutaneous Anthrax Blisters Swelling around the sore Painless skin sore with black center Inhalation Anthrax Fever and chills Chest discomfort Shortness of breath Extreme tiredness Body ache Gastrointestinal Anthrax Fever and chills Painful swallowing Diarrhea or bloody diarrhea Fainting Stomach pain Injection Anthrax Fever and chills Blisters Painless skin sore Vegetative pathogens produce nectrotizing exoenzymes and toxins, which destroy muscle and soft tissue Severe forms Massive tissue destruction Shock Renal failure TREATMENT/INCUBATION Cleansing with warm water and soap Antibiotics Incubation period: Cutaneous anthrax: 1 day Pulmonary anthrax: 1 – 7 days Gastrointestinal anthrax: 3 – 7 days Injection anthrax: 1 – 10 days Antibiotics such as: penicillin clindamycin Incubation period: Less than 24 hours Oral erythromycin or dicloxacillin 4. Impetigo (Pyoderma) Staphylococcus aureus Streptococcus pyogenes GP COCCUS Person to person contact Contaminated fomites Blisters (typically not painful, but itchy) Incubation period: Streptococcal: 1 – 3 days Staphylococcal: 4 – 10 days Acid Fast Stain 5. Leprosy (Hansen’s Disease) 6. Necrotizing Fasciitis (Flesheating bacteria) 7. Scarlet Fever (Scarlatina) ENGR. BLPK Mycobacterium leprae Streptococcus pyogenes Streptococcus pyogenes GP BACTERIUM GP COCCUS GP COCCUS Prolonged, close contact with an infected individual Bacteria enter a wound, such as from an insect bite, a burn, or a cut Person to person via large respiratory droplets Direct contact with patients or carriers Lepromatous leprosy – numerous nodules in skin and possible involvement of the nasal mucosa and eyes Tuberculoid leprosy – few skin lesions occur Peripheral nerve – severe, with loss of sensation Skin may be warm with red or purplish areas of swelling that spread rapidly Some people get ulcers, blisters, or black spots on the skin Patients often describe their pain as severe hurting much more than they would expect based on how the wound looks A very red sore throat Fever (101° F or above) Red rash with sandpaper feel Bright red skin in underarm, elbow, and groin creases Red and bumpy tongue Headache or body aches Swollen glands Nausea, vomiting, or abdominal pain Antibiotics (2 or 3 antibiotics are used at the same time) Incubation period: 5 years average Antibiotics given through a needle into a vein Incubation period: 1 - 3 days Antibiotics Incubation period: 1 – 7 days 8. Staphylococcal Scalded Skin Syndrome (SSSS) Staphylococcus Streptococcus aureus BACTERIAL INFECTION OF THE EYES CAUSATIVE DISEASE AGENT 9. Bacterial Conjunctivitis (Pinkeye) Haemophilus influenzae 10. Chlamydial Conjunctivitis Chlamydia trachomatis 11. Gonococcal Conjunctivitis (Gonorrheal Ophthalmia Neonatorum) Neisseria Gonorrhoeae (also known as gonococcus) 12. Trachoma (Chlamydia Keratoconjunctivitis) ENGR. BLPK Chlamydia trachomatis GP COCCUS Through the hands of healthcare workers Direct contact with a person having a purulent lesion or is an asymptomatic carrier Red blistering skin that looks like a burn or scald STAINING REACTION MODE OF TRANSMISSION GN BACTERIA Human-to-human transmission Contaminated fingers Contact lenswetting and lenscleaning agents GN BACTERIUM GN DIPLOCOCCUS GN BACTERIA Contact with genital discharges of infected people Contaminated fingers to eye Non-chlorinated swimming pools Neonate: Contact with infected birth canal during delivery Adult: finger-to-eye contact with infectious genital secretions Direct contact with infectious ocular or nasal secretions contaminated articles Flies serving as mechanical vectors Anti-staphylococcal antibiotic such as flucloxacillin Incubation period: 1 - 4 days SIGNS/SYMPTOMS Redness and swelling of the conjunctiva Watery eyes Itchy or scratchy eyes Discharge from the eye(s) Crusting of eyelids or lashes Neonates – mild scarring of conjunctivae and cornea Adult – nongonococcal urethritis or cervicitis Acute redness and swelling of conjunctiva and purulent discharge Scarring of cornea and conjunctiva Deformation of eyelids Blindness TREATMENT/INCUBATION Cold compress Stop wearing contact lenses Incubation period: 2 - 14 days Antibiotics (erythromycin) Incubation period: 1 – 2 weeks Antibiotics (single-dose intramuscular ceftriaxone) Incubation period: 5 – 14 days Antibiotics such as: erythromycin doxycycline sulfonamides Incubation period: 5 – 12 days BACTERIAL INFECTION OF THE EAR DISEASE CAUSATIVE AGENT 13. Otitis Media (Ear Infection) Streptococcus pyogenes Streptococcus pneumoniae Haemophilus influenza Moraxella catarrhalis Streptococcus aureus STAINING REACTION GP BACTERIA BACTERIAL INFECTION OF THE UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT STAINING DISEASE CAUSATIVE AGENT REACTION MODE OF TRANSMISSION SIGNS/ SYMPTOMS Ear pain Sleep disturbances Problem with hearing Air-borne spread Direct