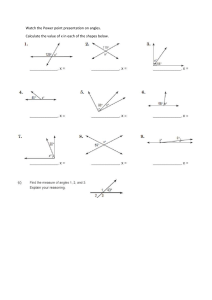
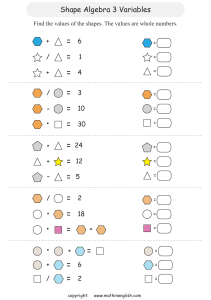
Teacher JOYA LAL Unit title GEOMETRY ( 3D) – CH 13 Subject group and discipline MYP year Mathematics 3 Unit duration 12 (weeks) Inquiry: Establishing the purpose of the unit Key concept Relationship It refers to the connections between quantities, properties or concepts and these connections may be expressed as models, rules or statements. Relationships provide opportunities to explore patterns in the world. Related concept(s) Generalization: A general statement made on the basis of specific examples. Space: The frame of geometrical dimensions describing an entity. Global context Scientific and technical innovation Exploration: Products, processed and solutions Statement of Conceptual Understanding: Different forms of generalizations of processed and products will help in making relevant connects and relationships Statement of Inquiry: Generalizing relationships between different dimensions of space can help analyze and generate products, processes and solutions. Inquiry questions Middle Years Programme Unit planner 1 Factual— ● What are different 2D and 3 D shapes around ? ● How to calculate volumes and surface areas of beakers? ● How is capacity calculated? ● What is the difference between area and surface area of various shapes? ● What is the difference between volume and capacity? Conceptual— ● How do 2 D shapes generate the 3D prisms ? ● How do we derive the formula of volume of a Pyramid through the volume of a Prism? ● How are the volumes of pyramids , cones and spheres related to corresponding prisms Debatable— ● How can we use mathematics to aesthetically organise shapes in a given space ? ● To what extent is Mathematics instrumental in designing smart space around us ? (Service as Action connection) ● To what extent surface area of a shape relate to the volume of the shape? Middle Years Programme Unit planner 2 Objectives Summative assessment A: Knowing and understanding Outline of summative assessment task(s) including assessment criteria: i. select appropriate mathematics when solving problems in both familiar and unfamiliar situations ii. apply the selected mathematicssuccessfully when solving problems iii. Solve problems correctly in a variety of contexts. B: Investigating patterns i. select and apply mathematicalproblemsolving techniques to discover complex patterns ii. describe patterns as general rulesconsistent with findings iii. prove, or verify and justify, generalrules. Middle Years Programme Unit planner Relationship between summative assessment task(s) and statement of inquiry: Sit down assessment Students will select and apply knowledge learnt in familiar and unfamiliar situations by applying relationships using generalisations and spatial reasoning of 3D shapes analysing the products in their behaviour with respect ot surface areas and volumes . They will use various problem solving techniques used throughout the unit such as derivation techniques to solve problems in different contexts with respect to Geometry . Generalizing relationships between different Students will understand mathematical relationships using different forms of shapes dimensions of space can help analyze and generate products, processes and solutions. and will be able to predict pattern based on Summative Assessment will assess the current dimensions . They will discover different forms of 3D shapes learnt by the general rules with respect to prisms and students. It will asses their understanding of pyramids . Volume , Surface areas and capacity . It will as well as capacity through the context also assess how they generalize the formula given. They will describe and model for Prisms and pyramids through the study of spaces general rules for relationships respective nets of solid shapes in the real using formula and simplifications. They world context . The students will also apply will justify and verify their findings using the concept of capacity with respect to various products . 