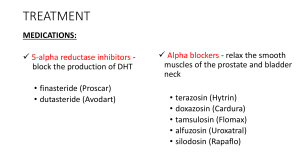
Module 6 Male Reproductive System Anatomy testis, or testicles-primary male sex organs, paired, oval-shaped, & enclosed in a sac (pl. testes, testicles) called the scrotum. The testes produce spermatozoa (sperm cells) and the hormone testosterone. Sperm(spermatozoon the microscopic male germ cell, which, when united with the pl. spermatozoa) ovum, produces a zygote (fertilized egg) that with subsequent development becomes an embryo. testosterone- the principal male sex hormone. Its chief function is to stimulate the development of the male reproductive organs & secondary sex characteristics such as facial hair. Seminiferous tubules-up to 900 coiled tubes within the testes in which spermatogenesis occurs epididymis- a coiled 20 foot tube atop each of the testes that carries mature sperm up to the vas deferens vas deferens, ductus deferens, or seminal duct- duct carrying the sperm from the epididymis to the urethra. (The urethra also connects with the urinary bladder & carries urine outside the body. A circular muscle constricts during intercourse to prevent urination.) seminal vesicles- two main glands located at the base of the bladder that open the vas deferens. The glands secrete a thick fluid, which forms part of the semen. prostate gland- encircles the upper end of the urethra. The prostate gland secretes a fluid that aids in the movement of sperm & ejaculation. scrotum- sac suspended on both sides of & just behind the penis. The testes are enclosed in the scrotum penis- male organ of urination & copulation (sexual intercourse) glans penis- enlarged tip on the end of the penis prepuce- fold of skin near the tip of the penis (foreskin of the penis) semen- composed of sperm, seminal fluids, & other secretions. genitalia (genitals)- reproductive organs (male or female) 1 Combining Forms balan/o epididym/o orchid/o, orchi/o, orch/o, test/o prostat/o vas/o vesicul/o andr/o sperm/o, spermat/o glans penis epididymis testis, testicle prostate gland vessel, duct seminal vesicle male spermatozoon (pl. spermatozoa), sperm Prefix trans- through, across, beyond Suffix -ism state of Disease and Disorder Terms anorchism- state of absence of testis (unilateral or bilateral) balanitis- inflammation of the glans penis balanorrhea- excessive discharge from the glans penis benign prostatic hyperplasia( BPH)- excessive development pertaining to the prostate gland (non-malignant enlargement of the prostate gland) cryptorchidism- state of hidden testes. (During fetal development, testes are located in the abdominal area near the kidneys. Before birth they move down into the scrotal sac. Failure of the testes to descend from the abdominal cavity into the scrotum before birth results in cryptorchidism, or undescended testicles.) epididymitis- inflammation of an epididymis orchiepididymitis- inflammation of the testis and epididymis orchitis, orchiditis, or testitis- inflammation of the testis or testicle prostatitis- inflammation of the prostate gland prostatocystitis- inflammation of the prostate gland and the bladder 2 prostatolith- stone in the prostate gland prostatorrhea- excessive discharge from the prostate gland prostatovesiculitis- inflammation of the prostate gland and seminal vesicles Disease and Disorder Terms Not Built from Word Parts erectile dysfunction- the inability of the male to attain or maintain an erection sufficient to perform sexual intercourse (formerly called impotence) hydrocele- scrotal swelling caused by a collection of fluid phimosis- a tightness of the prepuce (foreskin of the penis) that prevents its retraction over the glans. May be congenital or a result of balanitis. Circumcision is the usual treatment. priapism- persistent abnormal erection of the penis accompanied by pain & tenderness prostate cancer- cancer of the prostate gland testicular carcinoma- cancer of the testicle testicular torsion- twisting of the spermatic cord causing decreased blood flow to the testis. Occurs most often during puberty. Because of lack of blood flow to the testis, it is often considered a surgical emergency. varicocele- enlarged veins of the spermatic cord Surgical Terms Built from Word Parts balanoplasty epididymectomy orchidectomy, orchiectomy orchidopexy,orchiopexy orchidotomy, orchiotomy orchioplasty prostatectomy prostatocystotomy surgical repair of the glans penis excision of an epididymis excision of the testis. (Bilateral orchidectomy also is called castration) surgical fixation of a testicle (performed to bring undescended testicle(s) into the scrotum) incision into a testis surgical repair of a testis excision of the prostate gland incision into the prostate gland and bladder 3 prostatolithotomy prostatovesiculectomy vasectomy vasovasostomy vesiculectomy incision into the prostate gland to remove a stone excision of the prostate gland and seminal vesicles excision of a duct (partial excision of the vas deferens bilaterally, resulting in male sterilization) creation of artificial openings between ducts (the severed ends of the vas deferens are reconnected in an attempt to restore fertility in men who have had a vasectomy) excision of the seminal vesicle(s) Surgical Terms Not Built from Word Parts