contact MODE OF TRANSMISSION SIGNS/SYMPTOMS TREATMENT/INCUBATION Amoxicillin (dosage of 80 to 90 mg/kg/day) TREATMENT/INCUBATION 14. Diphtheria Corynebacterium diphtheriae GP BACILLUS Airborne droplets Direct contact Contaminated fomites pseudomembrane 15. Klebsiella Pneumoniae Klebsiella pnuemoniae GN BACILLUS Person to person Contaminated hand touches the wound Weakness Sore throat Fever Swollen glands in the neck Fever and chills Flu-like symptoms Cough Breathing issues most fatal 16. Pneumonia Streptococcus pneumoniae GP Coccus Pneumococcal GN BACILLUS pneumoniae Person to person Cough Fever Difficulty breathing Inhalation of contaminated dust and aerosols Birds to human Fever Headache Cough most common cause of pneumonia 17. Psittacosis (Ornithosis or Parrot Fever) ENGR. BLPK Chlamydophila Psittaci GN BACTERIA DTP vaccine– Diphtheria Tetanus Pertussis DTaP vaccine – Diphtheria Tetanus acellular Pertussis Incubation period: 2 – 5 days or longer Antibacterial drugs such as: aminogylcosides polymyxins tigecycline fosfomycin temocillin Incubation period: 1 – 3 weeks Antibiotics Cough medicine Fever reducers/pain relievers Incubation period: 1 – 3 days Antibiotics Incubation period: 10 days typical, possible up to 4 weeks 18. Rheumatic Fever 19. Strep Throat (Streptococcal Pharyngitis) Streptococcus pyogenes GP COCCUS GN BACILLUS Streptococcus pyogenes GP COCCUS Person to person Direct contact Contaminated dust or handkerchief BACTERIAL INFECTION OF THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM STAINING DISEASE CAUSATIVE AGENT REACTION 20. Botulism 21. Listeriosis Clostridium botulinum Listeria monocytogenes 22. Meningitis Can also be Fungal or Viral) ENGR. BLPK Streptococcus pneumoniae Streptococcus agalactiae Neisseria meningitidis Listeria monocytogenes Haemophilus influenza Sore throat with tender and swollen lymph nodes Red rash Difficulty swallowing Sore throat Fever Red and swollen tonsils, sometimes with white patches or streak of pus Swollen lymph nodes MODE OF TRANSMISSION GP BACILLUS Develops if a person ingests the toxin Organism grows in the intestine or wounds GN COCCOBACILLUS Ingestion of raw or contaminated milk, soft cheeses, or vegetables Mother-to-fetus SIGNS/SYMPTOMS GP DIPPLOCOCCI Spread from one person to another Double vision Blurred vision Drooping eyelids Slurred speech Dry mouth Muscle weakness Fever Intense headache Nausea Vomiting Delirium Coma Nausea Vomiting Photophobia (increased sensitivity to light) Altered mental status (confusion) Antibiotics such as: diuretics digoxin corticosteroids Incubation period: 1 – 5 weeks Antibiotics such as: penicillin amoxicillin Incubation period: 3 days average TREATMENT/ INCUBATION Antitoxin drug Incubation period: 2hrs - 8 days 12 - 36 hrs typical Antibiotics Incubation period: Probably a few days to 3 weeks Antibiotics Incubation period: 2 - 10 days, 2 days – 2 weeks (most common) 23. Q Fever (Query Fever) 24. Tetanus (Lockjaw) Coxiella bumetti Clostridium tetani GN BACTERIUM Arthropods (ticks, flies, lies, etc) Aerosol Fomites Person to person When dirt enters a GN BACILLUS wound or cut GP Bacillus Spore forming High fever Chills or sweats Fatigue Headache Muscle pain Chest pain Clay-colored stools Jaundice Painful muscular contractions Spasms Rigid paralysis Antibiotics such as: doxycycline hydroxychloroquine ciprofloxacin co-trimoxazole Incubation period: 2 - 3 weeks, 20 days avergae Penicillin and active immunization DTP/DTaP Incubation period: 3 days - 3 weeks, 8 days usual BACTERIAL INFECTION OF THE LOWER RESPIRATORY TRACT DISEASE 25. Legionnaires Disease (Legionellosis Disease, Pontiac Fever) 26. Primary Atypical Pneumonia (Mycoplasmal Pneumonia) CAUSATIVE AGENT STAINING REACTION GN Bacillus Legionella pneumophila Mycoplasma pneumonia(also called Koch’s bacillus) GP BACILLUS GN BACTERIUM Acid Fast stain 27. Tuberculosis (TB) Mycobacterium tuberculosis GP TO GV BACILLUS BACILLI-ROD SHAPE BACTERIA ENGR. BLPK MODE OF TRANSMISSION SIGNS/SYMPTOMS Inhaling mist from water sources (whirlpool baths, showers, cooling towers) Pneumonia with: Anorexia Malaise Headache High fever Chills Dry cough Pontiac fever (less serious infection) Droplet inhalation Direct contact with an infected person Contaminated articles Airborne droplets Direct contact with infected individuals Headache Malaise Dry cough Sore throat Chest discomfort Early symptoms Fever Night sweats Loss of appetite Weight loss Chronic symptoms Cough Chest pain Bloody sputum (saliva) TREATMENT/INCUBATION Antibiotic drug (erythromycin) Incubation period: 5 – 6 days Antibiotic therapy and support Incubation period: 1 – 4 weeks bacille Calmette-Guerin (BCG) vaccine Antibiotics such as: rifampicin isoniazid kanamycin Incubation period: 4 – 6 weeks 28. Whooping Cough (Pertussis) Bordatella pertussis GN COCCOBACILLUS First