3 algebraic formulas for surface areas and volumes. C: Communicating i. use appropriate mathematicallanguage (notation, symbols and terminology) in both oral and written explanations ii. use appropriate forms of mathematical representation to present information iii. move between different forms ofmathematical representation iv. communicate complete, coherent and concise mathematical lines of reasoning Students will represent real life situations by modelling relationship to space and shapes and will be able to generalize rule to make predictions with respect to nets of solid shapes . They will be able to explain and represent using pattern/ products and designs in a coherent and concise manner both using algebra and in words the real life contexts of volumes and surface areas . They will organize their findings logically as per context and questions. v. organize information using a logical structure Middle Years Programme Unit planner 4 D: Applying mathematics in real-life contexts i. identify relevant elements of authenticreal-life situations ii. select appropriate mathematical strategies when solving authentic reallife situations iii. apply the selected mathematicalstrategies successfully to reach a solution iv. justify the degree of accuracy of asolution Students will eliminate and accept values of Shapes in patterns based on their real life context. They will use algebraic techniques to solve real life problems. They will predict future values in case of a real life situation using the given pattern/ generalisations to 3 D space and will justify the accuracy of prediction using different methods. They will also identify and justify its authenticity with respect to the real life situation presented in the problem based on the 1D , 2 D and 3 D concepts of measurements . v. justify whether a solution makessense in the context of the authentic real-life situation Approaches to learning (ATL) Skill Categories Skill Cluster Communication skills Communication Skill indicator and description In order for students to identify and explain pattern and analyse general rule with respect to 3 D – forumlas .(Objective Ai, B ii, Ci,ii,iii) They need to make inferences, draw conclusions and make predictions with respect to shapes & spaces . Explicitly taught skill strategy: Problems solved in the classroom using various resources Middle Years Programme Unit planner 5 Critical Thinking In order for students to complete their formative assessment 1, assessing criteria A,C,D where they generalize / patterns in 2 D & 3 D spaces real life relationship and analyse it using different Formulae. ● Formative assessment 2 assessing criteria A,C,D (Aiii, Bi, Ciii,iv,v, Dii,iii,iv,v) Thinking They need to model relationship of different representation of 3 D shapes special with respect to surface areas and volumes . Explicitly taught skill strategy: deriving formulae in the classroom using various resources Thinking Transfer skills In order for students to find best fittin shape they apply their knowledge of capacity to various objects in their homes . (Objective Ai, ii, Ciii, Dii, iii) Action: Teaching and learning through inquiry Content Learning process Factual Knowledge: Learning experiences and teaching strategies - Surface Areas of 3 D shapes Week 1: Acquire: ● Different Geometry notation using nets of solid shapes (interactive online activity ) ● Resource #1a ● Students will learn the difference between 2 D & 3 d shapes with respect to Surface areas volumes . Middle Years Programme Unit planner 6 Resource#1b Connect: ● Students will express Surface area of 3 D shapes as the area of all the faces pattern/ generalizations they will notice and summarize rules for how to relate the 2 D bases to the respective 3 D containers as projections . Calculating their volumes in turn Resource #2a Transfer: International Mindedness: The students will appreciate the history of Geometry Euclid the father of geometry https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CrIdJKo0whs https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=WqzK3UAXaHs&list=PL26812DF9846578C3&t=276s Resource #2b Throughout the whole unit students will look at discoveries and contributions made by scientific and technical innovations over time. Student use the information provided and additional research to communicate an overview of history of Mathematics with respect to Platonic Solids . Students can create timeline showing major discoveries after Euclid using Adobe spark Free Timeline Maker with Online Templates | Adobe Spark Timeline of Mathematics | Mathigon Middle Years Programme Unit planner 7 Service as Action: Students can make a gallery walk about contribution of mathematicians from different cultures about with major contribution to number system. Middle Years Programme Unit planner 8 (Debatable inquire question #3) (Learning Outcome: Develop international