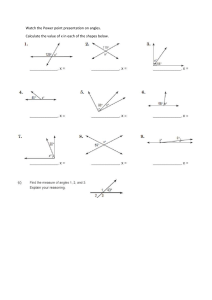
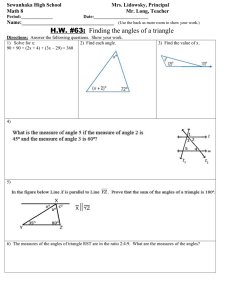
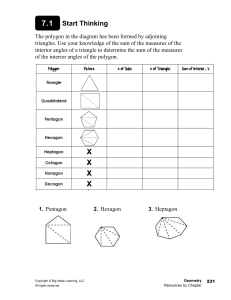
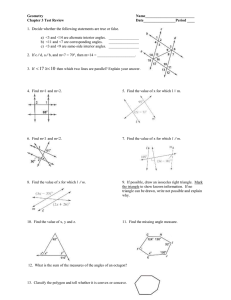
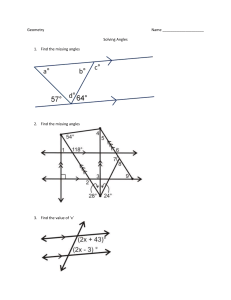
Sphere i i in Total area TA = 4πr2 Volume V = 43 πr3 Circumference Volume V = 13 Bh Area (Perimeter of circle) Lateral area LA =πrl Total area Volume TA = Ph + 2B V = 13 Bh = 2πr•h + 2πr2 Pyramid r Cone Total area TA = πrl + B Lateral area LA = 12 Pl Length of an ARC = Circumference • degrees = 2πr•(θ/360) Total area TA = 12 Pl + B Area of a SECTOR = Area of circle • degrees = πr2•(θ/360) Triangle Congruency e a s ARIA r Area of EQUILATERAL TRIANGLE Horizontal lines s = side length or x = number Ex: x = 4, x = -1 Area of 2-D Shapes Parallelogram A = bh Triangle A = 1/2 bh Trapezoid A = 1/2 (b1 + b2)•h Circle A = πr 2 Rhombus/Kite A = 1/2 d1•d2 Regular Polygon A = 1/2 aP Radius in Shapes Slope Midpoint Parallel Lines SAME SLOPE Perpendicular Lines OPPOSITE SIGN, RECIPROCAL C = 2πr C = πd A = πr radius= 1/2 diameter d r 9 3 y mm 3X r r t r r a r = radius eh 1 Z I r r ad y 3 e y 13 M 3 1 m 3 game 1 2 a r or y = number Ex: y = 4, y = -1 2 A = s √3 4 Vertical lines slope is undefined ixis.lk y Yz Yi Mfxitzxz.y.tk m Xi x Heron’s Formula Area = √s(s - a)(s - b)(s - c) s = semiperimeter = 1/2 perimeter a, b, c = lengths of sides of Δ a = apothem Distance kid 1st.tt T it Area of Δ when length of all 3 sides are known 900 d ixis.lkyd VXz X I Yz Yip Pythagorean Theorem aZ b2 Z c c a Cos Tan 0 opposite sino H hypotenuse r e O a sin H a adjacent cost H hypotenuse pyroxene a cos A ti f 0 opposite tano A adjacent pyroxene 0 o tan A f Polygon Angle Measures Sum of interior angles = 180(n - 2) n = # of sides of polygon Altitude on Hypoteneuse S OH µµ f Dy i e adjacent Interior Degrees of Shapes Sum of interior angles = 180(n - 2) Triangle (3-sides) Quadrilateral (4-sides) Pentagon (5-sides) Hexagon (6-sides) 180� 360� 540� 720� P = perimeter A = area V = volume d1, d2 = diagonals CAH e Dy adjacent n 2 n Interior Angle Measure =180 Exterior Angle Measure = 360in f L Y i o a e Dy adjacent TO A Geometric Mean h x y Number of DIAGONALS in n-sided polygon Number of diagonals = Sum of Ext Angles = 360� ALWAYS l = length w = width r = radius a = apothem b = base d = diameter n r b Sin s o v y = 0x + b, slope = 0 SSS Side Side Side Examples SAS Side Angle Side on opposite side ASA Angle Side Angle AA Angle Angle HL Hypoteneuse Leg CPCTC Corresponding Parts Congruent Triangles are Congruent 2 v E r a a + b = 180 Therefore the two angles are supplementary r Total area Volume TA = Ph + 2B V = Bh = (2l+2w)•h + 2lw = πr2•h Volume V = Bh = lw•h a Lateral area LA = Ph = 2πr•h