stage: Mild, coldlike symptoms Second Stage: produces severe, uncontrollable coughing fits Third stage: usually begins within 4 weeks of onset Droplets produced by coughing Pertussis vaccine Antibiotic (erythromycin) Incubation period: 7 – 10 days BACTERIAL INFECTION OF THE ORAL REGION DISEASE CAUSATIVE AGENT 29. Acute Necrotizing Ulcerative Gingivitis (ANUG) (also called Vincent’s angina and trench mouth) STAINING REACTION Fusobacterium nucleatum GN BACILLUS BACTERIAL INFECTION OF THE GASTRO-INTESTINAL TRACT STAINING DISEASE CAUSATIVE AGENT REACTION 30. Bacterial Gastritis and Gastric Ulcers 31. Campylobacter enteritis ENGR. BLPK MODE OF TRANSMISSION Helicobacter pylori Campylobacter jejuni Campylobacter coli GN BACILLUS GN BACILLI SIGNS/SYMPTOMS Bad breath Crater-like ulcers in the mouth Fatigue Fever Grayish film on the gums Pain in the gums Tobacco chewing Poor oral hygiene MODE OF TRANSMISSION Fecal-oral route Ingestion of contaminated food and water SIGNS/SYMPTOMS Upper abdominal pain with nausea or heartburn Diarrhea Nausea Vomiting Fever Malaise Abdominal pain TREATMENT/INCUBATION Antibiotics Proper ongoing oral hygiene Incubation period: 3 - 5 days TREATMENT/INCUBATION Antacids Antibiotics Incubation period: 1 – 3 days Patients should drink extra fluids as long as the diarrhea lasts azithromycin and fluoroquinolones are common treatments Incubation period: 1 – 10 days, 2 – 5 days average 32. Cholera Vibrio cholerae 33. Salmonellosis Salmonella enterica 34. Typhoid Fever (Enteric Fever) Salmonella typhi or Typhoid bacillus 35. Paratyphoid Fever (less severe infection) 36. Shigellosis (Bacillary Dysentery) ENGR. BLPK Salmonella paratyphi Shigella dysenteriae Shigella flexneri Shigella boydii Shigella sonnei GN BACILLI GN BACILLI GN BACILLUS GN BACILLUS Profuse watery diarrhea (“rice-water stools”) Vomiting Rapid heart rate Thirst and dehydration Low urine output Muscle cramps Loss of skin elasticity Low blood pressure Rehydration therapy (Oral Rehydration Salt ORS) Antibiotic – cotrimoxazole Zinc treatment Incubation period: A few hours – 5 days, 3 days typical Gastroenteritis with sudden onset of: Headache Abdominal pain Diarrhea Nausea Vomiting Dehydration (severe case) Since dehydration is the most common complication, take frequent sips of rehydration drink (such as pedialyte) Incubation period: 4 – 7 days Fecal-oral route Sustained fever as high as 39-40°C Stomach pains Headache Loss of appetite Constipation Rash Antibiotics such as: ampicillin ciprofloxacin ceftriaxone (pregnant) Incubation period: 14 days average, 7- 21 days typical Fecal-oral route Sustained fever as high as 39-40°C Stomach pains Headache Loss of appetite Constipation Rash Antibiotics such as: ampicillin ciprofloxacin Incubation period: 1 – 10 days (gastro), 1 – 3 weeks (enteric) Fecal-oral route Diarrhea (as many as 20 bowel movements a day) with blood, mucus, and pus Nausea Vomiting Abdominal cramps Fever Antibiotics such as: Trimethoprim/sulfamet hoxazole Ampicillin (penicillin) Azithromycin (zithromax) Ciprofloxacin (cipro) Incubation period: 1 – 7 days, >4days typical Drinking and eating contaminated food Ingestion of contaminated food Handling reptiles GN Bacilli GP BACILLI GP COCCUS 37. Clostridium Difficile – Associated Disease Clostridium difficile GP BACILLUS Dirty hands Touching unclean surfaces contaminated with feces from an infected person Watery diarrhea Fever Loss of appetite Nausea Belly pain and tenderness Antibiotics Incubation period: No longer than 7 days BACTERIAL SEXUALLY TRANSMITTED DISEASE DISEASE 38. Genital Chlamydial Infections, Genital Chlamydiasis 39. Gonorrhea 40. Syphilis ENGR. BLPK CAUSATIVE AGENT Chlamydia trachomatis (most common sexually transmitted pathogen) Neisseria gonorrhoeae Treponema pallidum STAINING REACTION GN BACTERIA GN DIPLOCOCCUS GV SPIROCHETE, tightly coiled MODE OF TRANSMISSION Direct sexual contact Mother-to-neonate (during birth) Sexual contact Adult-to-child (sexual abuse) Mother-to-neonate Direct sexual intercourse Mother-to-neonate (during birth) SIGNS/SYMPTOMS TREATMENT/INCUBATION Men: discharge from penis, burning sensation when urinating. Pain and swelling in one or both testicles Women: abnormal vaginal discharge, burning sensation when urinating Men: burning sensation when urinating, a discharge from penis (white, yellow, or green), painful or swollen testicles Women: painful or burning sensation when urinating, increase vaginal discharge, vaginal bleeding when periods Primary syphilis – painless lesion (chancre) Secondary syphilis – skin rash (especially on the palms and soles) Long latent period – no visible signs or symptoms Tertiary syphilis – damage to the CNS, Antibiotics such as: erythromycin doxycycline azithromycin levofloxacin ofloxacin Incubation period: Variable (days to months) Antibiotics such as: azithromycin intramuscular ceftriaxone Incubation period: 2 – 5 days Antibiotics Incubation period: 3 weeks to 3 months cardiovascular system, visceral organs, bones, sense organs Neurosyphilis and Ocular syphilis – severe headache, numbness, paralysis, dementia BACTERIAL INFECTIONS OF THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM STAINING DISEASE CAUSATIVE AGENT REACTION 41. Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever (Tickborne Rickettsia ricketsii GN BACTERIUM Typhus Fever or Spotted Fever Rickettsiosis) 42. Endemic Typhus Fever (Murine typhus fever) 43. Epidemic Typhus Fever (Louse-borne typhus) 44. Ehrlichiosis 45. Scrub Typhus (Bush Typhus) ENGR. BLPK Rickettsia typhi Rickettsia prowazekii Ehrlichia chaffeensis Orientia tsutsugamushi GN BACTERIUM GN BACTERIUM GN COCCOBACILLI GN BACTERIA MODE OF TRANSMISSION SIGNS/SYMPTOMS Moderate to high fever Extreme exhaustion (prostration) Muscle pain Severe headache Chills Conjunctival infection Maculopapular rash Shaking chills Headache Fever Faint, pink rash Headache Fever and chills Prostration General pains Rash (5th or 6th day) Fever and chills Headache Muscle pain Nausea/vomiting Diarrhea Confusion Conjunctival injection (red eyes) Fever and chills Rash Headache Enlarged lymph nodes Tick bite Flea bite Flea, lice, mites, and ticks Tick bite Mite bite TREATMENT/INCUBATION Antibiotic doxycycline Incubation period: 5 – 10 days Antibiotic doxycycline Incubation period: 1 – 2 weeks Antibiotic doxycycline Incubation period: 1 – 2 weeks, 12 days average Antibiotic doxycycline Incubation period: 5 – 21 days, 1 – 2 weeks typical Antibiotic doxycycline Incubation period: 6 – 20 days, 10 days average OTHER BACTERIAL INFECTIONS OF THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM STAINING DISEASE CAUSATIVE AGENT MODE OF TRANSMISSION REACTION 46. Lyme Disease 47. Plague 48. Tularemia (Rabbit Fever) ENGR. BLPK Borrelia burgdorferi Yersinia pestis Francisella tularensis GN SPIROCHETE GN BACILLUS GN BACILLUS Tick bite Flea bites (rodent to flea to human) Contact with contaminated fluid or tissue Infectious droplets Tick bite Ingestion of contaminated meat Inhalation of dust Animal bite SIGNS/SYMPTOMS Early signs Fever, chills, headache, fatigue, muscle and joint aches, swollen lymph nodes Later signs Severe headaches and neck stiffness Nerve pain Heart palpitations Bubonic plague Fever Headache Chills and weakness Tender and painful lymph nodes Septicemic plague Fever Headache Extreme weakness Abdominal pain Shock Pneumonic plague Fever Headache Weakness Rapid developing pneumonia with shortness of breath Fever as high as 104 °F (40 °C) Ulceroglandular “most common form of tularemia” Skin ulcer Headache Exhaustion Swollen and painful lymph glands TREATMENT/INCUBATION Antibiotics such as: doxycycline amoxicillin cefuroxime axetil Incubation period: 3 - 30 days Antibiotics such as: streptomycin gentamicin doxyclycline ciprofloxacin Incubation period: 2 - 6 days Antibiotics such as: streptomycin tetramycin Incubation period: 1 – 10 days, 3 days average Glandular Same signs with ulceroglandular, but without skin ulcer Oculoglandular Irritation and inflammation of the eye Swelling of lymph glands in front of the ear Oropharyngeal Sore throat Mouth ulcers Tonsillitis Swelling of lymph glands in the neck Pneumonic “most serious form of tularemia” Cough, chest pain, difficulty breathing Typhoidal Any combination of general symptoms ENGR. BLPK FUNGI FUNGAL INFECTIONS OF THE SKIN DISEASE CAUSATIVE AGENT MODE OF TRANSMISSION SIGNS/SYMPTOMS TREATMENT/INCUBATION Ringworm on the Skin Antifungal creams Ringworm on the Scalp Antifungal medications taken by mouth for 1 to 3 months Incubation period: 1. Dermatophytoses (Ringworm or Tinea) Three genera of Ascomycetes Microsporum Epidermphyton Triphyton Contact with infected animals Tinea pedis (Athlete’s foot) Tinea corporis (trunk) Tinea cruris (groin area) Tinea capitis (head) Tinea unguium (nails) Tinea pedis: Weeks Tinea corporis: 4 – 10 days Tinea cruris: 4 – 10 days Tinea capitis: 10 – 14 days Tinea unguium: Weeks FUNGAL INFECTIONS OF THE LOWER RESPIRATORY TRACT DISEASE CAUSATIVE AGENT MODE OF TRANSMISSION 2. Aspergillosis ENGR. BLPK various species of Aspergillus (moulds) Inhalation of airborne conidia (asexual spores produced by various fungi) SIGNS/SYMPTOMS Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis (ABPA) - similar to asthma Wheezing Shortness of breath Fever Cough Allergic Aspergillus Sinusitis Stuffiness Runny nose Headache Reduced ability to smell TREATMENT/INCUBATION Antifungal agents such as: corticosteroids itraconazole Incubation period: 15 days 3. Coccidioidomycosis (Valley Fever) 4. Histoplasmosis 5. Mucormycosis (previously called Zygomycosis) ENGR. BLPK Coccidioides immitis Inhalation of arthrospores, especially during