mindedness through global engagement, multilingualism and intercultural understanding) Week 2: Acquire: ● Students learn the connection between Cryosection of prisms & their volumes . Volumes of 3 D shapes Conceptual Knowledge: ● Deriving the formulae For Surface areas that and identifying pattern to 3 D shapes ● Students learn to derive the volume of a pyramids through the volume oa corresponding prizm (Resource #3a) Connect: Students solve questions involving surface areas and volume of 3d objects. Transfer: Exension: Students try to design their own complex shapes and derive their surface areas & volumes (Resource # 3b) (Interdisciplinary connection with DT ) Week 3: Capacity of beakers / vesicles Middle Years Programme Unit planner Acquire: ● Students review the concepts of Capacity ● Students are introduced to the concept of capacity Connect: 9 ● Finding the Volumes of complex shapes ● Students solve problems based on Surface areas & volumes (Resource #4 ● using Nearpod lesson (Resource #4c) Self Practice (self marking) online exercises : ● Formulae can appear in different, but equivalent, forms, or representations, which can help us to establish General patterns in 2D & 3 D space . Procedural knowledge: ● Modelling real-life situations with the structure of Beakers / Rooms / Utensils and geometric shapes allows for prediction, analysis and interpretation. ● Application of Formulae to complex shapes provide the means to find best fitting space to objects which model real-life situations. ● Patterns in Shapes / Space in form the development of Critical and creative tools Middle Years Programme Unit planner 10 that can be applied to find unknowns. Middle Years Programme Unit planner 11 Acquire: ● Students establish deeper understanding of 3 D shapes (using Nearpod lesson Resource #8) and various types of Prisms & Pyramids Connect: ● Understanding the difference between Volume & Surface area . Students research to difference between 1kg of Milk and 1 litre of Milk (ID connection with Science & Knowledge of BEAKERS OF VARIOUS SHAPES ) Service as Action: ● Students will research in groups / individually about shapes and volumes paced in various shapes and suggest the best possible packaging for the Diwali gifts for gifting the needy as part of their joy of giving week . (Learning Outcome: Creative thinking ) (Debatable question #3) Formative assessment Informal feedback: ● Teacher feedback during class based on class observation ● Structured feedback on formative tasks to prepare students for summative assessment Formative Assessment: ● Formative assessment 2 – Sit down assessment to be taken on Assess prep assessing criteria A ,C and D Middle Years Programme Unit planner 12 assessment 1 – Students in group / individually consider your team to be personal Designer and evaluate from a given set of shapes the best possible option for the client considering surface areas and volumes and compile it in a presentation (using PPT/sway/Flipgrid/Adobe Spark) ● Formative Middle Years Programme Unit planner 13 Differentiation Content: Offer ways of customizing the display of information: (As per the UDL guidelines) ● Regular classroom teaching: use of white board (whiteboard.fi) with each individual student whiteboard, Nearpod open ended questions, Transum self learning exercises to help visualise and learn using different methods. Offer alternatives for visual information: (As per the UDL guidelines) ● Provide auditory cues for key concepts using Math tool in one note where auditory notes will be provided. ● GeoGebra to visualise solid shapes & their measurements Provide options for language, mathematical expressions, and symbols(As per the UDL guidelines) ● Pre-teach vocabulary ( Geometry ) and symbols, especially in ways that promote connection to the learners’ experience and prior knowledge ● Highlight how ID , 2 D & 3 D shapes relate to measurements ● Highlight patterns, critical features, big ideas, and relationships (As per the UDL guidelines) ● Use multiple examples of cubes cuboids , prisms & pyramids to emphasize critical features of capacity . Learning extension: ● Extra challenging questions provided in task sheets and in the class Middle Years Programme Unit planner 14 ● Students can research on various puzzles originated on various parts of world based on properties of 3 D shapes and Platonic solids . Process: Increase mastery-oriented feedback (As per the UDL guidelines) ● Provide feedback