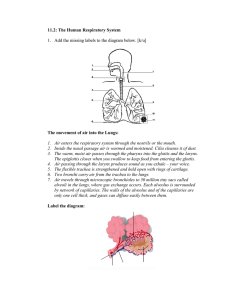
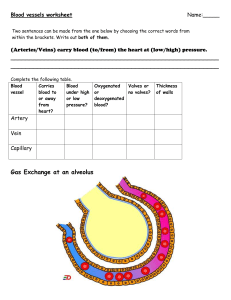
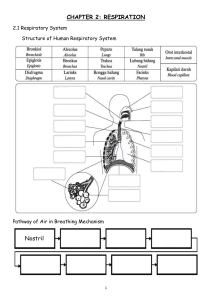
2.2 MOVEMENT & EXCHANGE OF GASES IN THE HUMAN BODY 1. Alveolus 2. Blood 3. Oxygen transport to whole body 4. Cell 5. Respiration in cell 6. CO2 Transport to alveolus Oxygen is diffuse through the wall of the alveolus into the walls of the capillaries and into the blood. (Because the air inhaled into the alveolus has a higher concentration of oxygen compared to the concentration of oxygen in the blood) Haemoglobin + oxygen → oxyhaemoglobin Haemoglobin will combine with oxygen to form oxyhaemoglobin. Haemoglobin → dark red-coloured compound in red blood cells. Oxyhaemoglobin → unstable compound and bright red in colour Blood with oxyhaemoglobin is transported (lungs →heart →other parts of the body) When the blood reaches the area around the body cells that has a low concentration of oxygen, oxyhaemoglobin will decompose to release oxygen molecules. Oxyhaemoglobin → haemoglobin + oxygen In the body cells, the process of cellular respiration occurs. Glucose + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water + energy Carbon dioxide diffuses into the blood capillaries and is transported to the alveolus to be removed during exhalation. Importance of the Adaptations of the Alveolar Structure To increases the rate of gaseous exchange between the alveolus and the blood capillaries. 1. 2. 3. 4. Thin walls of alveolus and blood capillaries (made up of only one layer of cells). Moist wall of alveolus (allows respiratory gases to dissolve and diffuse into the blood capillaries). Larger surface area of alveolus (for the exchange of gases). Compact network of capillaries covering the alveolus. 1. The figure below shows the exchange of gases in the alveoli. (a) Study the figure and answer the following questions. (i) Name structure X and Y in the space provided. [2M] (ii) Name process R and S in the space provided. [2M] (iii) Name gas P and Q in the space provided. [2M] (b) The figure below shows the structure of an alveolus and blood capillaries. Explain how oxygen is transported to the body cells starting from the alveoli. [3M] _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ (c) The figure below shows the structure of an alveolus. (i) Name the process involved in the gaseous exchange between the alveolus and blood capillaries. [1M] _____________________________________________________________________________________ (ii) Explain how this process occurs. [2M] _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ 2. (a) Explain the importance of gaseous exchange in human. [2M] _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ (b) The following are two equations which involve in the formation and decomposition of oxyhaemoglobin. Equation 1: Oxygen + Haemoglobin → Oxyhaemoglobin Equation 2: Oxyhaemoglobin → Oxygen + Haemoglobin (i) The process in Equation 1 is disrupted due to the defect of red blood cells. State the effect. [1M] _____________________________________________________________________________________ (ii) Where does the Equation 2 occur? [1M] _____________________________________________________________________________________ (iii) What happen to the oxygen in the product of Equation 2? [1M] _____________________________________________________________________________________ (c) Complete the following statements using the words below. [4M] capillary moist large thin (i) Alveolus has _____________________ surface area due to its small size. (ii) The alveolar surface is kept ____________________ as it is covered by the liquid. (iii) Alveolus has a _________________ wall where the thickness is only one layer of cells. (iv) Each alveolus is surrounded by a dense network of___________________. 1. a. b. Inhaled air enters the alveoli and diffuses into the blood capillaries. Oxygen combines with haemoglobin to form oxyhaemoglobin. Oxyhaemoglobin is transported to body cells and decomposed to release oxygen. Oxygen then diffuses into the body cells. c. (i) Diffusion (ii) Concentration of oxygen in the alveoli is higher and causes oxygen to diffuse from the lungs into the alveoli. Concentration of carbon dioxide is higher in the blood capillaries and causes carbon dioxide to diffuse from the blood capillary into the alveoli. 2. a. To supply oxygen for cellular respiration and remove carbon dioxide from the body. b. (i) Less oxygen transported to body cells (ii) In body cells (iii) Oxygen diffuses into the body cells and used in cell respiration. c. (i) Large (ii) Moist (iii) Thin (iv) Capillary