wind and dust storms Histoplasma capsulatum var. capsulatum Inhalation of conidia (asexual spores) from soil various Zygomycetes, including bread moulds Penetrating injuries inflicted by contaminated objects (splinters from a woodpile) Aspergilloma “fungus ball” Cough and coughing up blood Shortness of breath Chronic Pulmonary Aspergillosis Weight loss Cough and coughing up blood Fatigue Shortness of breath Invasive Aspergillosis Fever Chest pain Cough and coughing up blood Shortness o breath Respiratory infection with Fever Chills Cough Pain Disseminated include Lung lesions and abscesses (collection of pus) throughout the body Malaise Fever Chills Eadache Myalgia Chest pains Nonproductive cough (no sputum produced) Rhinocerebral (sinus and brain) mucormycosis One-sdied facial swelling Headache Nasal or sinus congestion Black lesion on upper inside of mouth Pulmonary (lung) mucormycosis Fever Cough and chest pain Shortness of breath Cutaneous (skin) mucormycosis Blisters and ulcers Antifungal medications Incubation period: 1 – 3 weeks Antifungal medications (itraconazole) Incubation period: 3 – 17 days Antifungal medications such as: amphotericin B posaconazole isavuconazole Incubation period: 1 – 2 weeks Swelling around a wound Gastrointestinal mucormycosis Abdominal pain Nausea and vomiting Gastrointestinal bleeding Disseminated mucormycosis People who are already sick from other medical conditions FUNGAL INFECTIONS OF THE ORAL REGION DISEASE CAUSATIVE AGENT MODE OF TRANSMISSION 6. Thrush Candida albicans Contact with secretions or excretions of mouth, skin, vagina, or feces of patients or carriers Mother-to-neonate (during birth) FUNGAL INFECTIONS OF THE GENITO-URINARY STSTEM DISEASE CAUSATIVE AGENT 7. Yeast Vaginitis Candida albicans (yeast) Trichomonas vaginalis (protozoan) Mobiluncus and Gardnerella (mixture of bacteria) SIGNS/SYMPTOMS MODE OF TRANSMISSION Contact with secretions or excretions of mouth, skin, vagina, or feces of patients or carriers Mother-to-neonate (during birth) FUNGAL INFECTIONS OF THE CENTRAL NERVOUS STSTEM DISEASE CAUSATIVE AGENT MODE OF TRANSMISSION 8. Cryptococcosis (Cryptococcosis Meningitis) ENGR. BLPK Cryptococcus neoformans White creamy patches on the inner cheeks, tongue, roof of mouth, and throat Redness or soreness Loss of taste Cottony feeling in the mouth Inhalation of microscopic fungus from the environment SIGNS/SYMPTOMS Vulvar pruritis (itching) Burning sensation Dysuria (painful urination) White discharge SIGNS/SYMPTOMS In the lungs Cough Shortness of breath Chest pain Fever In the brain Fever and headache Neck pain Nausea and vomiting Sensitivity to light Confusion or changes in behavior TREATMENT/INCUBATION Antifungal medicines such as: clotrimazole miconazole nystatin fluconazole Incubation period: 2 - 5 days TREATMENT/INCUBATION Antifungal medicines such as: fluconazole Incubation period: 2 - 5 days TREATMENT/INCUBATION Antifungal medications for at least 6 months Incubation period: unknown 9. Black Piedra 10. Pneumocystis Pneumonia 11. Sporotrichosis Piedraia hortae (a mould) Pneumocystis jiroveci (formerly pneumocystis carinii) Sporothrix schenckii (Rose Gardener's Disease) Person to person Person to person through air Microscopic fungus can enter the skin through small cuts or scrapes Scratches or bites from animals Soft black nodules in hair shaft Fever and chills Cough and difficulty breathing Chest pain Fatigue (tiredness) Cutaneous (skin) sporotrichosis Small painless bump then will later on grow larger and may look like an open sore or ulcer Pulmonary (lung) sporotrichosis Cough Shortness of breath Chest pain Fever Disseminated sporotrichosis Joint pain Difficulty thinking Headache Seizures Antifungal agents (oral terbinafine) Prescription medicine such as: trimethoprim/ sulfamethoxazole (TMP/SMX) Incubation period: 3 weeks to 3 months Antifungal medications (itraconazole) Incubation period: 1 – 3 weeks approx. Antifungal creams 12. Tinea Nigra Hortaea werneckii (a mould) Direct contact with fungus Rash Patches (white, pink, red, or brown) Spots in neck, chest, back, and arms Irregular nodules or gelatinous sheaths along hair shaft (can be white, cream-colored, or brown) 13. Tinea Versicolor (Pityriasis Versicolor) Malassezia furfur (a mould) People with oily skin 14. White Piedra (Tinea Blanca) Trichosporon beigelii (a mould) Contaminated soil Defective or abnormal gene ENGR. BLPK Brownish-black patch on the skin Incubation period: Few weeks to 20 years, 2 – 7 weeks typical Antifungal creams, lotions, or shampoos Antifungal agents such as: Oral azole antifungals and shampoos PROTOZOA PROTOZOAL INFECTIONS OF THE SKIN CAUSATIVE DISEASE AGENT 1. Leishmaniasis MODE OF TRANSMISSION Leishmania donovani PROTOZOAL INFECTIONS OF THE EYES DISEASE CAUSATIVE AGENT Sandfly bite SIGNS/SYMPTOMS Cutaneous