that is frequent, timely, and specific Provide options for self-regulation (As per the UDL guidelines) ● Support activities that encourage self-reflection and identification of personal goals Facilitate personal coping skills and strategies (As per the UDL guidelines) ● Additional help to be provided outside classroom during zero lesson ● Class recordings available for students to pace their learning ● Extra time provided in assessments for learning support students ● Additional time provided for submissions to enable self paced learning Product: ● All students will learn to identify pattern and establish real life relationships using shapes around us . ● Students will be able to use the logic of shapes to generalise pattern to solve for surface areas and volumes of complex shapes . Resources Textbooks: ● Oxford Mathematics ● Haese Mathematics Middle Years Programme Unit planner 15 Online Graphing and interactive activity software’s: ● Transum ● Nearpod ● Geogebra ● Desmos: Resource #1a Surface Areas https://www.transum.org/Software/SW/Starter_of_the_day/Students/Surface_Area.asp?Level=2 Resource #1aa Volumes https://www.transum.org/Software/SW/Starter_of_the_day/Students/Volume.asp Resource #1b ( difference between Surface Areas & volumes https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=muw-MQeIkO4 Resource # 2a PROPANE TANK https://www.map.mathshell.org/download.php?fileid=828 Resource # 2b Capacity & volumes https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GKCE8ohIBqE Resource #3a https://nearpod.com/t/math/6th/surface-area-volume-part-b-L720020 Resource #3b https://www.nctm.org/Classroom-Resources/Illuminations/Interactives/Geometric-Solids/ Middle Years Programme Unit planner 16 Resource#4a GeoGebra https://www.geogebra.org/m/avkgxbea#material/rCxXxFhE Resource #4b DESmos https://teacher.desmos.com/activitybuilder/teacherguide/5e6931dfc628310c3b172700 https://www.transum.org/Maths/Activity/Volume/default.asp?Level=2 https://www.pbslearningmedia.org/resource/mkcpt.math.g.triangularprism/finding-the-volume-of-a-triangular-prism/#.WlaXkK6nHIU Middle Years Programme Unit planner 17 Resource # 5a https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qJwecTgce6c Resource #6 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=G_51PEKRItU Resource #7 https://docs.google.com/spreadsheets/d/1MNdYC_MSebo37_8rejnyE6cjG3EnDfBr9QK5t1L5sk4/edit#gid=0 Resource #8 https://nearpod.com/t/math/7th/volume-of-prisms-pyramids-68-L69925765 Other Resources: 1. 2. 3. 4. https://www.khanacademy.org/math/cc-sixth-grade-math/cc-6th-geometry-topic/geometric-solids/e/identify-parts-of-3d-shapes https://www.khanacademy.org/math/cc-sixth-grade-math/cc-6th-geometry-topic/geometric-solids/e/identify-geometric-solids--3d-fig https://www.khanacademy.org/math/cc-sixth-grade-math/cc-6th-geometry-topic/cc-6th-volume-with-fractions/e/find-volume-by-mult https://www.khanacademy.org/math/cc-sixth-grade-math/cc-6th-geometry-topic/cc-6th-surface-area/v/surface-area-word-problem-ex Middle Years Programme Unit planner 18 Reflection: Considering the planning, process and impact of the inquiry Prior to teaching the unit During teaching After teaching the unit Middle Years Programme Unit planner 19 Students are already well versed with the concept of Areas and perimeters of standard shapes and their formulas . This unit will further enhance their understanding of the dimensions in real life , difference between surface areas and volumes and capacity . They will be able to understand the different types of sphapes and spaces in rela life . They will explore the application capacity in real life . In line with the IB learner profile, in this unit students will strive to be: Knowledgeable: By understanding and applying logic ( not memorise just the formulas to detife the volumes ) Thinkers: By recognising and applying their knowledge and conceptual understanding to real life and unfamiliar contexts. They will able to make predictions based on given information about the best shape fitting in the given space . Communicators: By learning to communicate mathematically in a logical and coherent manner and by communicating using different forms of shapes and its application in the correct manner with respect to the given context . Middle Years Programme Unit planner 20 Inquirers: Students will learn to inquire more about concepts and how they can be related to real life situations. Middle Years Programme Unit planner 21