Supplementary Angles ADD UP TO 180� Cylinder Lateral area LA = Ph = (2l + 2w)•h a + b = 90 Therefore the two angles are complementary Conditionals: IF, THEN ••• Converse - SWITCH if/then ••• Inverse - NEGATE if/then ••• Contrapositive - SWITCH if/then, NEGATE Prism/Cube l = slant height h = height n(n - 3) 2 CuteCalculus.com i e Complementary Angles ADD UP TO 90� P = perimeter of base B = area of the base GEOMETRY, Sheet 1 SOH Sin = O/H CAH cos = A/H Circles 150 300 150 750 450 20 a XFL 7 b a a b 2 Jb r xoatzb X b xeffouatrqr inan.gr b d a b c c w b atb d ctd d w x2 b atb ab od p ao e chona Circles F 90 i e i Cc xyz 180 xtytz yooo.ec d a at btc atbtctd.gg b d c M Midsegment vis s s SAS Base M tzb tbd vein Asina.es va or Segment Addition Postulate 4 22 A BBisan c B AB 1 BT_AT anglebisector Equation of a circle with center (h, k) X h h k 2 y k 2 center Tutoring available @CuteCalculus r2 p r i n AAS S A e i I 2 34 A l y a Ss A H n n aa H i HL 9 10 n iz 56 1314 1516 78 Alternate Interior Angles ARE EQUAL: 3 and 6, 4 and 5, 11 and 14, 12 and 13 Alternate Exterior Angles ARE EQUAL: 1/8, 2/7, 9/16, 10/15 5,6 E l A A ASA a a n i iz 34 Base i S S 1800 3600 a b XR S S SSS Same side Interior angles are SUPPLEMENTARY Same side Exterior angles are SUPPLEMENTARY b B l I n n obtuse straight Line atbtotdte 30 60 90 X xf3 2X f x S xg S x Angles I 90 T goo right acute x Triangle Congruency Sector 9 aneradius 60 450 X X x 2X Xf3 45 45 90 tangent v diameter 2 X inner Em'e r tan = O/A Special Right Triangles 150 x TOA Alternate INTERIOR are on opposite sides of the transversal, inside the parallel lines. Alternate EXTERIOR are on opposite sides of the transversal, outside the parallel lines. a b od is a dc od a b b a de 10080850950 oooooo asoooso nooooo oooowoo 850950 oooso as FOR MORE HELP DM @CuteCalculus iz 34 fo Same Side INTERIOR are on same side of the transversal, inside the parallel lines. Same Side EXTERIOR are on same side of the transversal, outside the parallel lines. Same Side Interior Angles ADD TO EQUAL 180: 3/5, 4/6, 11/13, 12/14 Same Side Exterior Angles ADD TO EQUAL 180: 1/7, 2/8, 9/15, 10/16 iz 34 5,6 Corresponding angles CORRESPOND to the exact same position on a parallel line intersection of the transversal. For example, angles 1 and 5 are both in the top left position at both intersections. Corresponding Angles ARE EQUAL: 1/5, 2/6, 3/7, 4/8, 9/13, 10/14, 11/15, 12/16 iz 34 so 78 Vertical angles are ACROSS THE INTERSECTION from each other and are equal. For example, angles 2 and 3 are across the intersection and are therefore equal. Vertical Angles ARE EQUAL: 1/4, 2/3, 5/8, 6/7 Reference sheets available for Algebra 1 & 2, Precal and Calculus