leishmaniasis Leishmania Tropica Skin sores Swollen glands Visceral leishmaniasis “kala-azar” Leishmania Donovani Fever Enlarged liver and spleen Most cases heal without treatment Lymphadenopathy Anemia Incubation period: Leukopenia 2 months approx. Mucosal leishmaniasis Less common form Consequence of infection with some species of the parasite that cause cutaneous leishmaniasis MODE OF TRANSMISSION 2. Amebic Eye Infections Acanthamoeba Contaminated water Wearing contact lenses 3. Toxoplasmosis ENGR. BLPK Toxoplasma gondii TREATMENT/INCUBATION Ingestion of oocysts in cat feces SIGNS/SYMPTOMS Sensation of something in the eye Eye pain Eye redness Blurred vision Sensitivity to light Excessive tearing A very high fever (38°C or higher) Aching muscles Tiredness Feeling sick Swollen glands Sore throat TREATMENT/INCUBATION Aggressive medical and surgical treatment Incubation period: unknown Healthy people Drugs such as pyrimethamine and sulfadiazine plus folinic acid Pregnant women, newborns, and infants Antibiotic spiramycin Person with ocular disease Prescribed medicine by ophthalmologist Person with compromised immune system pyrimethamine and sulfadiazine Incubation period: 10 – 23 days (foodborne) 5 – 20 days (infective oocysts) PROTOZOAL INFECTIONS OF THE GENITO-URINARY TRACT DISEASE CAUSATIVE AGENT MODE OF TRANSMISSION SIGNS/SYMPTOMS asymptomatic in men Itching or irritation inside penis Burning after urination or ejaculation Discharge from the penis Women Itching, burning, redness or soreness of the genitals Discomfort during urination Change in vaginal discharge (clear, white, yellowish, or greenish with an unusual fishy smell) TREATMENT/INCUBATION Men 4. Trichomoniasis Trichomonas vaginalis Parasite passes from an infected person to an uninfected person during sex PROTOZOAL INFECTIONS OF THE GASTRO-INTESTINAL TRACT DISEASE CAUSATIVE AGENT MODE OF TRANSMISSION 5. Amebiasis (Amebic Dysentery) Entamoeba histolytica ENGR. BLPK Ingestion of focally contaminated food or water by flies transporting cyst from feces to food Ingestion of contaminated food and water Direct hand to mouth Anal intercourse involving multiple sex partners Antibiotic medications such as: metronidazole tinidazole SIGNS/SYMPTOMS I. INTESTINAL Non-invasive– asymptomatic carriers Invasive Amoebic colitis o Inflammation of colon o Abdominal pain, diarrhea, fever Fulminant colitis o Severly ill with high fever o Intestinal bleeding, perforation Incubation period: 5 - 28 days TREATMENT/INCUBATION Antibiotics such as: metronidazole tinidazole iodoquinol diloxanidefuroate Incubation period: 5 days or longer, 2 – 4 weeks average Amoeboma o Inflammatory thickening of intestinal wall II. EXTRA-INTESTINAL Amoebic liver abscess o 10x more common in men Lung abscess o Direct spread from liver abscess Brain o Death in 12-72 hours 6. Balantidiasis Balantidium coli Fecal-oral route (pig feces) 7. Cyclosporiasis 8. Giardiasis Cyclospora cayetanesis Giardiasis lamblia (Giardia intestinalis) Flagellated protozoan, infects small intestine ENGR. BLPK Direct person to person via fecal-oral route Fecal-oral route Diarrhea Abdominal pain Dysentery Weight loss Nausea and vomiting Loss of appetite Weight loss Stomach cramps/pain Bloating Increase gas Nausea and vomiting Fatigue Diarrhea Abdominal cramps Bloating Abdominal gas Fatigue Weight loss Antibiotics such as: tetracycline metronidazole iodoquinol Incubation period: 4 - 5 days typical Antibiotics such as: trimethoprimsulfamethoxazole Incubation period: 2 -14 days or more Antibiotics such as: metronidazole tinidazole nitazoxanide Incubation period: 6 – 22 days, 9 days average PROTOZOAL INFECTIONS OF THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM DISEASE CAUSATIVE AGENT MODE OF TRANSMISSION 9. African Trypanosomiasis (African Sleeping Sickness) 10. American Trypanosomiasis (Chagas’ Disease or Kissing Bug) Trypanosoma brucei ssp. gambiense Trypanosoma brucei ssp. rhodesiense Trypanosoma cruzi Tsetse flies (Glossina palpalis) Triatomine bug (Kissing bug) 11. Babesiosis Babesia microti Tick bite reservoir: rodents and cattles 12. Malaria Four species in genus Plasmodium Plasmodium vivax Plasmodium ovale Plasmodium malariae Plasmodium falciparum (Anopheles Mosquito) ENGR. BLPK Injection of sporozoites intro bloodstream by an infected female Anopheles mosquito Contaminated needles and syringes Organ transplant SIGNS/SYMPTOMS Early stages Intense headache Insomnia Anemia Local edema and rash Later stages Body wasting Falling asleep Coma Death Acute phase Fever Fatigue Body aches Headache Rash Loss of appetite Diarrhea Vomiting Chronic phase Heart failure Cardiac arrest Difficulties with eating or passing stool Fever and chills Sweats Headache and body ache Loss of appetite Nausea and fatigue Flu-like illness Shaking chills Headache Muscle aches Tiredness