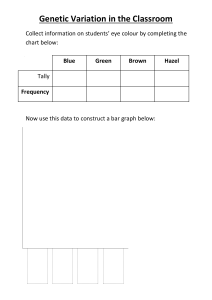
Variation LO: state the causes of continuous and discontinuous variation -define a mutation and the factors which can cause mutations TASK: These are all genetically identical twins. However, they don’t look exactly alike? Discuss with your partner possible reasons for this. Organisms can be genetically identical (clones) but still show variation due to environmental differences between them Eg. One of these twins had an increased supply of blood in the uterus so it was born larger. Some characteristics are purely genetic while others are environmental or a combination of both Genetic, environmental or a combination of both? Normal hair colour Eye colour Weight Good at maths Foot size Height Hand size Skin colour Ability to sing Nose shape Mouth shape Tongue rolling Cut on hand Missing tooth Blood type Personality Freckles Language you talk Your name Your sex Inherited diseases Ability to draw Length of hair Colour of birds feathers TASK: Measuring variation • • Measure height in cm using tape measure Eye colour: (blue, green, hazel, brown, grey, black) • Natural hair colour: (blonde, brown, red, black) • Can you roll your tongue? (yes/no) 1. Record your results in a table Discontinuous Variation • Are distinct, separate peaks/bars • • • • Distinct phenotypes eg. Blood type A,B, AB, O Tends to have no overlap between categories Are controlled by a small number of genes Are largely unaffected by the environment What did we find? • Height shows a continuous variation – there is a range of values with most people roughly in the middle • Eye colour, hair colour etc show a discontinuous variation – there are distinct groups but some are more common Eye colour in 9K 8 7 6 5 4 Frequency 3 2 1 0 blue green hazel brown grey black Continuous Variation • Is a continuous range of values so get a smooth bell curve (normal distribution) • • • • Are no distinct categories to place individuals e.g height Tends to have overlap between categories Are controlled by a large number of genes Are significantly affected by the environment Mark scheme Genotype + environment = phenotype Summary 1. Sudden random changes in genes that are passed from one generation to the next are A mutations B hybrids. C antibodies. D daughter cells. 2. Mutations can become adaptations if A. they are harmful to the organism. B. they make the organism less able to survive in the environment. C. they help an organism to survive and reproduce in the environment. D. are neither harmful nor beneficial to the organism. Investigating variation Name Height (cm) Hand span (cm) Is there a relationship between your height and hand span? Homework 1. Create a title page for this module 2. Make a family tree of your parents, yourself and any brothers / sisters. List the differences between you which you have inherited and those which are due to the environment