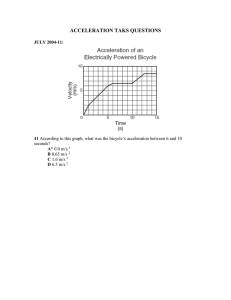
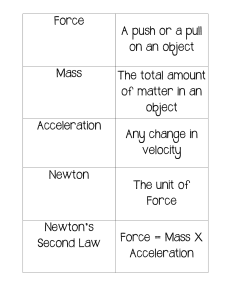
Law of Acceleration An introduction to the relationship between force, mass, and acceleration Lesson Outline Newton's Second Law of Motion Force and Acceleration Mass and Acceleration Did You Know? Mountainous roads have a feature called "runaway truck ramps" to allow large trucks and buses to stop safely. Why do large vehicles need this ramp? How does it relate to the law of acceleration? Large vehicles may gain speed due to the force of gravity. Gravel is a common material for runaway truck ramps. It provides enough friction to bring a runaway truck to a stop. Newton's states that the acceleration Second Law equals the net force acting on of Motion an object divided by mass Statement Also known as the "law of acceleration" Expression force Describes how force and mass affect acceleration F a= m acceleration OR mass F = ma Force and Acceleration smaller acceleration less force larger acceleration more force At constant mass, acceleration increases as force increases. Think About It! Which will move faster after being pushed—a block of foam or a heavy brick? Why? Mass and Acceleration larger mass less mass larger acceleration smaller acceleration At constant force, acceleration decreases as mass increases. Newton's Second Law of Motion Expression force F a= m acceleration OR mass F = ma Practice Test 1. How fast will an 800kg car accelerate if it is pushed with 4000N of force? Practice Test 2. How fast will a 0.15kg hockey puck accelerate if it is hit with 1.2 N of force? Answer This! 1. Given a force of 100 N and an acceleration of 10 m/s2, what is the mass? Answer This! 2. What is the acceleration of a 10 kg mass pushed by a 5 N force? Summary Force and Acceleration At constant mass, acceleration increases as mass increases.