Nausea and vomiting Diarrhea TREATMENT/INCUBATION Antimicrobial medication (pentamidine) Incubation period: Few days to several weeks or months Anti-protozoan medications such as: benznidazole nifurtimox Incubation period: 7 - 14 days Combination of quinine and clinamyacin Incubation period: 1 – 6 weeks Anti-protozoan medications such as: doxycycline quinine quinidine Incubation period: P. vivax: 12 – 18 days P. ovale:12 – 18 days P. malariae:18 – 40 days P. falciparum: 9 – 14 days HELMINTHS HELMINTH INFECTIONS OF THE SKIN DISEASE 1. Onchocerciasis (River Blindness) Nematode CAUSATIVE AGENT Onchocerca volvulus MODE OF TRANSMISSION Bite of an infectious Simulium blackfly SIGNS/SYMPTOMS Itchy skin rashes Nodules under the skin Vision changes HELMINTH INFECTIONS OF THE MUSCLE AND SUBCUTANEOUS TISSUES DISEASE CAUSATIVE AGENT MODE OF TRANSMISSION Nematode/Roundworms 2. Trichinellosis (Trichinosis) Trichinella spiralis Consumption of raw or undercooked meat of animals infected with larvae of worm Trichinella Incubation Period: 8-15 days 3. Dracunculiasis (Guinea Worm Disease) Nematode/Roundworms ENGR. BLPK Dracunculus medinensis Drinking unfiltered water containing copepods (small crustaceans) SIGNS/SYMPTOMS Mild Nausea Diarrhea Vomiting Fatigue Fever Abdominal discomfort Heavy Heart and breathing problems Difficulty coordinating movements Severe Death People do not usually have symptoms until about one year after they become infected Fever Swelling Diarrhea Reddish papuleblister Blister ruptures, becomes abscessed – very painful TREATMENT/INCUBATION Anti-parasitic agent (ivermectin) Incubation period: 9 – 24 months TREATMENT/INCUBATION Prescription drugs such as: thiabendazole albendazole mebendazole prednisone Incubation period: 2 – 28 days, 9 days typical Local cleansing of lesion Drug therapy such as: metronidazole and thiabendazole Anti-inflammatory drugs Incubation period: 10 – 14 months (about 12 months) HELMINTH INFECTIONS OF THE EYES DISEASE MODE OF TRANSMISSION CAUSATIVE AGENT SIGNS/SYMPTOMS Nematode 4. Loiasis Loa loa (African eyeworm) Bite of an infected deerfly of the genus Chrysops Itchy, non-painful swelling of the body that come and go Eye worm that crawls across the surface of the eyes Itching all over the body Muscle pain Joint pain Fatigue TREATMENT/INCUBATION Surgery in order to remove the eye worm dethylcarbamazine(kills the parasite in the body) Incubation period: Adult worms can live up to 17 years in human host HELMINTH INFECTIONS OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM DISEASE 5. Paragonimiasis trematodes/flukeworms ENGR. BLPK CAUSATIVE AGENT Paragonimus westermani MODE OF TRANSMISSION Eating raw or undercooked infected crab or crayfish SIGNS/SYMPTOMS Abdominal pain Discomfort Low-grade fever that may occur 2 to 15 days after infection TREATMENT/INCUBATION Prescription drugs such as: praziquantel triclabendazole Incubation period: 6 – 10 weeks HELMINTH INFECTIONS OF THE GASTRO-INTESTINAL TRACT DISEASE CAUSATIVE AGENT 6. Ascariasis Ascaris lumbricoides nematode` 7. Hookworm infection (Ancylostomiasis) Ancylostoma duodenale or Necator americanus MODE OF TRANSMISSION SIGNS/SYMPTOMS Ingestion of infective eggs from soil contaminated with human feces Abdominal discomfort Hookworm eggs are passed in the feces of an infected person Nematode 8. Pinworm infection (Enterobiasis or Helminthiasis) Incubation period: About 2 months Enterobius vermicularis Fecal-oral route Localized rash Abdominal pain Diarrhea Loss of appetite Weight loss Fatigue Anemia Itching around the anus that can lead to difficulty sleeping and restlessness Weight loss Nematode 9. Whipworm infection (Trichuriasis) 10. Strongyloidiasis Trichuris trichiura Strongyloides stercoralis Whipworm eggs are passed in the feces of infected persons soil contaminated with freeliving larvae Nematode 11. Beef Tapeworm Taenia saginata Taeniasis Cestodes/ Tapeworms ENGR. BLPK Passed in the feces of an infected person TREATMENT/INCUBATION Preventive chemotherapy Light infections Usually have no symptoms Heavy infections Frequent painful passage of stool that contains mixture of mucus, water, and blood Abdominal pain Bloating Heartburn Intermittent episodes of diarrhea and constipations Dry cough Rashes Abdominal pain Loss of appetite Anthelmintics such as: albendazole mebedazole Incubation period: 5 weeks to 9 months Anthelmintics such as: mebendazole pyrantel pamoate albendazole Incubation period: 4 – 6 weeks Anthelmintics such as: Albendazole Mebedazole Incubation period: 15 – 30 days, 10 days minimum Anti-parasitic medications such as: ivermectin alebndazole Incubation period: 28 days approx. Anthelmintics such as: albendazole Ingestion of raw or undercooked infected beef Weight loss Upset stomach praziquantel niclosamide Incubation period: 2 – 3 months Cestodes/ Tapeworms 