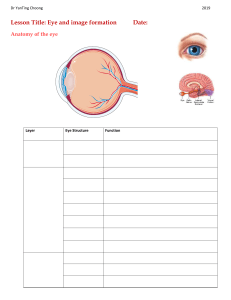
Friday, 15 September 2023 B2 Lesson 3 Learn the terminology behind different types of glass and their relationship to light. Study concave and convex lenses. How can I classify materials depending on how much light the let through? Transparent • If a material is transparent it will let light into a room and the light rays will not be scattered. Translucent • Translucent materials normally have irregular surfaces and the light rays are scattered as they pass through. That is why you don’t see a clear image. Opaque • Opaque materials do not let light to pass through. All light rays are absorbed. page 198 Complete activity 9 from the booklet Refraction The speed of light depends on the material through which the light is travelling. When light enters a different material (e.g. from air into glass), the speed of light changes. This causes the light to bend or refract. air glass The speed of light is affected by the density of the material through which it is travelling. When light enters a more dense material, its speed decreases and this is why refraction occurs. Concave lenses Diverging or concave lenses refract the parallel rays of light so that they spread apart from one another. Refraction in a glass block Lenses Lenses work by refracting light at a glass-air boundary. Although refraction occurs at the boundary, we will treat all lenses as bending the rays at the lens axis. Convex Lens Convex or converging lens make rays of light come together, or converge. Page 203 Complete activities 10 -11