circumcision- surgical removal of the prepuce (foreskin) hydrocelectomy- surgical removal of a hydrocele penile implant- surgical implantation of a penile prosthesis to correct erectile dysfunction. suprapubic prostatectomy- excision of the prostate gland through an abdominal incision made above the pubic bone. Used to treat benign prostatic hyperplasia & prostate cancer. transurethral incision of the prostate gland (TUIP)- a surgical procedure that widens the urethra by making a few small incisions in the bladder neck and the prostate gland. No prostate tissue is removed. TUIP may be used instead of TURP when the prostate gland is less enlarged. transurethral microwave thermotherapy (TUMT)- a treatment that eliminates excess cells present in benign prostatic hyperplasia by using her generated by microwave. transurethral resection of the prostate gland (TURP)- successive pieces of the prostate gland tissue are resected by using a resectoscope inserted through the urethra. The capsule is left intact. Usually performed when the enlarged prostate gland interferes with urination. Diagnostic Terms Not Built from Word Parts transrectal ultrasound- an ultrasound procedure used to diagnose prostate cancer. Sound waves are obtained by placing a probe into the rectum. The sound waves are transformed into an image of the prostate gland prostate-specific antigen (PSA)- a blood test that measures the level of prostate-specific antigen in the blood. Elevated test results may indicate the presence of prostate cancer. 4 digital rectal examination (DRE)- a physical examination in which the physician inserts a finger into the rectum and feels for the size & shape of the prostate gland through the rectal wall. Used to screen for BPH and cancer of the prostate. BPH usually presents as a uniform, nontender enlargement, whereas cancer usually presents as a stony hard nodule. Complementary Terms Built from Word Parts andropathy oligospermia spermatolysis diseases of the male (that is, peculiar to the male, such as a testis) condition of scanty sperm (in the semen) dissolution (destruction) of sperm Complementary Terms Not Built from Word Parts acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS)- a disease that affects the body’s immune system, transmitted by exchange of body fluid during the sexual act, reuse of contaminated needles, or receiving contaminated blood transfusion (also called acquired immune deficiency syndrome) artificial insemination- introduction of semen into the vagina by artifical means chlamydia- a sexually transmitted disease, sometimes referred to as a silent STD because many people are not aware they have the disease. Symptoms that occur when the disease becomes serious are painful urination and discharge from the penis in men & genital itching, vaginal discharge, and bleeding between menstrual periods in women. The causative agent is C. trachomatis. coitus- sexual intercourse between male & female (also called copulation) condom- cover for the penis worn during coitus ejaculation- ejection of semen from the male urethra genital herpes- sexually transmitted disease caused by Herpesvirus homitis type 2 (also called herpes simplex virus) gonads- male and female sex glands gonorrhea- contagious, inflammatory sexually transmitted disease caused by a bacterial organism that affects the mucous membranes of the genitourinary system 5 heterosexual- person who is attracted to a member of the opposite sex homosexual- person who is attracted to a member of the same sex human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)- a type of retrovirus that causes AIDS. HIV infects T-helper cells of the immune system, allowing for opportunistic infections such as candidiasis, P. carinii pneumonia, tuberculosis, and Kaposi sarcoma. human papilloma virus (HPV)- a prevalent sexually transmitted disease causing benign or cancerous growths in male & female genitals (also called venereal warts) orgasm- climax of sexual stimulation prosthesis- an artificial replacement of an absent body part puberty- period when secondary sex characteristics develop and the ability to reproduce sexually begins sexually transmitted disease (STD)-diseases, such as syphilis, gonorrhea, and genital herpes, transmitted during sexual contact (also called venereal disease) sterilization- process that renders an individual unable to produce offspring syphilis- infectious sexually transmitted disease having lesions that can affect any organ or tissue; a syphilitic mother may transmit the disease to her unborn infant because of the causative organism is able to pass through the placenta trichomoniasis- a sexually transmitted disease caused by a one-cell organism, Trichomonas. It infects the genitourinary tract. Men may be asymptomatic or may develop urethritis, an enlarged prostate gland, or epididymitis. Women have vaginal itching, dysuria, and vaginal or urethral discharge. Abbreviations AIDS BPH DRE HIV HPV PSA STD TUIP TURP aquired immunodeficiency syndrome benign prostatic hyperplasia digital rectal examination human immunodeficiency virus human papilloma virus prostate-specific antigen sexually transmitted disease transurethral incision of the prostate transurethral resection of the prostate 6