12. Pork Tapeworm Taenia solium Consumption of raw or undercooked pork products Taeniasis 13. Dog Tapeworm 14. Fish Tapeworm Dipylidium caninum Diphyllobothrium latum Ingestion of eggs Consumption of an infected fish Cestodes/Tapeworm 15. Dwarf Tapeworm Cestodes/Tapeworm 16. Rat Tapeworm Cestodes/Tapeworm ENGR. BLPK Hymenolepis nana Hymenolepis diminuta Poor sanitation and personal hygiene Focally contaminated food or water Ingestion of beetle containing the larval stage Abdominal pain Loss of appetite Weight loss Upset stomach Dogs may experience Irritation and may lick their behinds a lot Weight loss Abdominal discomfort Diarrhea Vomiting Weight loss Nausea Weakness Loss of appetite Diarrhea Abdominal pain Enteritis Anorexia Headaches Anal pruritus (itch) Abdominal distress Anthelmintics such as: albendazole praziquantel niclosamide Incubation period: 8 – 10 weeks De-worming drugs Incubation period: 20 days approx. Anti-parasitic medications such as: praziquantel niclosamide Incubation period: 3 – 6 weeks Anti-parasitic medications such as praziquantel Incubation period: 4 – 6 week Anti-parasitic medications such as: praziquantel niclosamide nitazoxanide Incubation period: 2 – 4 weeks Abdominal pain and diarrhea can occur 1 to 2 months after infection 17. Fasciolopsiasis (Intestinal Fluke) Fasciolopsis buski Ingestion of raw or undercooked aquatic plants that have the organic encysted on them 18. Fascioliasis (Liver Fluke) 19. Clonorchiasis (Chinese or Oriental liver fluke) Fasciola hepatica Clonorchis sinensis Eggs are passed in stool of infected people and animals Ingestion of undercooked sheep or goat liver that contained immature forms of parasite Ingestion of raw or undercooked fish/pickles that contains parasitic cysts If heavy infection Intestinal obstruction Abdominal pain Nausea and vomiting Fever Allergic reactions and swelling of face and legs Anemia Acute migratory phase 4 to 7 days after exposure and can last several weeks and months Chronic phase Inflammation and blockage of bile ducts Clinical features on both phase: Fever Malaise Abdominal pain Eosinophilia (allergic reaction or cancer) Hematomegaly (enlarged liver) Abdominal liver tests Inflammation Intermittent obstruction of biliary ducts Severe cases Abdominal pain Nausea Diarrhea Untreated infections ENGR. BLPK Inflammation of biliary system that can lead to cancer Anti-parasitic medication (praziquantel) Incubation period: 3 – 6 months Anti-parasitic medication (triclabendazole) Incubation period: Few days to 3 months Anthelmintics such as: albendazole praziquantel Incubation period: Variable HELMINTH INFECTIONS OF THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM DISEASE CAUSATIVE AGENT 20. Filariasis 21. Schistosomiasis (Bilharziasis or Blood Flukes) Wuchecheria bancrofti Brugia malayi Brugia timori MODE OF TRANSMISSION Person to person through the bite of an infected mosquito Schistosoma Skin comes in contact with contaminated freshwater wherein certain type of SNAILS carry schistosomes HELMINTH INFECTIONS OF THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM DISEASE CAUSATIVE AGENT 22. Cysticercosis ENGR. BLPK Cysts of Taenia solium SIGNS/SYMPTOMS Mostly asymptomatic Small percentage of person can develop lymphedema (swelling in arms and legs) Hardening and thickening of the skin (Elephantiasis) Men can develop swelling of the scrotum Rash or itchy skin Fever Chills Cough Muscle aches Inflammation or scarring In children Anemia Malnutrition Learning difficulties MODE OF TRANSMISSION Fecal-oral route SIGNS/SYMPTOMS Cysts in muscles Can feel lumps under the skin (lumps can sometimes be tender) Cysts in the eyes Cysts may float in the eye and cause blurry or disturbed vision May also cause swelling and detachment of retina TREATMENT/INCUBATION Anti-parasitic drugs such as: albendazole diethylcarbamazine (DEC) Incubation period: 8 – 16 months Anti-parasitic medication (praziquantel) Incubation period: 4 – 6 weeks or longer TREATMENT/INCUBATION Anti-parasitic and antiinflammatory drugs such as: albendazole corticosteroids Incubation period: Months to years Neurocysticercosis (cysts in the brain, spinal cord) Seizures Headaches Confusion Lack of attention to people and surroundings Difficulty with balances Hydrocephalus Death 23. Hydatid Cyst Disease ENGR. BLPK Echinococcus granulosis or Echinococcus multilocularis Ingestion of eggs of the parasite Cysts in liver or lungs, but may also occurs in any organ including heart, brain, and bones Surgical removal of cysts with a combination of specific anti-parasitic drug therapy Incubation period: Variable (12 months to years) Review and edited by: Engr. AB "Trust in the Lord with all you heart and lean not on your own understanding and in all your ways acknowledge him and he shall direct your path"- Proverbs 3; 5-6




